What is Tangeritin?
Tangeritin (C20H20O7) is a naturally occurring polymethoxyflavone primarily found in citrus peels such as tangerines, hence the origin of its name. Structure-wise, this compound is categorized under flavonoids, a diverse group of phytonutrients found in almost all fruits and vegetables, associated with an array of health benefits.
Possessing a palette of biological activities, tangeritin has piqued the scientific community's interest. It is lauded for its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, and anticancer properties. Nacknowledging these properties, it becomes clear the importance of accurate and robust analytical methods to measure and understand the distribution of tangeritin in various matrices and how it contributes to the aforementioned therapeutic impacts.
Creative Proteomic provides tangeritin analysis platforms to accurately detect and quantify this compound, helping the pharmaceutical and basic research fields discover new therapeutic strategies and interventions. In addition, our tangeritin assays also serve the food and beverage industry.
Specific Tangeritin Analysis Offered by Creative Proteomics
Through our advanced technological platforms like our state-of-the-art mass spectrometry techniques, we offer comprehensive tangeritin analytical services. These are not limited to, but include:
Tangeritin Composition Analysis: Delve into tangeritin's molecular structure, elemental composition, and functional groups, offering crucial insights into its chemical makeup.
Tangeritin Derivative Characterization: Identify and analyze unique tangeritin derivatives, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of its chemical diversity.
Tangeritin Biological Activity Profiling: Investigate tangeritin's interactions with biological systems, elucidating mechanisms of action and potential applications in diverse biological contexts.
Pharmacological Evaluation: Assess tangeritin's potential therapeutic applications, tailoring insights for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical development.
Tangeritin Metabolomic Profiling: Examine tangeritin's metabolic pathways within biological systems, providing valuable information on its bioavailability and transformations.
Quantitative Analysis: Accurately determine tangeritin concentrations in different samples, ensuring precision for both research and industrial applications.
Toxicological Assessment: Evaluate the safety profile of tangeritin, essential for regulatory compliance and ensuring its suitability for various applications.
Customized Projects: Tailor tangeritin analysis to specific research or industry needs, ensuring a personalized and effective approach that aligns with unique requirements.
Tangeritin Analysis Techniques
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) - This technique's major advantage lies in its ability to analyze complex mixtures with high sensitivity and selectivity. It is widely used in drug discovery and development, environmental analysis, food and beverage testing, and forensic investigations. The Thermo Scientific Q Exactive hybrid quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometer is a popular instrument choice characterized by its high performance and excellent resolution.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) - GC-MS offers accurate and reliable results and can analyze volatile and semi-volatile compounds. It finds extensive application in forensics, environmental analysis, food testing, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemical industries. The Agilent 5975C inert XL Gas Chromatograph/Mass Spectrometer is recognized for its advanced design and robust performance.
Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS) - This technique provides highly selective and sensitive quantitation by eliminating interfering substances, making it excellent for drug detection and pharmacokinetic studies. The AB SCIEX Triple Quad 5500 LC/MS/MS System is widely adopted due to its ultra-high sensitivity and superior data quality.
Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (TOF-MS) - Offering high-speed data acquisition and high-resolution results, TOF-MS is popular for drug discovery, protein identification, and general screening applications. The Agilent 6224 TOF LC/MS is renowned for its exceptional sensitivity and accuracy.
Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (Q-TOF MS) - Combining the advantages of quadrupole precursor ion selection with high-resolution, accurate-mass tof analysis, Q-TOF MS is ideal for pharmaceuticals, proteomics, metabolomics, and environmental applications. The Waters Xevo G2-XS QTOF is well-received for its superior sensitivity, selectivity, and robustness.
Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry - Known for its ultra-high resolution, accuracy, and stability, Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry is suitable for detailed characterization and quantification in the realms of proteomics, metabolomics, and pharmaceuticals. The Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Fusion Lumos Tribrid Mass Spectrometer is acclaimed for its outstanding resolving power and versatile options for advanced proteomics.
