What is Gallocatechin?
Gallocatechin (GC) is a natural phenolic compound and a variety of epicatechin, categorized under the class of flavonoids known as flavan-3-ols or catechins. Well identified in numerous plants, most notably Green Tea leaves, gallocatechin has significant pharmacological and biological roles. Acting as powerful antioxidants, they help neutralize free radicals, deter inflammation, decrease the occurrence of degenerative diseases, and may potentially inhibit cancer. The inherent health benefits of gallocatechin underline its widely acknowledged significance in the food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries.
Scientifically studying and understanding gallocatechin aids in fully exploiting its potential and predicting its possible implications. Advanced analysis of gallocatechin allows for proper standardization of therapeutic extracts and the development of targeted treatment modalities.
Creative Proteomics offers a comprehensive solution to the analysis of gallocatechin across several sectors.
Specific Project Offered by Creative Proteomics in Gallocatechin Analysis:
Gallocatechin Composition Analysis: We provide comprehensive analysis of different products and materials which may contain gallocatechin, including plant tissue, food, beverage samples, dietary supplements, and herbal medicines. The precise determination of gallocatechin composition can contribute to the product characterization, quality control, and safety evaluation efforts.
Gallocatechin Metabolomics Study: Gallocatechin is a biologically active compound, which involves in various metabolic pathways. Our gallocatechin metabolomics study focuses on the comprehensive profiling of gallocatechin related metabolites in bio-samples, which can facilitate the research of biological functions, metabolic regulation, and disease correlation.
Gallocatechin Quantification Analysis: It is crucial to quantify gallocatechin accurately in biological and environmental samples for dietary exposure assessment, therapeutic level monitoring, and environmental impact analysis. We utilize precise and sensitive analytical methods for the quantification of gallocatechin.
Gallocatechin Analysis Techniques
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Separates gallocatechin in complex mixtures, often coupled with UV or mass spectrometry for accurate quantification.
