Why Need Flavones Analysis?
Flavones, a subset of natural compounds belonging to the flavonoids, are widely distributed in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal plants. Classified as a phenolic class within secondary metabolites, specifically polyphenols, flavones exhibit a distinct double bond between two carbon atoms (C2-C3) in the C ring and comprise two phenolic groups, one of which is a benzene ring.
Due to their pervasive presence across diverse biological species and inherent biological activities, flavones have captured significant attention in the pharmaceutical, food, and health industries. Renowned for their myriad health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-obesity, and cardiovascular protective effects, flavones stand out as versatile compounds.
Moreover, flavones showcase potent antioxidant properties, positioning them as potential defenders against oxidative stress and related diseases. Their ability to modulate key cellular enzyme function makes them promising therapeutic targets across a spectrum of diseases.
The diverse sub-types of flavones, each characterized by distinct chemical structures and pharmacological effects, emphasize the importance of specific analysis approaches. In this context, conducting a detailed analysis of flavones becomes not only invaluable but also a scientific and industrial imperative.
In simpler terms, flavones analysis plays a crucial role in unraveling their therapeutic potential, ensuring safety, and assessing efficacy. This analysis forms a robust foundation for research and development in pharmaceuticals, nutrition, and cosmetics. At Creative Proteomics, we leverage our expertise and cutting-edge technology to provide a comprehensive flavones analysis service.
Flavones Analysis at Creative Proteomics
Flavones qualitative analysis: Explore the diverse world of flavones compounds in your samples, identifying specific molecules for targeted research.
Flavones quantitative analysis: Accurately measure flavones in various matrices such as food, plasma, and urine, ensuring reliable results.
Flavones structural analysis: Our expert team characterizes complex structures, revealing substitution patterns and conjugate types with precision.
Flavones metabolomics research: We offer a comprehensive analysis of flavones-related metabolic profiling.
Flavones-related microbial metabolism: We will explore the microbial metabolism mechanism of flavones and provide a deeper understanding of the interactions between flavones and organisms.
Personalized flavone analysis: Creative Proteomics can also customize flavones analysis project based on your specific requirements. Our goal is to provide the most accurate and reliable analysis results and to offer a reliable foundation for your research, development or production.
Flavone Analysis Techniques
At Creative Proteomics, we employ High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS) or High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS) on advanced platforms such as Agilent 1290 Infinity LC system, Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Elite or Thermo Fisher Q Exactive™ series.
