Agricultural crop improvement is a science and technology-driven discipline aimed at enhancing crop productivity, quality, and resilience. Its primary objectives include:
- Increasing Yield: We work towards boosting crop yields to meet the ever-growing global food demand.
- Improving Quality: Our efforts focus on improving taste, nutritional value, and flavor to meet market demands.
- Enhancing Disease Resistance: We develop crop varieties resistant to pests, fungi, and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides.
- Boosting Stress Resistance: We breed crops capable of withstanding drought, saline soils, high temperatures, and other adverse environmental conditions.
Metabolomics plays a pivotal role in agricultural and crop improvement by providing comprehensive insights into the metabolic processes of plants. Metabolites are the small molecules that drive the biochemistry of plants, influencing growth, development, and responses to stressors. Understanding these metabolic pathways is crucial for achieving the goals of crop improvement.
Metabolomics offers a holistic view of crop metabolism, enabling us to:
- Identify Key Metabolites: We can pinpoint the metabolites responsible for crop quality, disease resistance, and stress responses.
- Customize Crop Traits: With metabolomics, we can tailor crops to meet specific market demands and environmental challenges.
- Monitor Environmental Responses: We track how crops respond to environmental changes, guiding adaptive strategies.
- Optimize Genetic Engineering: Our expertise in metabolomics aids in the precise modification of crops to desired traits.
At Creative Proteomics, we employ state-of-the-art mass spectrometry-based metabolomics techniques, such as Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). These technologies provide unparalleled accuracy and sensitivity in detecting and quantifying a wide range of metabolites, allowing us to build a comprehensive picture of crop metabolism.
Agricultural Crop Improvement Metabolomics Solutions
 Crop Quality Enhancement
Crop Quality Enhancement
Our Metabolomics services enable you to unlock the secrets of crop quality. We identify and quantify key metabolites responsible for taste, aroma, and nutritional value, providing insights that guide the development of crop varieties with superior sensory and nutritional attributes.
 Crop Disease Resistance and Stress Response
Crop Disease Resistance and Stress Response
Combatting crop diseases and environmental stressors is made easier with Metabolomics. We help you understand how crops respond at the metabolic level. By identifying specific metabolites linked to resilience and stress responses, we empower your breeding programs to create robust crops that reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
 Genetic Modification and Engineering
Genetic Modification and Engineering
Precision in genetic modification is paramount. Our Metabolomics services play a crucial role by allowing comprehensive assessments of how genetic alterations impact crop metabolism. This ensures that your desired traits, such as increased yield or improved nutritional content, are expressed as intended.
 Crop Breeding and Variety Development
Crop Breeding and Variety Development
Our Metabolomics expertise assists in the selective breeding of crop varieties. By identifying natural variations in metabolite profiles, we guide you in choosing the most promising candidates for crossbreeding, ultimately resulting in the development of improved crop varieties.
 Environmental Adaptation
Environmental Adaptation
As the climate changes, crops must adapt. Metabolomics comes to the rescue by scrutinizing metabolic changes in response to stressors like drought, soil salinity, and temperature fluctuations. This information empowers you to develop crops capable of thriving in challenging conditions, contributing to global food security.
 Crop Shelf Life Enhancement
Crop Shelf Life Enhancement
Post-harvest preservation is essential. Metabolomics identifies metabolites linked to deterioration, allowing us to inform strategies for preserving crop freshness and quality, reducing wastage, and benefiting both producers and consumers.
 Optimization of Agricultural Practices
Optimization of Agricultural Practices
Metabolomics isn't just about genetics; it extends to optimizing agricultural practices. By monitoring metabolic responses to factors like fertilization, irrigation, and crop rotation, our Metabolomics services offer insights that drive informed decision-making. This optimization results in increased crop yields, resource efficiency, and enhanced sustainability.
Common Crops We Can Analyze
| Wheat |
Potato |
Sorghum |
Grapes |
| Rice |
Tomato |
Oats |
Apples |
| Maize (Corn) |
Cotton |
Sunflower |
Bananas |
| Barley |
Canola (Rapeseed) |
Peanuts |
Coffee |
| Soybean |
Sugar Beet |
Citrus Fruits |
Tea |
Metabolomics Technologies for Enhancing Agricultural Crop Improvement
| Metabolomics Technology |
Instrument Model |
Applications |
| Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) |
Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC coupled with Agilent 6545 Q-TOF MS |
- Quantifying diverse metabolites.
- Profiling changes in metabolite concentrations.
- Identifying biomarkers associated with specific crop traits.