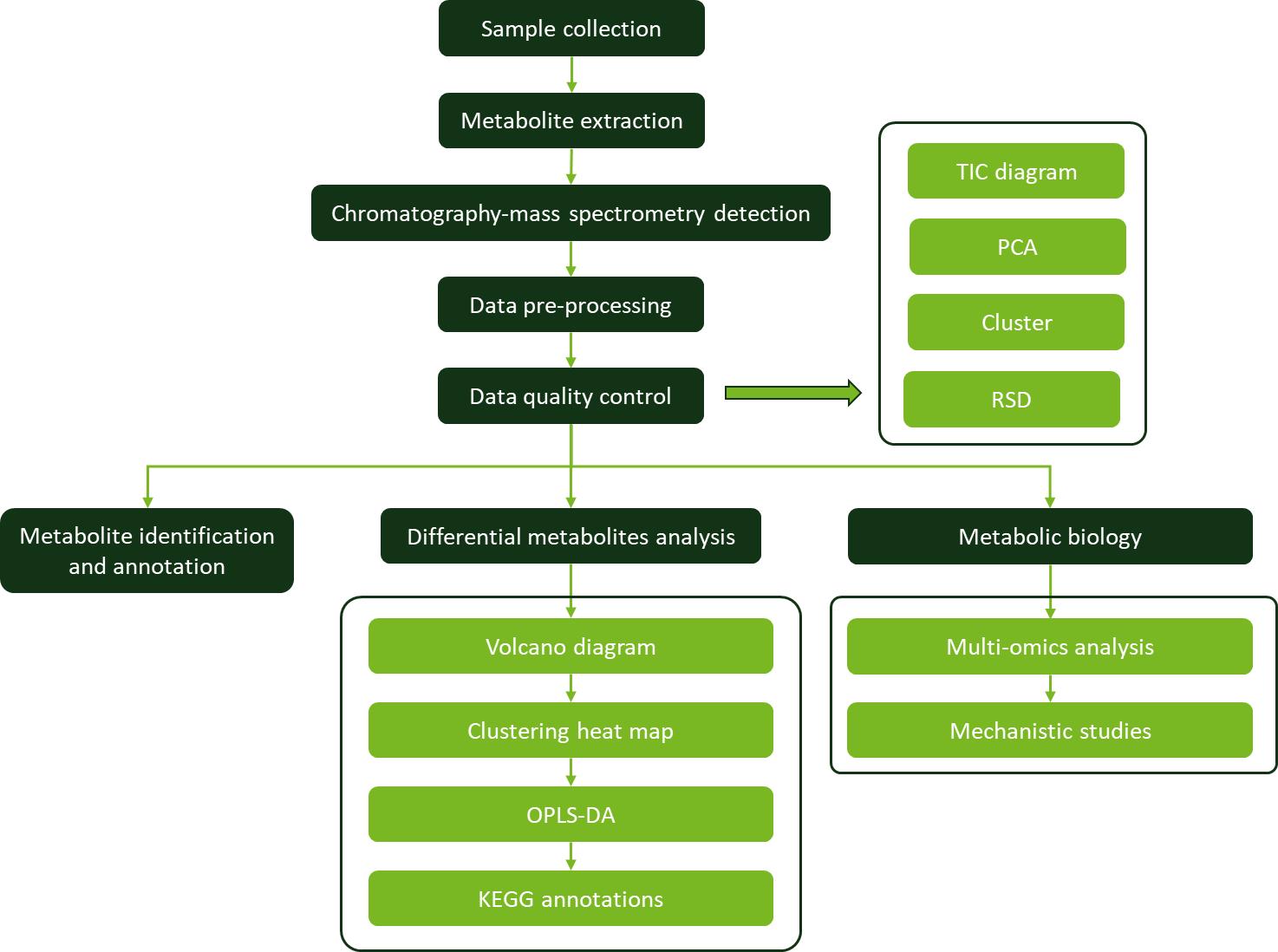 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Tangeritin and Its Derivatives Analyzed (including but not limited to)
| Tangeritin |
3',4'-Dimethoxyflavone |
5,6,7,8-Tetramethoxyflavone |
5,7,8-Trimethoxyflavone |
| 3',4',5'-Trimethoxyflavone |
Nobiletin |
Sinensetin |
Hesperetin |
| Isosinensetin |
Naringenin |
|
|
Sample Requirements for Tangeritin Assay
| Sample Type |
Sample Quantity |
| Plant Extracts |
10-50 mg |
| Fruit Peel |
5-10 g |
| Citrus Juice |
5-20 mL |
| Serum/Plasma |
0.5-1 mL |
| Essential Oils |
5-10 μL |
| Dietary Supplements |
20-50 mg |
| Food Products |
10-20 g |
Deliverables from Tangeritin Analysis
- Comprehensive data report providing a detailed overview of the analysis, including tangeritin concentration and related findings
- Raw data files
- Free follow-up consultation for data interpretation and results discussion
Case. Phenolic Profiling and Neuroprotective Activities of Moro and Usao Varieties of Citrus aurantium Extracts
Background
The study aims to compare the phenolic composition and neuroprotective activities of extracts from Moro (MSO) and Usao (USO) varieties of Citrus aurantium (sour orange). Phenolics are known for their health benefits, and understanding the differences between these varieties can provide insights into potential therapeutic applications.