Mass Spectrometry (MS): Determines molecular weights and provides structural information, crucial for identifying gallocatechin derivatives.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: Elucidates the molecular structure, confirming gallocatechin identity and detecting structural variations.
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS): Combines liquid chromatography's separation capabilities with mass spectrometry for enhanced sensitivity.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Suitable for volatile gallocatechin derivatives, providing complementary information to other techniques.
Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy: Used with HPLC for rapid and cost-effective quantification of gallocatechin concentrations.
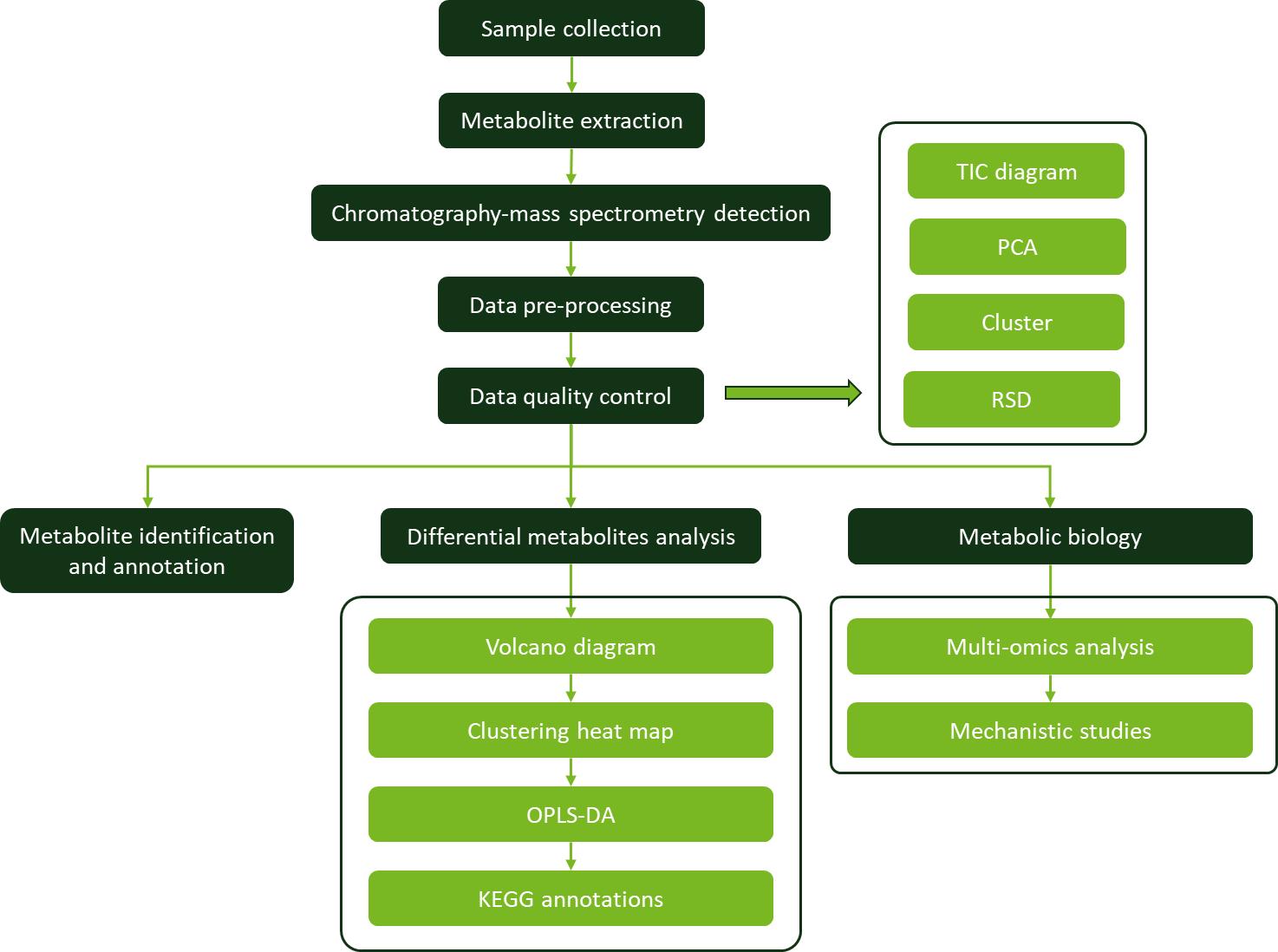 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Gallocatechin Analyzed (including but not limited to)
| Gallocatechin |
Gallocatechin gallate |
Epigallocatechin |
Epigallocatechin gallate |
Sample Requirements for Gallocatechin Assay
| Sample Type |
Recommended Sample Volume |
Additional Notes |
| Biological Fluids |
0.5 - 1 mL |
Serum, plasma, urine, etc. |
| Plant Extracts |
50 - 100 mg |
Dried and ground plant material |
| Food and Beverages |
Varies |
Specific instructions provided based on the matrix type |
Deliverables of Gallocatechin Analysis
- Comprehensive final report with all details of the analysis including methodology, sample preparation, chromatograms, and results.
- Raw data and processed data of mass spectrometry.
- Detailed pathways and potential functions of detected gallocatechins.
Case. Pharmacokinetic Study of Gallocatechin-7-Gallate (J10688) from Pithecellobium Clypearia in Rats
Background
Pithecellobium clypearia Benth., a traditional Chinese medicine, contains J10688, a compound with anti-influenza virus activity. This study aims to explore the pharmacokinetics of J10688, contributing to its preclinical evaluation and guiding similar compound studies.
Sample
Male and female SD rats (6–8 weeks old) weighing 200-240 g were used. J10688 was dissolved in 60% hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Blood samples were collected at various time points post-injection, and plasma samples were stored at -80 °C before analysis.