By coupling chromatographic separation with mass spectrometry, we achieve reliable detection and quantification of flavones, even in complex biological matrices. The superior sensitivity, selectivity, and accuracy of these instrumentation platforms provide comprehensive profiling and quantification of flavones, enabling their functional studies and quality control.
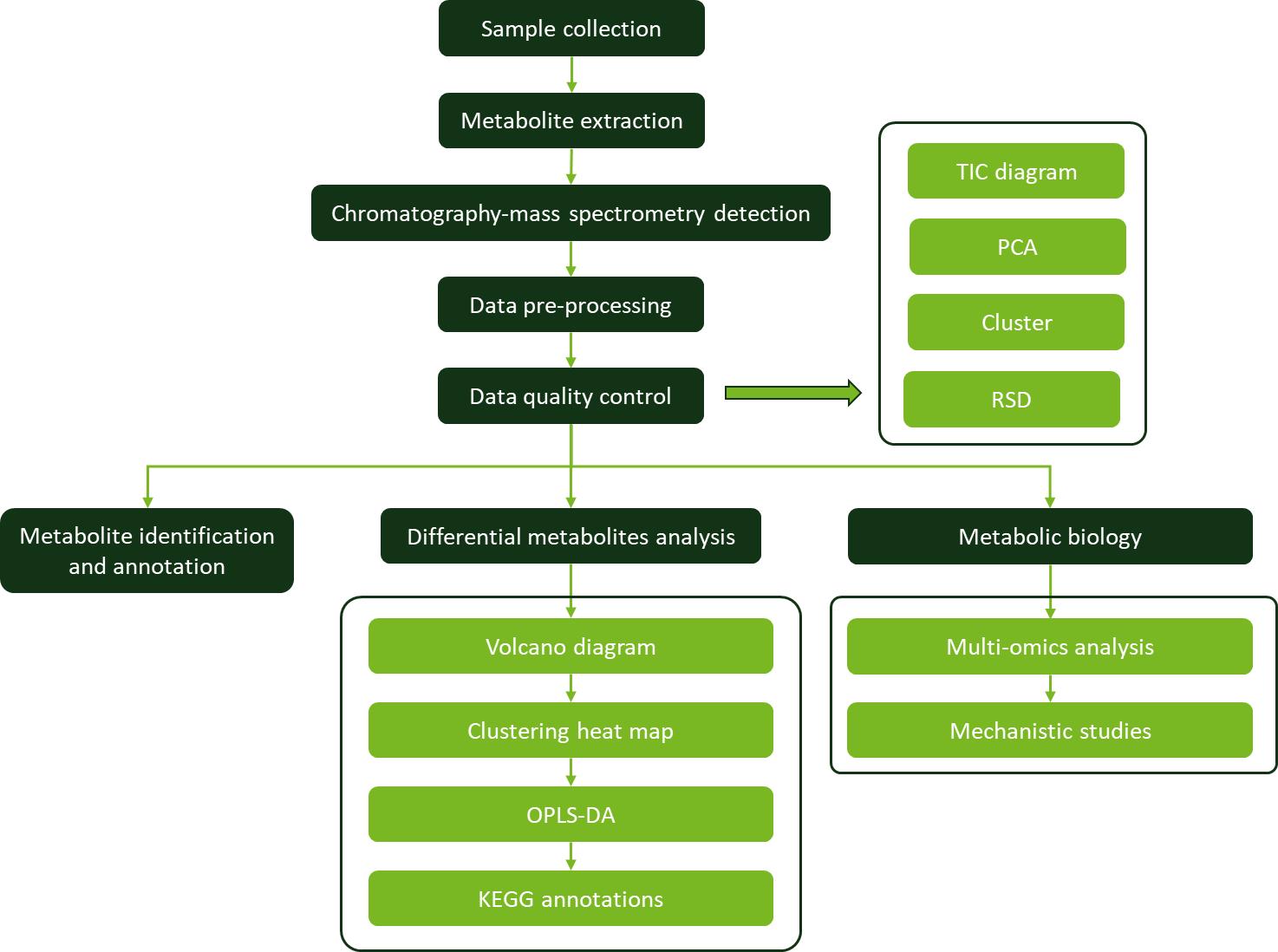 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Flavones Analyzed (including but not limited to)
Sample Requirements for Flavones Assay
| Sample Type |
Sample Quantity |
| Plant Extracts |
50 mg |
| Serum |
100 μL |
| Cell Culture |
1 x 10^6 cells |
| Food Products |
5 g |
| Urine |
10 mL |
| Tissue Biopsy |
20 mg |
| Essential Oils |
1 mL |
| Pharmaceutical Formulations |
2 tablets/capsules |
| Environmental Samples |
100 mg |
Deliverables of Flavones Analysis
- A comprehensive experimental procedure
- Parameters of liquid chromatography and mass spectrometer
- Raw data and analyzed results
- Data summary including the flavones types identified, their quantitation results, and a detailed discussion of the results.
Case. Integration of HPLC and Sensitive NMR for Rapid Identification of Flavonoids
Background:
Flavonoids are a diverse group of plant secondary metabolites with potential health benefits, making their identification crucial in various fields such as herbal medicine, dietary supplements, and food quality control. Traditional methods for flavonoid identification, including HPLC and MS, have limitations, especially in distinguishing isomeric compounds. This study presents an integrated approach using HPLC and NMR for efficient and accurate identification of flavonoids.
Sample:
The study analyzed 46 flavonoids, including flavones, flavonols, and flavanones, covering a range of structures, substitution patterns, and glycosylation states. Plant extracts from elderflowers, heather, lemon peels, and bitter orange peels were used for method validation and applicability.
Technical Platform and Procedure:
Materials and Extraction:
- Compounds were sourced from various suppliers, and plant extracts were prepared using accelerated solvent extraction.
NMR Spectroscopy:
- NMR data for the 46 reference compounds were recorded in pyridine-d5 at 298 K.
- Varian UnityInova 600 MHz spectrometer was used with experiments from the Varian pulse sequence library.
- Comprehensive 1D and 2D NMR experiments, including HSQC and HMBC, were performed.
HPLC Analysis:
- Two HPLC systems (Agilent and Merck) with different columns were used.
- A ternary solvent system (H2O/MeOH/MeCN) with 0.1% formic acid provided enhanced separation for flavonoid glycosides and aglyca.
HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS Analysis:
- Analysis was performed by UHPLC coupled to an LTQ XL mass spectrometer.
- Electrospray ionization (negative mode) and a linear gradient system were employed for mass spectrometric detection.
SPE-Trapping and Elution with Pyridine-d5:
- Non-polar flavonoid naringenin was used as a sample for SPE-trapping and elution with pyridine-d5.
