What is Luteolin?
Luteolin is a natural flavonoid, belonging to the flavone class of polyphenol compounds. It is widely distributed in various plants, including fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs. Some common dietary sources of luteolin include celery, parsley, thyme, peppers, and chamomile tea.
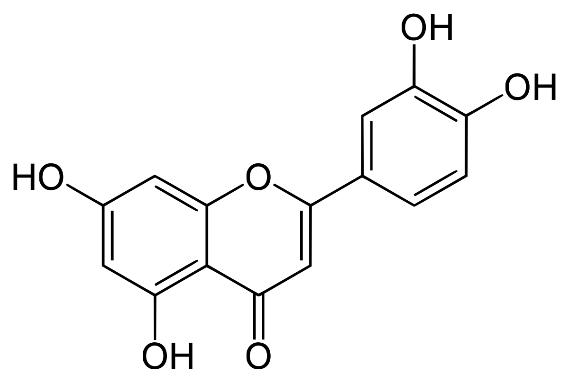 Luteolin
Luteolin
This compound has attracted attention due to its potential health benefits and antioxidant properties. Luteolin has been studied for its anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and neuroprotective effects. It is believed to exert these effects through various mechanisms, including the modulation of signaling pathways and the inhibition of inflammatory mediators.
Research suggests that luteolin may help reduce inflammation by inhibiting the activity of pro-inflammatory enzymes and cytokines. Additionally, it has been investigated for its potential to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in certain types of cancers.
Moreover, luteolin has been studied in the context of neuroprotection, with some evidence suggesting its ability to protect against neurodegenerative disorders. It is believed to exert its neuroprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptotic processes in the brain.
Creative Proteomics offers precise and accurate analytical services for luteolin, enabling the determination of its unique characteristics. Our services include measuring concentration levels in biological samples, assessing the strength of its antioxidant effects, and investigating interactions with other biochemical elements. These services cater to scientists engaged in research across various fields, including pharmacology, food science, biochemistry, and more.
Specific Luteolin Analysis Offered by Creative Proteomics
At Creative Proteomics, we offer a wide array of services for the detailed luteolin analysis. Our primary focus is maintaining high quality, precision, and accuracy in all projects we undertake. The specific project directions provided for Luteolin analysis include:
Luteolin Structural Analysis: Understanding the detailed molecular structure of luteolin using advanced spectroscopic techniques.
Luteolin Functional Analysis: Evaluating the various biological activities and properties of luteolin.
Luteolin Distribution Analysis: Studying the distribution pattern of luteolin in different plant species and parts.
Luteolin Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis: These help identify the precise quantities and the presence of luteolin in a given sample.
Luteolin Analysis Techniques
Mass spectrometry, due to its excellent sensitivity and specificity, has been extensively applied to the analysis of luteolin. Creative Proteomics not only owns state-of-art mass spectrometers but also holds advanced softwares and databases for accurate data interpretation.
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS): Our LC-MS analyses are conducted using cutting-edge instruments, including:
- Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC System: Delivering high-resolution separations for accurate detection.
- Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Plus Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer: Facilitating precise quantification and structural elucidation.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): For specific applications, we leverage advanced GC-MS technology, prominently featuring:
- Agilent 7890B Gas Chromatograph: Ensuring optimal separation of volatile compounds.
- Agilent 5977B Mass Selective Detector: Providing sensitive and selective detection of Luteolin and its derivatives.
