What is Strawberry (Fragaria spp.)?
Strawberry (Fragaria spp.), a member of the Rosaceae family, is a perennial plant renowned for its vibrant red berries. These delectable fruits are not just a delight to the palate; they are also a rich source of essential nutrients. The genus Fragaria encompasses various species and cultivars, each with its unique characteristics and flavor profiles.
Strawberry (Fragaria spp.) Metabolism
Understanding the metabolic intricacies of strawberries is pivotal for enhancing their cultivation, nutritional content, and overall quality. At Creative Proteomics, we specialize in metabolic analysis, providing comprehensive insights into the biochemical processes that underpin these succulent fruits. Our expertise in strawberry metabolism analysis encompasses a wide array of research aspects:
Nutrient Composition Analysis
We conduct in-depth analysis of the nutritional profile of strawberries. Our services include the quantification of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients. Additionally, we investigate how different growth conditions impact nutrient content.
Flavor Compounds Investigation
The unique aroma and flavor of strawberries stem from volatile compounds. We identify and quantify these compounds, shedding light on the factors that influence flavor development.
Assessing Antioxidant Capacity
Strawberries are renowned for their antioxidant-rich content. We measure the levels of antioxidant compounds and explore their role in promoting health and protecting against oxidative stress. Our experts also delve into strategies to boost strawberry antioxidant content.
Unraveling Metabolic Pathways
Our research dives deep into the metabolic pathways governing strawberry ripening, fruit development, and responses to environmental stressors. We identify key enzymes and genes that regulate these processes, opening avenues for targeted manipulation.
Enhancing Quality and Shelf Life
Quality is paramount in the strawberry industry. We assess the factors affecting strawberry quality, including post-harvest handling and storage conditions. Our team devises strategies to extend shelf life while preserving nutritional value.
Varietal Studies
We specialize in conducting varietal studies to compare metabolite profiles among different strawberry varieties. This enables the identification of unique metabolic signatures associated with specific varieties, streamlining the selection and breeding of strawberries with desired traits.
Disease and Stress Response Studies:
Our expertise extends to investigating the impact of diseases or environmental stresses on strawberry metabolism. Through metabolomics analysis, we unveil metabolic changes induced by stressors, contributing to the development of strategies aimed at enhancing the resilience and quality of strawberries.
Strawberry Metabolomics Service by Creative Proteomics
Metabolite Profiling: Encompass comprehensive metabolite profiling within Fragaria spp. samples. This involves the identification and quantification of a wide spectrum of compounds, thereby facilitating the detailed characterization of the chemical composition of strawberries.
Metabolic Pathway Analysis: Delve into the intricate web of metabolic pathways in strawberries. Our analysis reveals the connections and interactions among various metabolites, helping you decipher the metabolic intricacies.
Data Interpretation: Benefit from our expert data interpretation services. We provide comprehensive insights, ensuring that you gain a deep understanding of your metabolomics data.
Statistical Analysis: Harness the power of advanced statistical methods to extract meaningful conclusions from complex metabolomics datasets. Our statistical analysis enhances the significance of your findings.
Strawberry Metabolomics Analysis Techniques
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS): We utilize the Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC coupled with the Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Plus mass spectrometer for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. This technique efficiently separates and identifies metabolic products within strawberries, ensuring accurate quantitative analysis.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS/MS): Our analysis relies on the Agilent 7890B gas chromatograph coupled with the Agilent 7000C quadrupole mass spectrometer for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. This technology is employed to detect and analyze volatile organic compounds in strawberries, providing comprehensive metabolic insights.