Sample
Fruits of Moro and Usao varieties of Citrus aurantium were used for the extraction of phenolic compounds. A total of 58 phenolics and 4 limonoids were identified and analyzed in the study.
Technical Platform and Procedure
Identification of Phenolics: A total of 58 phenolics and 4 limonoids were identified using UHPLC-MS/MS.
Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discrimination Analysis (OPLS-DA): 59 compounds with significant differences between MSO and USO were analyzed, revealing 25 important phenolics.
UHPLC Analysis: 15 compounds were identified and quantified by comparing standard chromatograms and retention times.
Antioxidant Activities: Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assays were employed to assess antioxidant capacities.
Neuroprotective Activities: HT22 cell line was used to evaluate the protective effects against glutamate- and erastin-induced neurotoxicity, with doses of MSO and USO extracts ranging from 1 to 20 mg/mL.
Results
Phenolic Differences: MSO had higher levels of specific phenolic acids and flavonoid-C-glycosides, while USO exhibited higher levels of certain flavanone-O-glycosides and coumarins.
Methoxylated Flavonoids: USO extracts showed higher amounts of methoxylated flavonoids, indicating potential health benefits.
UHPLC Analysis: Neohesperidin was the predominant phenolic in MSO, while hesperidin dominated in USO.
Antioxidant Activities: MSO demonstrated higher ORAC and DPPH radical scavenging activities than USO.
Neuroprotective Activities: Both MSO and USO extracts exhibited protective effects against glutamate- and erastin-induced neurotoxicity, with USO demonstrating higher potency as an anti-ferroptotic agent.
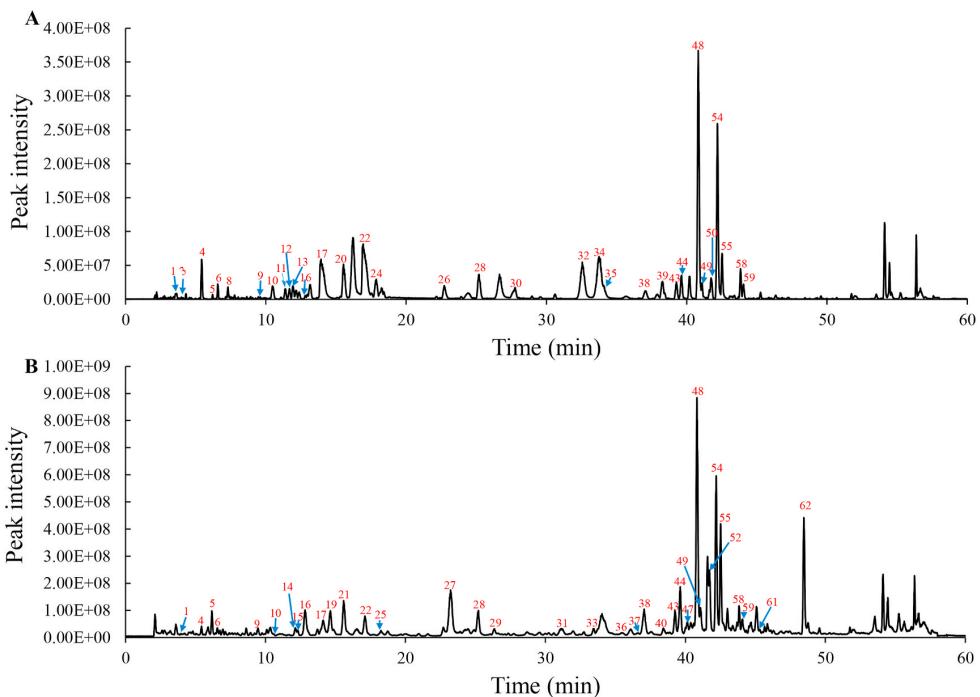 The total ion chromatograms of MSO (A) and USO (B) in the positive ion mode.