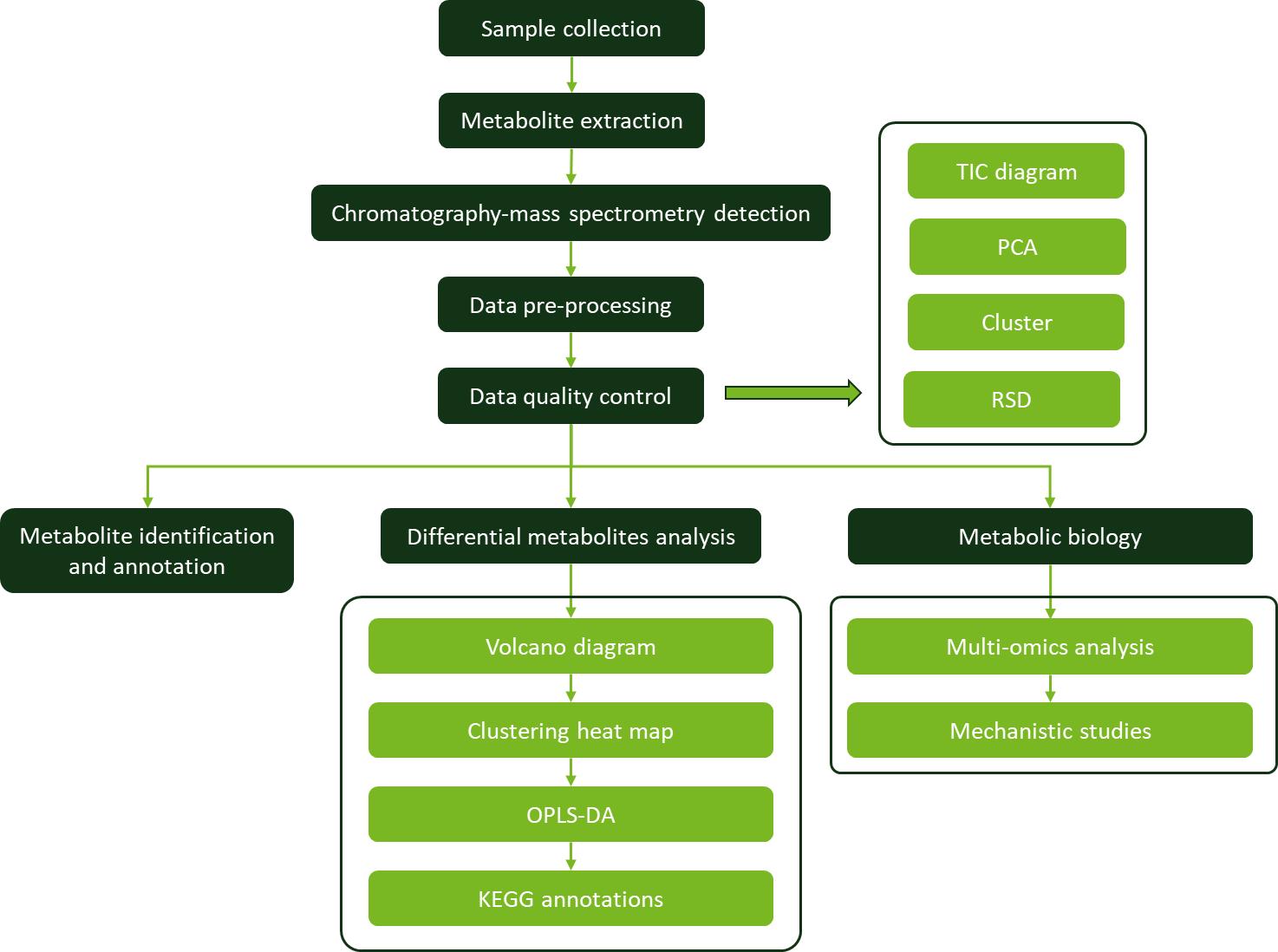 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Luteolin Analyzed (including but not limited to)
| Luteolin |
Luteolin Glucoside |
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside |
Luteolin-3'-O-glucuronide |
| Luteolin-4'-O-glucuronide |
Luteolin-5-O-glucuronide |
Luteolin-3'-O-methyl ether |
Luteolin-4'-O-methyl ether |
| Luteolin-7-O-methyl ether |
Luteolin-3'-O-sulfate |
Luteolin-4'-O-sulfate |
Luteolin-5'-O-glucoside |
| Luteolin-7-O-glucuronide |
Luteolin-4'-O-glucoside |
Luteolin-6-C-glucoside |
Luteolin-8-C-glucoside |
| Luteolin-3'-O-rhamnoside |
Luteolin-4'-O-rhamnoside |
Luteolin-7-O-rhamnoside |
|
Sample Requirements for Luteolin Assay
| Sample Type |
Recommended Quantity |
| Plant Extracts |
0.1-1 gram |
| Dietary Supplements |
50-100 milligrams |
| Biological Tissues |
50-100 milligrams |
| Plasma or Serum Samples |
0.5-1 milliliter |
| Cell Cultures |
1-5 million cells |
| Food Products |
Varies (5-10 grams) |
| Herbal Infusions |
5-10 grams |
| Environmental Samples |
Soil: 10-50 grams, Water: 50-100 ml |
| Pharmaceutical Formulations |
50-100 milligrams |
Case. Exploring the Pharmacological Potential and Flavonoid Composition of Passiflora loefgrenii
Background
Passiflora loefgrenii, a relatively understudied plant species, has been investigated for its pharmacological potential and flavonoid composition. While Passiflora species are known for their diverse bioactive compounds, the specific properties of P. loefgrenii remain largely unexplored.
Sample
Three different extracts were obtained from various parts of the P. loefgrenii plant: young leaves (YL), adult basal leaves (AL), and stems (ST). These samples were subjected to detailed analysis to uncover the flavonoid composition and potential pharmacological applications.