- Exploring metabolic responses to environmental stressors. |
| Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) |
Thermo Fisher Scientific TRACE 1310 GC coupled with Thermo Fisher Scientific ISQ LT Single Quadrupole MS |
- Analyzing volatile metabolites.
- Profiling primary metabolites, including sugars, organic acids, and amino acids.
- Evaluating the impact of genetic modifications on crop metabolism. |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy |
Bruker AVANCE NEO 600 MHz NMR Spectrometer |
- Profiling of metabolites without extensive sample preparation.
- Examination of metabolic changes under varying environmental conditions.
- Validation of data obtained from mass spectrometry techniques. |
Case. Metabolomics Analysis of Dioscorea Species: Unlocking Insights into Metabolic Diversity
Background
Yam production, a vital food source in low-income countries, faces challenges due to its high production cost and low yield compared to cassava. Despite its potential, yam remains understudied and underutilized in breeding programs. Genomics and metabolomics offer promising tools for improving yam crops. This study aimed to comprehensively analyze the metabolome of Dioscorea species, providing insights for breeding programs and addressing food security.
Samples
Forty-nine accessions from four Dioscorea species were sourced from the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) in Nigeria. Tuber and leaf material were collected for spatial metabolomics analysis, providing a diverse sample set.
Technological Methods
Reagents: Analytical-grade reagents were used for accuracy.
Plant Material: The study collected diverse accessions, sectioning tuber materials into representative sections, and harvested tuber and leaf material from specific accessions after 9 months of growth in a polytunnel.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Profiling: Metabolite extraction, derivatization, and GC-MS analysis were performed. Modifications included phase separation by centrifugation, storage of polar phase aliquots at -20°C, and the use of splitless injections onto the GC. Matches to the NIST database required a probability of over 80%.
Data Processing and Statistics: The study combined polar and non-polar datasets, removing duplicates. Data analyses were conducted using XLSTAT add-ins within Microsoft Excel. Generalised Procrustes Analysis (GPA), agglomerative hierarchical clustering (AHC), and Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) were employed. Metabolite-metabolite correlations were determined using Spearman correlation coefficients, and Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance with Monte Carlo permutations was used for p-value calculation. Conover-Iman post hoc tests were Bonferroni-corrected.
Results:
- A comprehensive GC-MS metabolite library was established for Dioscorea species, covering intermediary and specialized metabolites.
- Metabolic pathway maps of yam tubers were created.
- Variations in metabolite composition among Dioscorea species were observed, aligning with chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic studies.
- Metabolite profiles showed potential as markers for trait inheritance and quality traits, offering a promising avenue for breeding programs.
- Leaf metabolite profiles exhibited similar trends to tuber profiles, suggesting the possibility of using leaf material for initial phenotypic screening.
 Heat-map of metabolite–metabolite correlation for D. dumetorum.
Heat-map of metabolite–metabolite correlation for D. dumetorum.
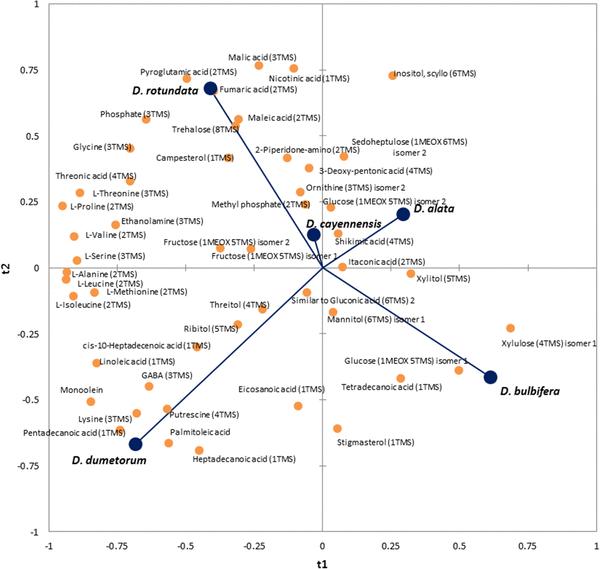 A reduced PLS-DA model classifies species based on leaf and tuber metabolite profiles.
A reduced PLS-DA model classifies species based on leaf and tuber metabolite profiles.
Reference
- Price, Elliott J., et al. "Metabolite profiling of yam (Dioscorea spp.) accessions for use in crop improvement programmes." Metabolomics 13 (2017): 1-12.


 Heat-map of metabolite–metabolite correlation for D. dumetorum.
Heat-map of metabolite–metabolite correlation for D. dumetorum. A reduced PLS-DA model classifies species based on leaf and tuber metabolite profiles.
A reduced PLS-DA model classifies species based on leaf and tuber metabolite profiles.