- Elution efficiency was determined to be >95% with pyridine.
Results
Facile Route for Flavonoid Analysis:
- The study proposes a straightforward method for flavonoid analysis using a combination of HPLC retention times and NMR experiments.
- Comprehensive data, including UV and mass spectral data, HPLC retention times, and fully assigned NMR resonances, were provided for the 46 compounds.
NMR as a Key Tool for Identification:
- NMR data, especially proton and HSQC spectra, played a crucial role in distinguishing isomeric flavonoids.
- The comprehensive NMR data set facilitated unambiguous assignments and comparisons for rapid identification.
Database for Rapid Identification:
- A user-friendly MS Access database was created, containing detailed information on the 46 flavonoids, aiding in rapid and efficient identification.
- The database allows users to compare NMR data, UV spectra, and HPLC retention times for quick and accurate identification.
Application in Plant Extract Analysis:
- The proposed method was successfully applied to analyze plant extracts, demonstrating its suitability for complex sample matrices.
- Identification of specific flavonoids in elderflower, heather, lemon peel, and bitter orange peel extracts was achieved using the integrated HPLC-NMR approach.
Advantages and Future Implications:
- The presented approach offers advantages in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency compared to traditional methods.
- The developed database and methodology can serve as a valuable resource for routine analysis and identification of flavonoids in various applications.
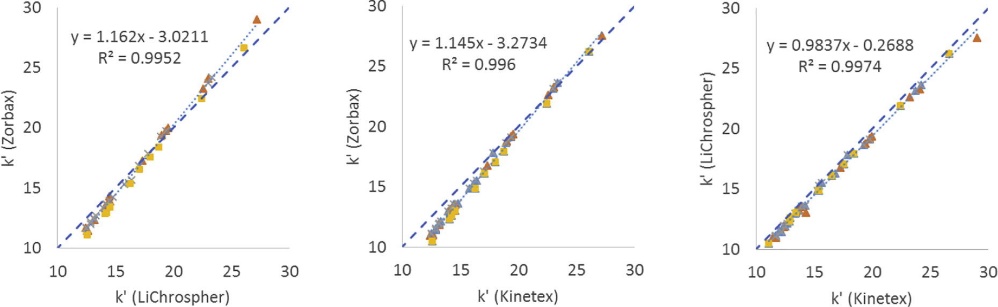 Comparison of utilized columns in the present study in a k' vs. k'-plot.
Comparison of utilized columns in the present study in a k' vs. k'-plot.
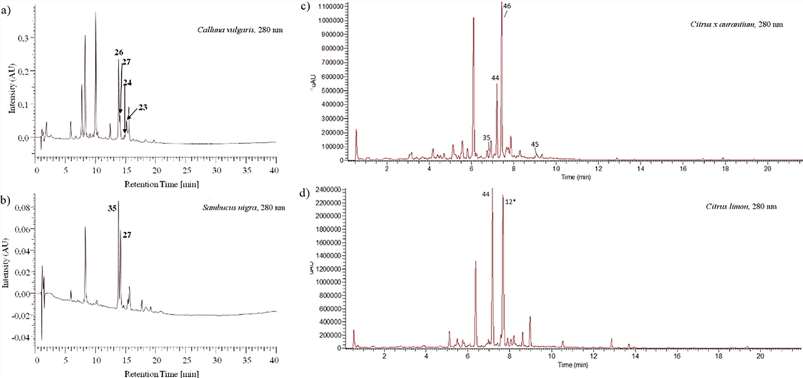 HPLC and UHPLC chromatographic profiles of C. vulgaris (a), S. nigra (b) and C. x aurantium (c), C. limon (d), respectively.
HPLC and UHPLC chromatographic profiles of C. vulgaris (a), S. nigra (b) and C. x aurantium (c), C. limon (d), respectively.
Reference
- Blunder, Martina, et al. "Efficient identification of flavones, flavanones and their glycosides in routine analysis via off-line combination of sensitive NMR and HPLC experiments." Food chemistry 218 (2017): 600-609.


 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service Comparison of utilized columns in the present study in a k' vs. k'-plot.
Comparison of utilized columns in the present study in a k' vs. k'-plot. HPLC and UHPLC chromatographic profiles of C. vulgaris (a), S. nigra (b) and C. x aurantium (c), C. limon (d), respectively.
HPLC and UHPLC chromatographic profiles of C. vulgaris (a), S. nigra (b) and C. x aurantium (c), C. limon (d), respectively.