Technical Platform and Procedure
The study employed a combination of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array Detection (HPLC-DAD) and Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS) techniques. The antioxidant activity of the samples was assessed using the 2,2'-di-phenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) quenching assay. The evaluation included the determination of IC50 values and the generation of dose–response curves.
Results
1. Flavonoid Composition:
- The HPLC-DAD and ESI-MS/MS analysis revealed a similar composition among the extracts, with flavonoids identified as the main constituents.
- Luteolin emerged as the predominant aglycone, with major flavonoids including orientin, 7-O-α-rhamnosyl 6-C-ß-glucosyl luteolin, and 6-C-α-rhamnosyl luteolin.
2. Antioxidant Activity:
- The AL extract exhibited notable antioxidant activity against DPPH radicals, with an IC50 of 350 ± 0.01 μg/ml.
- The results were compared with reference compounds quercetin and ascorbic acid, showing promising antioxidant potential in P. loefgrenii.
3. Comparison with Other Passiflora Species:
- A comparative analysis with P. incarnata highlighted distinct differences in flavonoid profiles, emphasizing the uniqueness of P. loefgrenii.
- P. loefgrenii demonstrated a dominance of C-glycosyl flavones with luteolin as the aglycone, suggesting its potential as a biomarker.
4. Pharmacological and Therapeutic Implications:
- The study implies that P. loefgrenii could be explored for its diverse pharmacological properties beyond the commonly associated sedative effects of Passiflora species.
- The presence of luteolin glycosides in P. loefgrenii suggests potential health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, with implications for disease prevention and health maintenance.
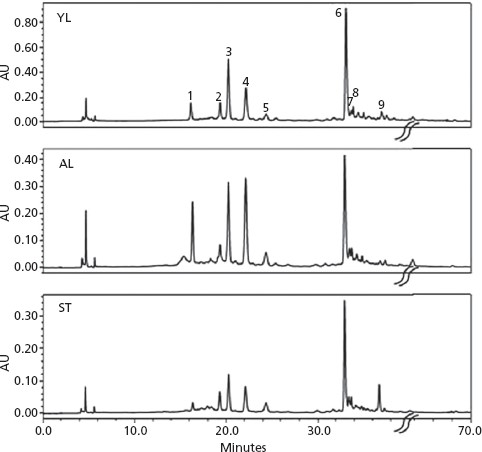 HPLC-DAD (350 nm) chromatograms of flavonoids from P. loefgrenii young upper leaves (YL), basal adult leaves (AL) and stems (ST).
HPLC-DAD (350 nm) chromatograms of flavonoids from P. loefgrenii young upper leaves (YL), basal adult leaves (AL) and stems (ST).
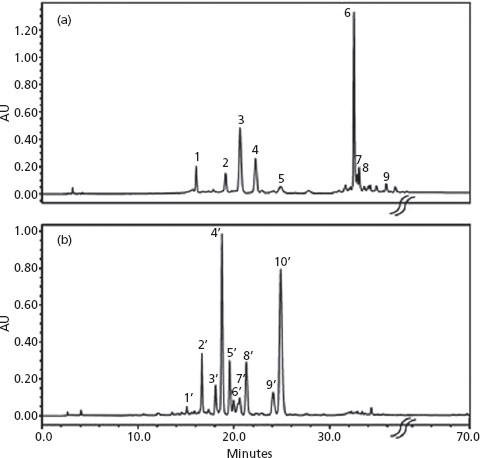 Comparison between HPLC-DAD (350) chromatograms of flavonoids from P. loefgrenii (A) and Passiflorae herba (B).
Comparison between HPLC-DAD (350) chromatograms of flavonoids from P. loefgrenii (A) and Passiflorae herba (B).
Reference
- Argentieri, Maria Pia, et al. "Phytochemical analysis of Passiflora loefgrenii Vitta, a rich source of luteolin-derived flavonoids with antioxidant properties." Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 67.11 (2015): 1603-1612.


 Luteolin
Luteolin Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service HPLC-DAD (350 nm) chromatograms of flavonoids from P. loefgrenii young upper leaves (YL), basal adult leaves (AL) and stems (ST).
HPLC-DAD (350 nm) chromatograms of flavonoids from P. loefgrenii young upper leaves (YL), basal adult leaves (AL) and stems (ST). Comparison between HPLC-DAD (350) chromatograms of flavonoids from P. loefgrenii (A) and Passiflorae herba (B).
Comparison between HPLC-DAD (350) chromatograms of flavonoids from P. loefgrenii (A) and Passiflorae herba (B).

