Phenols, a class of organic compounds characterized by a hydroxyl (-OH) functional group attached to an aromatic ring, have garnered considerable attention due to their diverse biological roles and potential health effects. Phenols and their metabolites are involved in processes such as antioxidant defense, cell signaling, and regulation of gene expression. Understanding the presence and concentration of phenols in various biological samples is essential for unraveling their physiological significance and identifying potential biomarkers for health and disease.
Creative Proteomics, with its decades of experience and cutting-edge technology, offers a comprehensive suite of phenols detection services. Our commitment to advancing scientific understanding is exemplified by our extensive range of phenols-related projects, which cater to diverse research needs and applications.
Phenols Detection Projects at Creative Proteomics
Peering into Environmental Phenols Profiling: Environmental impact echoes through our projects as we delve into phenols profiling in diverse environmental samples. Through this, we contribute to the broader understanding of environmental health and offer vital data for informed decision-making.
Unearthing Phenols Biomarkers: Creative Proteomics embarks on a journey of biomarker discovery, where Phenols take center stage. By meticulously analyzing phenolic compounds in biological fluids, we pave the way for potential breakthroughs in disease diagnostics and personalized medicine.
Glimpsing into Herbal Medicine Phenols: Our expertise extends even to the realm of herbal medicine. We unravel the intricate phenolic content within these traditional remedies, ensuring their quality and efficacy through rigorous analysis.
Quantifying Phenols in Food and Beverages: Our expertise extends to quantifying phenols in food and beverages, facilitating precise nutritional analysis and quality assurance. With meticulous attention to detail, we unravel the Phenolic composition of consumables, empowering informed dietary choices.
Phenols Detection Techniques
Our phenols detection services rely on cutting-edge mass spectrometry-based techniques, which enable accurate and sensitive measurement of phenols and their metabolites. We utilize state-of-the-art instruments, including but not limited to:
- Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS): Our LC-MS systems, such as the Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC System coupled with the Agilent 6550 iFunnel Q-TOF LC/MS, enable high-resolution analysis of complex phenols mixtures.
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Creative Proteomics employs GC-MS technology, exemplified by the Thermo Scientific™ TSQ™ 9000 GC-MS/MS System, for targeted phenols analysis with exceptional sensitivity.
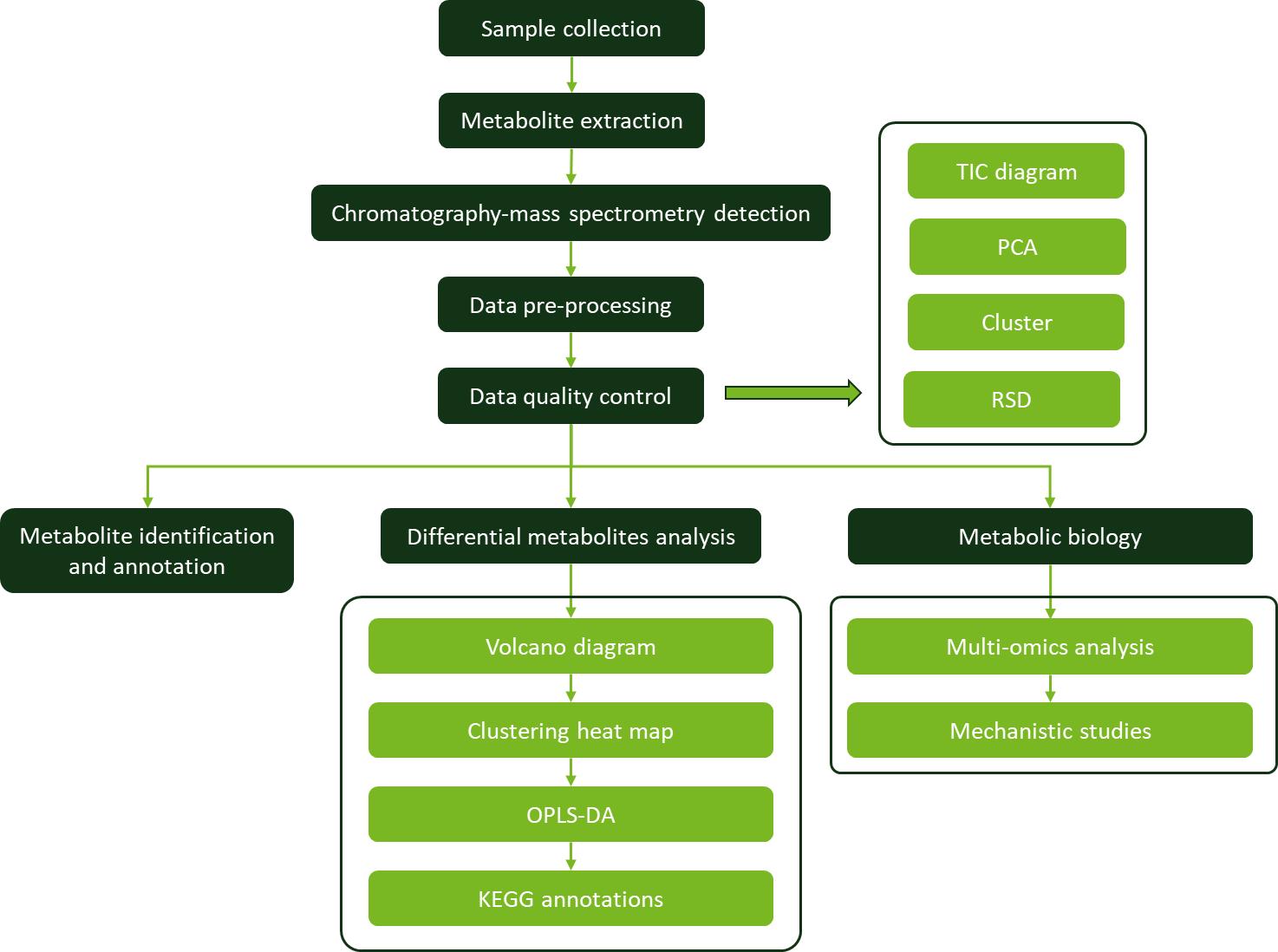 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Phenols Analyzed (including but not limited to)
