What are Isoflavonoids and Why Analyze Them?
Isoflavonoids form a class of flavonoids, which are secondary metabolites ubiquitously present in leguminous plants. The incredible health benefits attributed to these compounds across numerous medical and scientific journals have brought them to the limelight in recent years.
Intake of isoflavonoids has shown strong inverse correlations with various cardiovascular diseases, different types of cancer, especially breast and prostate cancer, as well as menopausal discomforts. Their antioxidant, anticancer, and estrogenic/anti-estrogenic properties make these compounds potential candidates for drug production. Furthermore, isoflavonoids play crucial roles in assisting plants in warding off diseases and assaults from pests.
The analysis of isoflavonoids hence provides a comprehensive understanding of these compounds from their structural properties to their potential therapeutic applications.
Isoflavonoids Analysis at Creative Proteomics
At Creative Proteomics, we are committed to unboxing the untapped potential of isoflavonoids. Our analytical services cater to the requirements of food safety, pharmacology, environmental studies, and much more. Our offerings include but are not limited to:
- Isoflavonoid Quantitative Analysis: This service involves accurate quantification of various isoflavonoids in different samples such as food, beverages, and other biological samples. It is performed using advanced analytical techniques like HPLC, UHPLC, GC-MS/MS, and LC-MS/MS.
- Isoflavonoid Profiling: Isoflavonoid profiling service allows for comprehensive analysis and identification of the various isoflavonoids present in your samples. This helps in understanding the detailed isoflavonoid composition and could be crucial in product development and quality control processes.
- Isoflavonoid Metabolic Pathway Analysis: We offer exploration of the metabolic pathways of isoflavonoids, which can help researchers better understand their pharmacokinetic properties and mechanism of action.
- Isoflavonoid Derivatives Analysis: This service can help to identify and quantify various isoflavonoid derivatives which may have different biological activities from the parent compounds.
- Isoflavonoid Bioavailability Studies: Understanding the bioavailability of isoflavonoids is essential for determining their therapeutic potential. We provide services to evaluate how well these substances can be absorbed and utilized by the body.
- Isoflavonoid Function and Activity Studies: We conduct in-depth research on isoflavonoid function and activities, aiding in understanding their potential benefits and risks, as well as exploring their therapeutic applications.
- Customized Isoflavonoid Research Services: We also offer tailor-made research services depending on your specific project needs in the isoflavonoid research field.
Isoflavonoids Analysis Techniques
Sample Preparation Techniques: Tailored extraction methods, including Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) and Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE), are utilized for diverse sample types, optimizing recovery and purity.
Chromatographic Separation: Liquid Chromatography (LC), specifically High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), is employed for effective chromatographic separation, enhancing mass spectrometric selectivity and ensuring accurate results.
Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry: Utilizing the Agilent 6460 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer for targeted quantification, this technique ensures unparalleled sensitivity for accurate concentration determination.
High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Our use of High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry with the Thermo Scientific Orbitrap allows for precise identification and profiling of isoflavonoids, broadening the range of detectable compounds.
Quality Control Measures: Stringent quality control measures, including calibration standards, internal standards, and quality control samples, validate instrument performance and ensure the accuracy and precision of the analysis.
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Thorough data analysis, encompassing peak integration, compound identification, and concentration determination, is conducted using advanced software tools. The results are interpreted by our experts, providing clients with comprehensive reports for actionable insights.