Technical Platform and Procedure
Chromatographic Conditions: LC–MS method with Agilent 1200 liquid chromatography-6100 mass spectrometer using Zorbax SD-C18 column. Mobile phase: acetonitrile-water (0.1% formic acid) (23:77, v/v). Negative scan mode for mass spectrometry.
Validation: Specificity, linearity, LLOQ, precision, accuracy, extraction recovery, matrix effect, and stability were assessed following US FDA guidelines.
Pharmacokinetic Study: Three dose groups (1, 3, and 10 mg/kg) of J10688 were administered intravenously. Blood samples were collected, and pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using DAS 3.0 pharmacokinetic program.
Results
Specificity and Linearity: Chromatograms showed specificity, and calibration curves exhibited good linearity (ranging from 10 to 2000 ng/mL) with correlation coefficients (r) between 0.9993 and 0.9999.
Accuracy and Precision: Intra- and inter-day precision for J10688 was below 7.98%, and accuracy ranged from 100.15% to 107.27%, meeting acceptance criteria.
Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effect: Recovery values ranged from 99.65% to 102.91%, and matrix effect demonstrated suitability for J10688 and IS extraction with no significant interference.
Stability: QC samples remained stable after different conditions, including short-term and long-term storage, freeze/thaw cycles, and autosampler storage.
Pharmacokinetic Study: J10688 exhibited rapid distribution, short elimination half-life (t1/2), and non-linear pharmacokinetics at higher doses. Exposure levels correlated with doses, but the 10 mg/kg dose showed non-proportional pharmacokinetic parameters, suggesting potential saturation of metabolic processes.
![Full scan mass spectra of (A) J10688 with the m/z 441.0 [M–H]– and (B) IS with the m/z 301.0 [M–H]–.](upload/image/gallocatechin-analysis-service-1.jpg) Full scan mass spectra of (A) J10688 with the m/z 441.0 [M–H]– and (B) IS with the m/z 301.0 [M–H]–.
Full scan mass spectra of (A) J10688 with the m/z 441.0 [M–H]– and (B) IS with the m/z 301.0 [M–H]–.
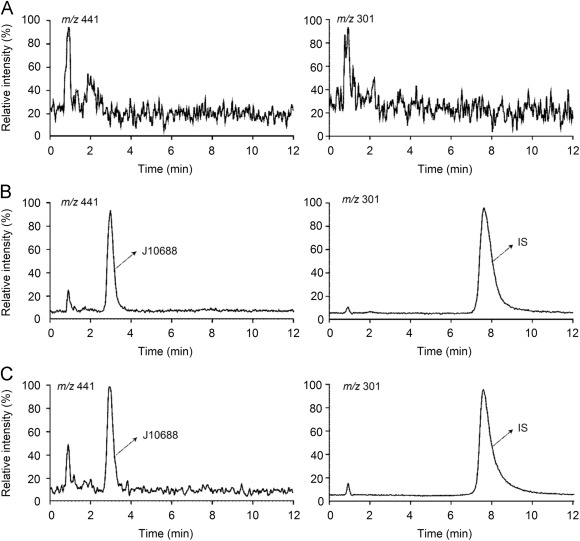 Typical chromatograms of J10688 and IS.
Typical chromatograms of J10688 and IS.
Reference
- Li, Chao, et al. "Pharmacokinetic study of gallocatechin-7-gallate from Pithecellobium clypearia Benth. in rats." Acta pharmaceutica sinica B 6.1 (2016): 64-70.


 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service![Full scan mass spectra of (A) J10688 with the m/z 441.0 [M–H]– and (B) IS with the m/z 301.0 [M–H]–.](upload/image/gallocatechin-analysis-service-1.jpg) Full scan mass spectra of (A) J10688 with the m/z 441.0 [M–H]– and (B) IS with the m/z 301.0 [M–H]–.
Full scan mass spectra of (A) J10688 with the m/z 441.0 [M–H]– and (B) IS with the m/z 301.0 [M–H]–. Typical chromatograms of J10688 and IS.
Typical chromatograms of J10688 and IS.