| Phenol |
Catechol |
Resorcinol |
Hydroquinone |
Guaiacol |
| Eugenol |
Vanillin |
Gallic acid |
Protocatechuic acid |
Syringic acid |
| Salicylic acid |
Benzoic acid |
Tyrosol |
Curcumin |
Rosmarinic acid |
| Quercetin |
Rutin |
Chlorogenic acid |
Ellagic acid |
Isoflavones |
| Flavonoids |
Lignans |
Tannins |
Coumarins |
Capsaicin |
| P-coumaric acid |
Ferulic acid |
Caffeic acid |
Sinapic acid |
Galangin |
| Naringenin |
Stilbenes |
Pyrogallol |
Homogentisic acid |
Vanillic acid |
| 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) |
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) |
3-Hydroxytyrosol |
4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde |
|
Sample Requirements for Phenols Assay
| Sample Types |
Minimum Sample Size |
| Plant Samples |
Roots, stems and leaves, floral parts, fruits/seeds, rhizomes, buds/tender leaves, tissue sections, pollen, bark, trunk/wood, resin/gum, resin acids, seedlings/young plants, rhizosphere soil, root exudates. |
50 mg - 1 g |
Applications of Phenols Analysis
Plant Physiology and Ecology: Analyzing plant phenols helps researchers understand their roles in growth, development, and responses to environmental stresses. Phenols can act as antioxidants, signaling molecules, and defense compounds.
Plant Breeding and Crop Improvement: Phenol analysis aids in identifying and selecting plants with desirable phenolic profiles, leading to the development of improved crop varieties with enhanced nutritional, antioxidant, and stress tolerance traits.
Phytomedicine and Herbal Remedies: Many medicinal plants contain phenolic compounds with therapeutic properties. Analyzing plant phenols contributes to the identification of bioactive compounds used in traditional medicine and the development of new herbal remedies.
Nutritional Science: Plant phenols contribute to the health-promoting properties of diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Analyzing phenolic content helps in assessing the nutritional quality and potential health benefits of plant-based foods.
Pharmaceutical Research: Some plant phenolic compounds have potential pharmaceutical applications, such as anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antiviral effects. Analysis aids in identifying and characterizing these compounds for drug development.
Food and Beverage Industry: Plant phenols impact the sensory, nutritional, and functional properties of foods and beverages. Analyzing phenolic profiles helps ensure product quality, authenticity, and health claims.
Environmental Monitoring: Plant phenols can act as indicators of plant stress, pollution, and ecosystem health. Analyzing phenols in plants contributes to environmental monitoring and assessment of pollution impacts.
Natural Resource Management: Phenol analysis assists in the identification and classification of plant species, supporting conservation efforts and sustainable use of plant resources.