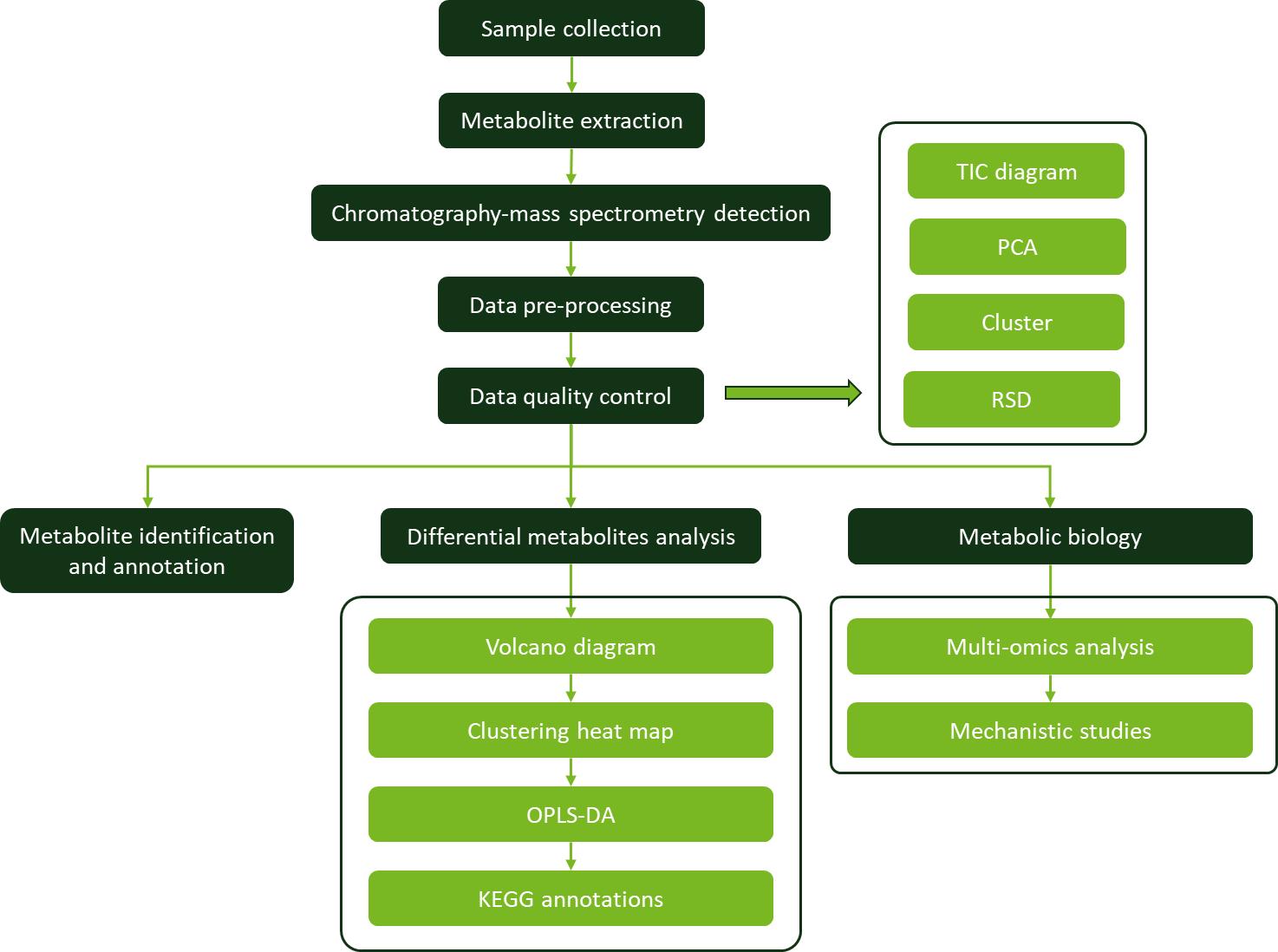 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Isoflavonoids Analyzed (including but not limited to)
| Biochanin A |
Biochanin B |
Calycosin |
Coutareagenin |
Daidzein |
| Dalbergin |
Equol |
Formononetin |
Furanonaringenin |
Genistein |
| Glycitein |
Isoformononetin |
Laxiflorane |
Lonchocarpane |
Medicarpin |
| Neovestitol |
Nivetin |
Ononin |
Phytoestrogens |
Prunetin |
| Puerarin |
Sissotrin |
Tectorigenin |
2'-Hydroxygenistein |
3'-Hydroxybiochanin A |
| 3'-Hydroxyformononetin |
3'-Methoxydaidzein |
6''-Hydroxybiochanin A |
6''-Hydroxydaidzein |
7-Hydroxyisoflavone |
| Vestitol |
|
|
|
|
Sample Requirements for Isoflavonoids Assay
| Sample Type |
Recommended Quantity |
| Plant Extracts |
50 mg |
| Food Products |
10 g |
| Serum/Plasma |
0.5 mL |
| Plant Leaves |
100 mg |
| Seeds |
20 g |
Deliverables of Isoflavonoids Analysis
Our commitment to transparency and customer satisfaction prompts us to ensure our clients stay well-informed throughout the project lifecycle. The deliverables from our Isoflavonoids Analysis encompass:
- Detailed experimental protocol and procedure
- Raw data and processed data
- Comprehensive analysis report
- Expert insights and recommendations based on the analysis
Case. Effects of UV-B Irradiation on Flavonoid and Isoflavonoid Accumulation in Lotus Corniculatus Leaves
Background:
The study investigates the impact of UV-B irradiation on the physiological and molecular responses of Lotus corniculatus leaves, focusing on changes in flavonoid and isoflavonoid contents. Flavonoids and isoflavonoids play crucial roles in plants' defense mechanisms and stress responses.