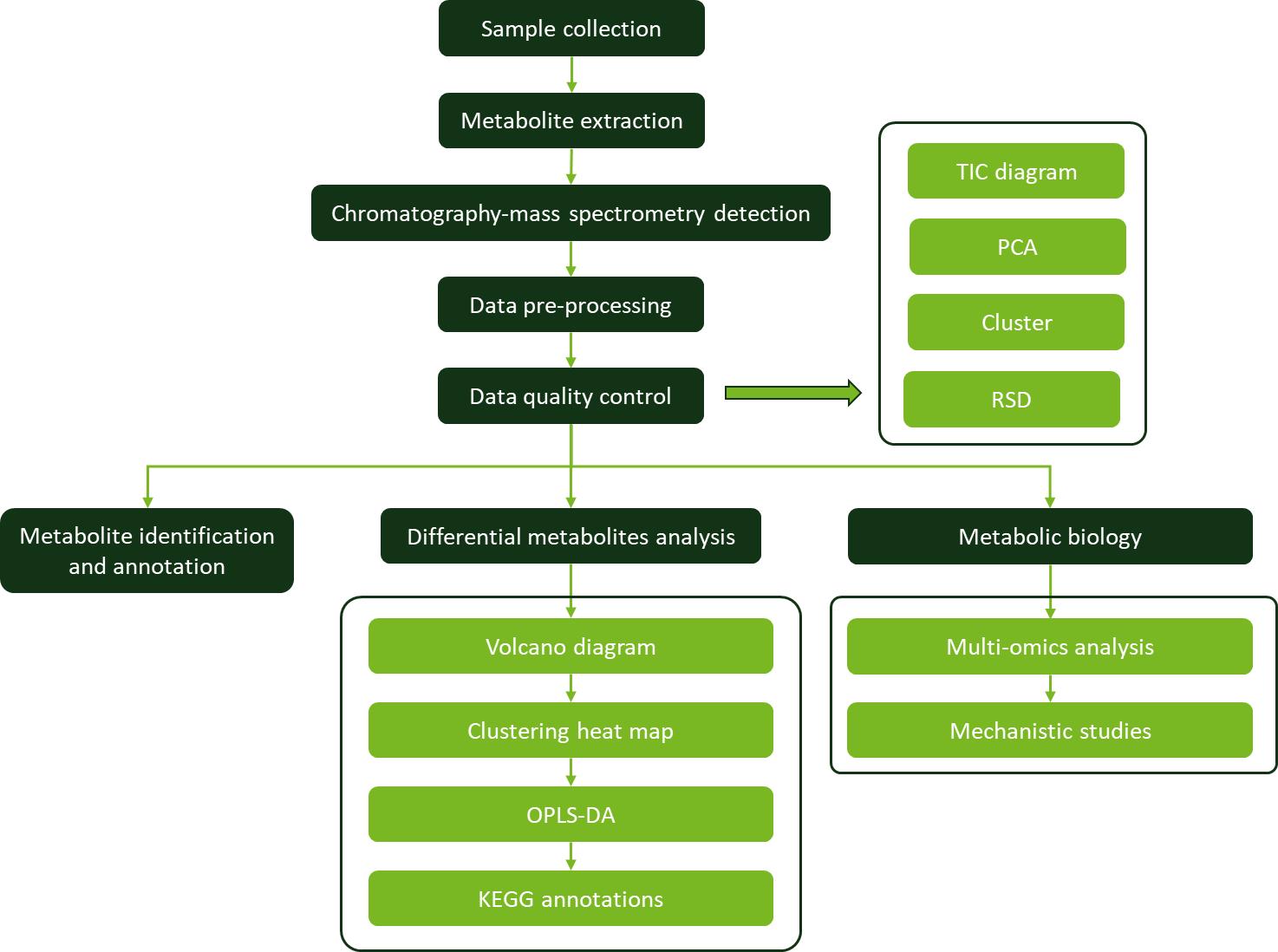 Workflow for Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Metabolomics Service
Sample Requirements for Strawberry Metabolomics
| Sample Type |
Sample Description |
Recommended Sample Quantity |
Additional Notes |
| Fresh Strawberries |
Fully ripe fresh strawberries, stems removed, and cleaned |
100-200 grams |
Samples should be frozen or processed promptly to prevent metabolite degradation. |
| Frozen Strawberries |
Fresh strawberries frozen and kept at low temperatures |
100-200 grams |
Samples should be maintained in a frozen state, avoiding repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Fresh Strawberries from Different Parts |
Includes strawberry pulp, skin, leaves, etc. |
100-200 grams (per part) |
Samples from each part should be collected and processed separately to analyze metabolic differences. |
| Fresh Strawberries at Different Growth Stages |
Strawberries at different maturity stages |
100-200 grams (per stage) |
Samples from different growth stages should be collected and processed separately to analyze metabolic changes. |
| Stress-Induced Strawberries |
Strawberries subjected to stress, such as infection or grown under specific environmental conditions |
100-200 grams |
Samples should be collected from strawberries subjected to stress, and the stress conditions should be documented. |
Case. Metabolomic Profiling of Strawberry Plants Under Osmotic Stress Reveals Differential Metabolite Responses
Background
The study investigates the metabolic responses of strawberry plants (cv. Camarosa) to osmotic stress induced by water deficit and excess salt (NaCl) treatments. Osmotic stress can impact plant metabolism, and understanding these responses is crucial for crop improvement and stress tolerance.