Agricultural Pest Management: Some plant phenolic compounds have allelopathic effects on competing plants or pests. Analyzing phenols aids in developing eco-friendly pest management strategies.
Phenol-Related Enzymes and Pathways: Phenol analysis helps elucidate the biosynthetic pathways and enzymatic reactions involved in phenol metabolism, providing insights into plant biochemistry.
Climate Change Research: Phenolic compounds play a role in plant responses to climate change. Analyzing phenols contributes to understanding plant adaptations and vulnerabilities to changing environmental conditions.
Bioremediation and Phytoremediation: Plants can accumulate phenolic compounds from contaminated environments, potentially aiding in the removal of pollutants. Phenol analysis supports studies on phytoremediation potential.
Chemical Ecology: Analyzing plant phenols contributes to the study of plant interactions with herbivores, pathogens, and symbiotic organisms, enhancing our understanding of chemical ecology.
Genetic and Metabolic Engineering: Phenol analysis provides information for genetic engineering efforts aimed at modifying phenolic pathways in plants for specific traits or applications.
Dietary Supplements and Functional Foods: Phenolic compounds extracted from plants are used in dietary supplements and functional foods. Phenol analysis ensures product quality and efficacy.
Case 1. Exploring Phenolic Metabolites in Australian Native Plants: Potential Applications and Diversity
Background:
The study aimed to explore the phenolic metabolites present in various Australian native plants and their potential applications due to their antioxidant, anti-aging, and anti-microbial properties. Phenolic compounds, including phenolic acids, flavonoids, isoflavonoids, lignans, stilbenes, and other polyphenols, are well-known secondary metabolites with diverse health benefits.
Samples:
Four selected Australian native plants were investigated: lemongrass, sandalwood nuts, wattle seeds, and old man saltbush. These plants were chosen due to their potential as sources of valuable phenolic compounds for various industries, such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food.
Methods:
The untargeted screening and characterization of phenolic metabolites were carried out using LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry). MS/MS spectra were compared with libraries and published literature to confirm the identities of the phenolic metabolites. Phenolic acids, flavonoids, isoflavonoids, lignans, stilbenes, and other polyphenols were characterized based on their fragmentation patterns and mass-to-charge ratios. External standards were used for confirmation where possible.
Results
A total of 155 phenolic metabolites were tentatively identified across the four selected Australian native plants. Lemongrass exhibited the highest diversity of phenolic compounds, with 100 identified metabolites, while sandalwood nuts, wattle seeds, and old man saltbush contained 56, 64, and 70 metabolites, respectively. Various classes of phenolic compounds, including chlorogenic acid, p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid, protocatechuic acid, quinic acid, sinapic acid, gallic acid, quercetin 3-glucoside, pyrogallol, and cinnamic acid, were abundant in these plants. The study's findings emphasize the potential of these Australian native plants as valuable sources of phenolic metabolites for industrial applications in the fields of medicine, cosmetics, and nutrition.
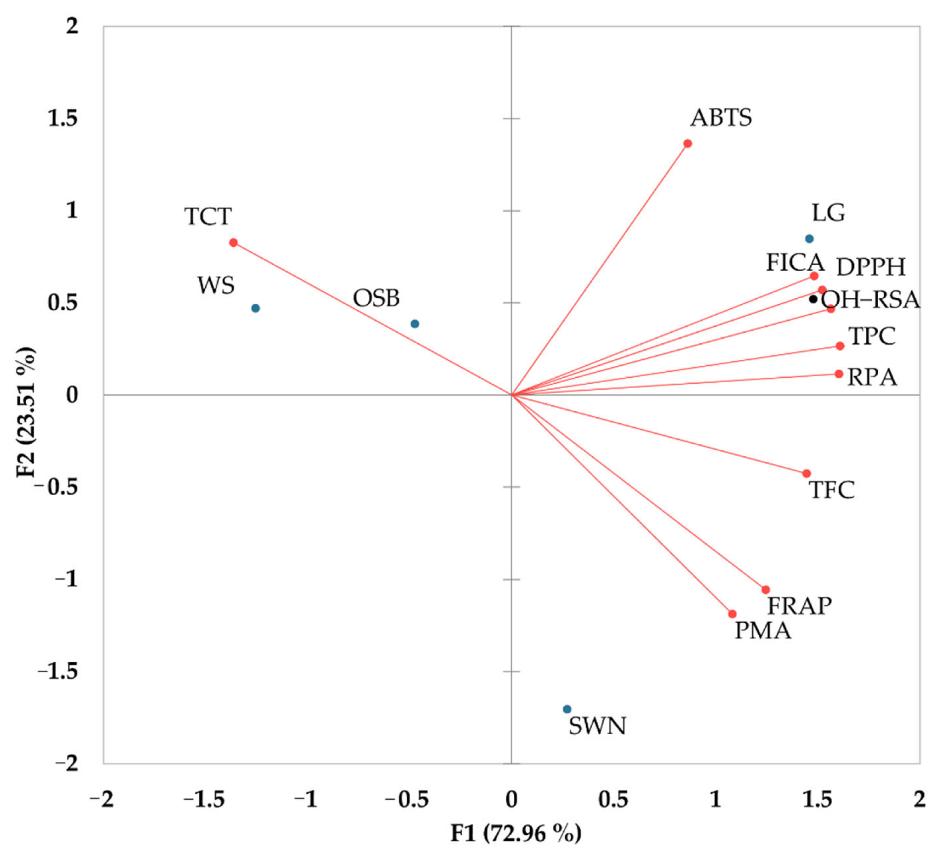 Biplot analysis of phenolic contents and their antioxidant activities in Australian native plants.