Sample:
Lotus corniculatus L. cultivar 'INIA Draco' from Uruguay was the primary plant material, with additional analysis conducted on European cultivar 'Polom' from Slovakia. Seedlings propagated from shoot cuttings were grown under controlled conditions for 30 days. UV-B radiation, mimicking equatorial levels, was applied for 16 hours.
Technical Platform and Procedure:
UV-B Irradiation: Applied for 16 hours using a fluorescence lamp with a spectral output measured to simulate conditions near the equator.
Sample Preparation: Leaves were collected at various time points during UV-B exposure and subjected to different analyses.
Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis Analysis: Concentrations of chlorophyll a and b were measured, and the maximum potential quantum efficiency of Photosystem II (PSII) was assessed.
Flavonoid and Isoflavonoid Analysis: HPLC analysis of dried leaf samples, with identification using UV-absorption and MS spectra. Detection at 220 nm and 350 nm. MS identification included LC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS analyses.
Gene Expression Analysis: Four genes encoding pterocarpan reductase (PTR) involved in vestitol biosynthesis were analyzed using qPCR.
Results
UV-B irradiation led to a significant decrease in chlorophyll concentrations, indicating negative effects on photosynthesis.
Hydrogen peroxide levels increased, suggesting metabolic changes due to oxidative stress.
Flavonoid and isoflavonoid accumulation increased, with kaempferol glycosides being the dominant flavonoids.
Vestitol, a key isoflavonoid, showed a substantial increase under UV-B, accompanied by changes in other isoflavonoids.
Gene expression analysis revealed the induction of genes related to vestitol biosynthesis, supporting the observed increase in vestitol levels.
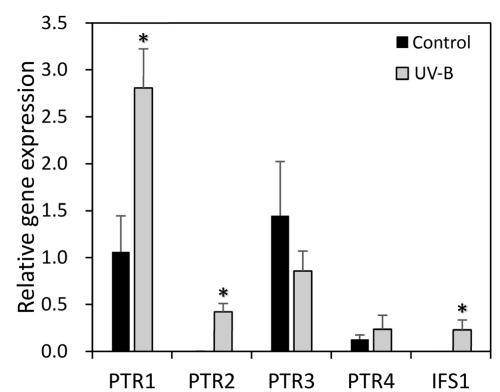 Relative expressions levels of pterocarpane reductase (PTR) and isoflavone synthase (IFS) in leaves of Lotus corniculatus after UV-B irradiance
Relative expressions levels of pterocarpane reductase (PTR) and isoflavone synthase (IFS) in leaves of Lotus corniculatus after UV-B irradiance
Reference
- Kaducová, Mária, et al. "Accumulation of isoflavonoids in Lotus corniculatus after UV-B irradiation." Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology (2022): 1-10.


 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service Relative expressions levels of pterocarpane reductase (PTR) and isoflavone synthase (IFS) in leaves of Lotus corniculatus after UV-B irradiance
Relative expressions levels of pterocarpane reductase (PTR) and isoflavone synthase (IFS) in leaves of Lotus corniculatus after UV-B irradiance