Samples
Strawberry plants were cultivated in a controlled greenhouse environment in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The experiment included four treatments: normal irrigation (control), 95% ETc water deficit (DS1), 85% ETc water deficit (DS2), and 80 mmol L−1 NaCl salt stress (SS). Strawberry samples were harvested at full ripeness and subjected to metabolomic analysis.
Technological Methods
Sample Preparation:
- Frozen strawberry samples underwent an extraction process using a solution composed of 75% methanol with 0.1% formic acid.
- After extraction, samples were vortexed and sonicated, followed by centrifugation to obtain supernatants.
- Reserpine, used as an internal standard, was added to the extraction solvent.
- Extracts were further filtered to ensure purity before analysis.
LC-MS/MS Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis:
- Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis was conducted using a high-performance liquid chromatography system coupled with a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry detector (Q-TOF-MSD).
- Separation of metabolites occurred on a C18 column with a specific gradient elution program.
- Mass spectrometry operated in both negative and positive ionization modes to capture a wide range of metabolites.
GC-MS Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis:
- Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis was performed using a Shimadzu GCMS-QP2010 Ultra instrument.
- The polar and apolar fractions of the samples were analyzed separately.
- Chromatographic separation took place on a Rxi-1MS column with distinct temperature programs optimized for each fraction.
Results
Data Processing and Statistical Analysis:
- Mass spectra calibration, peak detection, and data processing were executed with specialized software tools.
- Multivariate statistical methods, including PCA and OPLS-DA, were employed to visualize sample groupings and distinctions among treatments.
- To identify metabolites significantly affected by osmotic stress, univariate statistical analyses such as t-tests and fold change calculations were conducted.
- False discovery rate (FDR) correction was applied to control the error rate in statistical comparisons.
Tentative Metabolite Identification:
- Tentative identification of metabolites was carried out by comparing accurate mass measurements, isotopic profiles, and fragmentation patterns with entries in online databases.
- For GC-MS compounds, comparisons were made to the National Institute of Standards and Technology mass spectra library (NIST 11).
- Several metabolites were found to exhibit significant alterations in response to osmotic stress, encompassing phytosterols, amino acids, sugars, and phenolic compounds.