Biplot analysis of phenolic contents and their antioxidant activities in Australian native plants.
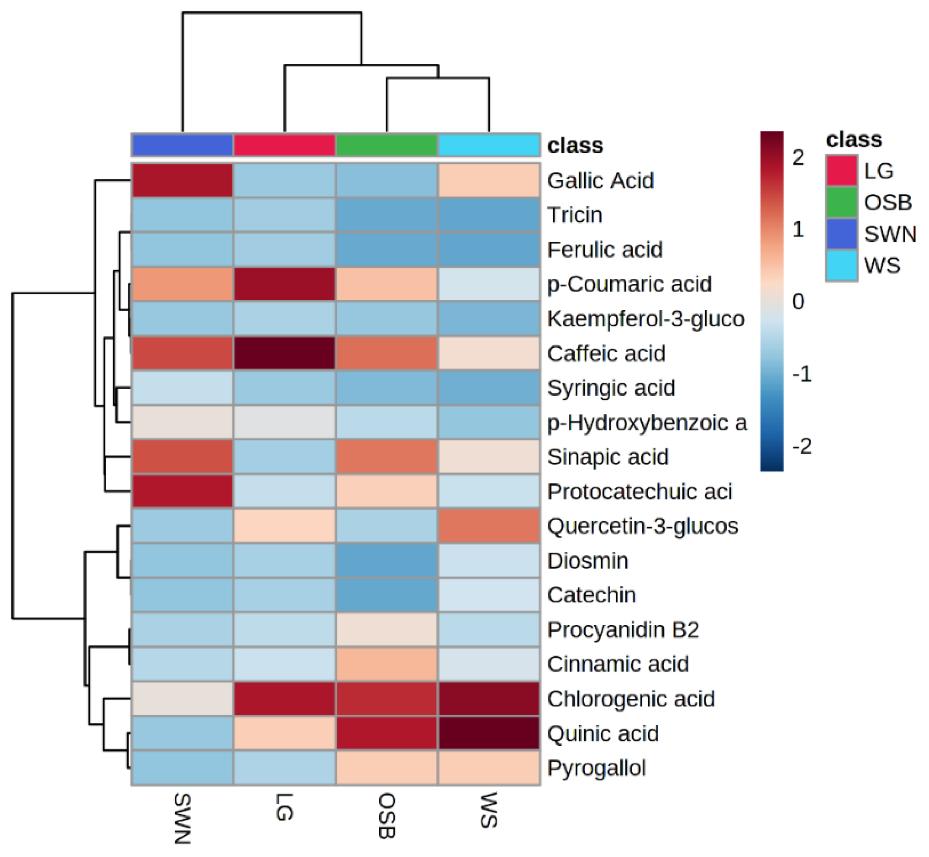 Heatmap hierarchical clustering of quantified phenolic metabolites.
Heatmap hierarchical clustering of quantified phenolic metabolites.
Reference
- Ali, Akhtar, Jeremy J. Cottrell, and Frank R. Dunshea. "Lc-ms/ms characterization of phenolic metabolites and their antioxidant activities from australian native plants." Metabolites 12.11 (2022): 1016.


 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service Biplot analysis of phenolic contents and their antioxidant activities in Australian native plants.
Biplot analysis of phenolic contents and their antioxidant activities in Australian native plants. Heatmap hierarchical clustering of quantified phenolic metabolites.
Heatmap hierarchical clustering of quantified phenolic metabolites.