The total ion chromatograms of MSO (A) and USO (B) in the positive ion mode.
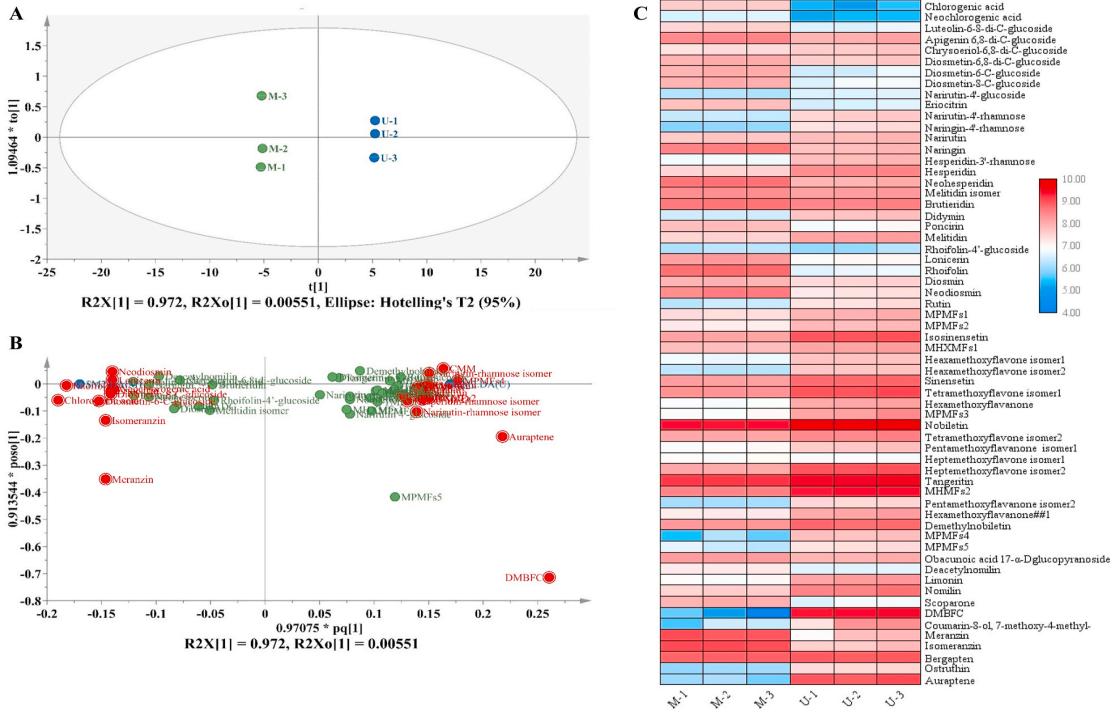 OPLS-DA and heat map of identified phenolics in MSO and USO extracts.
OPLS-DA and heat map of identified phenolics in MSO and USO extracts.
Reference
- Wen, Lingrong, et al. "Phenolics in Citrus aurantium fruit identified by UHPLC-MS/MS and their bioactivities." LWT 147 (2021): 111671.


 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service The total ion chromatograms of MSO (A) and USO (B) in the positive ion mode.
The total ion chromatograms of MSO (A) and USO (B) in the positive ion mode. OPLS-DA and heat map of identified phenolics in MSO and USO extracts.
OPLS-DA and heat map of identified phenolics in MSO and USO extracts.