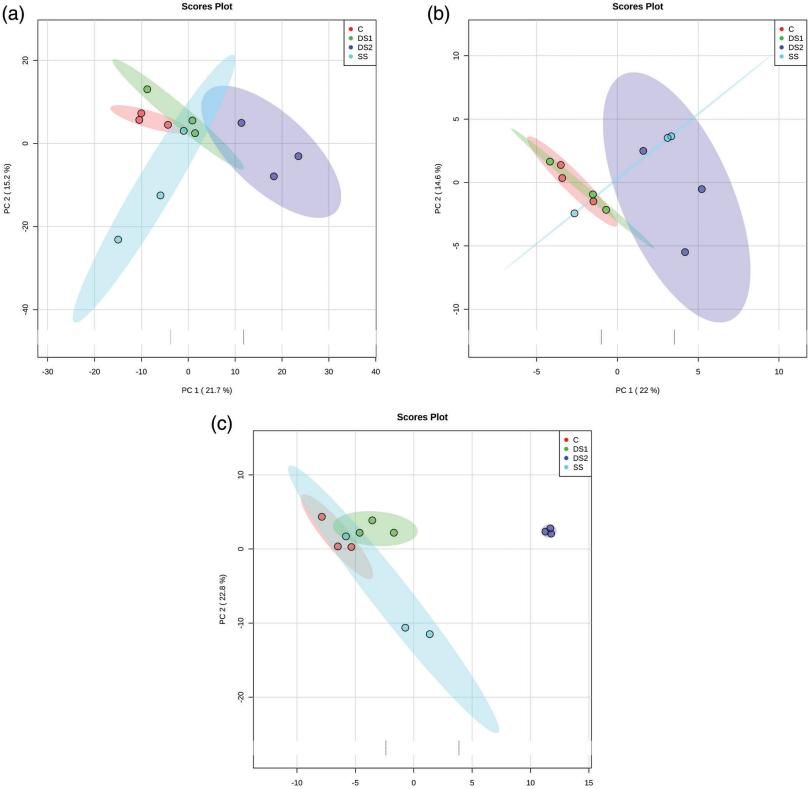 PCA scores plot.
PCA scores plot.
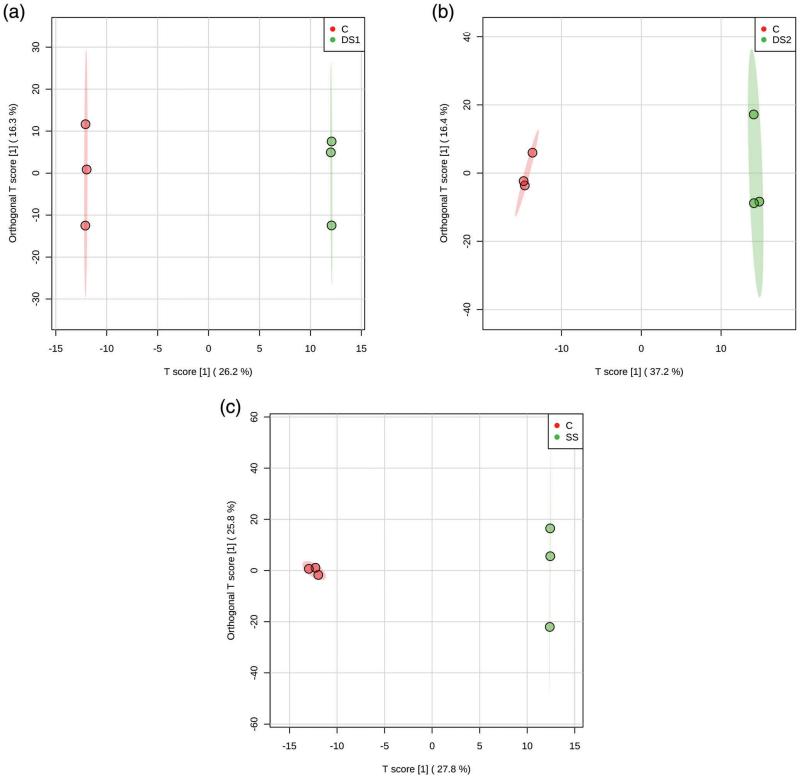 OPLS-DA scores plot derived from LC-MS/MS (ESI− and ESI+) and GC-MS datasets
OPLS-DA scores plot derived from LC-MS/MS (ESI− and ESI+) and GC-MS datasets
Reference
- Antunes, Ana CN, et al. "Untargeted metabolomics of strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa ‘Camarosa’) fruit from plants grown under osmotic stress conditions." Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 99.15 (2019): 6973-6980.


 Workflow for Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Metabolomics Service PCA scores plot.
PCA scores plot. OPLS-DA scores plot derived from LC-MS/MS (ESI− and ESI+) and GC-MS datasets
OPLS-DA scores plot derived from LC-MS/MS (ESI− and ESI+) and GC-MS datasets

