Sesamum indicum, with its rich oil content and diverse phytochemicals, has been a subject of intense scientific scrutiny. Metabolomics, a holistic approach to understanding an organism's metabolome, plays a pivotal role in unraveling the metabolic intricacies of this plant species. The metabolome encompasses the complete set of small molecules, or metabolites, within an organism, providing insights into its biochemical state.
Metabolomics is a multi-faceted discipline that involves the systematic identification and quantification of metabolites, offering a snapshot of the dynamic metabolic processes occurring within Sesamum indicum. This approach aids in deciphering the intricate interplay between genes, environment, and physiological conditions, contributing significantly to our understanding of sesame's growth, development, and response to external stimuli.
Metabolomics Analysis Methods We Offer
1. Metabolite Profiling
Our metabolite profiling service is designed to provide a detailed analysis of the metabolites present in Sesamum indicum seeds. We utilize advanced analytical techniques, including Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS), to identify and quantify a wide range of metabolites, from lipids and flavonoids to volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This service offers a comprehensive overview of sesame seed composition.
2. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
Understanding the metabolic pathways within Sesamum indicum is crucial for unraveling its biochemical intricacies. Our metabolic pathway analysis service employs cutting-edge bioinformatics tools to map out the complex metabolic networks in sesame seeds. This aids researchers in identifying key metabolic routes and interactions, shedding light on how different compounds are synthesized and regulated.
3. Metabolite Quantification
Accurate quantification of metabolites is essential for meaningful research outcomes. We ensure precise measurement of metabolites within Sesamum indicum seeds using high-precision instruments. Our quantitative analysis enables researchers to track changes in metabolite levels under various conditions, facilitating data-driven conclusions.
4. Customized Research Collaborations
At Creative Proteomics, we understand that each Sesamum indicum research project is unique. We offer customized research collaborations, allowing you to tailor our services to your specific research objectives. Whether you require specialized analyses, experimental design consultation, or assistance with data interpretation, our team of experts is here to support your project's success.
5. Integrated Multi-Omics Approaches
For a holistic understanding of Sesamum indicum biology, consider integrating metabolomics with other omics disciplines such as genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics. Our team can assist you in designing multi-omics experiments, facilitating a comprehensive exploration of the plant's metabolism and its regulatory mechanisms.
Specific Sesamum indicum Analysis Projects We Provide
Nutrient Profiling: Metabolomics enables us to profile the nutritional content of sesame seeds comprehensively. We identify and quantify essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals, contributing to informed dietary recommendations.
Bioactive Compound Discovery: Sesame seeds are rich in bioactive compounds like lignans and antioxidants. Metabolomics aids in the systematic discovery and quantification of these compounds, shedding light on their potential health benefits.
Optimal Growth Conditions: Understand how different environmental factors impact sesame growth and metabolism. Our metabolomics services help optimize growth conditions, enhancing crop yield and nutritional quality.
Breeding for Desirable Traits: Link metabolite profiles to desirable traits in sesame. Accelerate breeding programs by selecting plants with specific metabolic characteristics, expediting the development of improved varieties.
Purity and Authenticity: Ensure the purity and authenticity of sesame products with metabolomics. Detect potential adulteration or contamination, safeguarding product integrity.
Shelf-Life Assessment: Assess the shelf-life of sesame-derived products by monitoring changes in metabolite profiles over time. Optimize storage conditions for extended product freshness.
Sustainable Practices: Evaluate the environmental impact of sesame cultivation through metabolomics. Analyze plant and soil metabolites under different practices to promote sustainable agriculture.
Biodiversity Conservation: Preserve wild or endangered sesame varieties by characterizing their metabolic fingerprint. Develop conservation strategies and monitor genetic diversity.
Sesamum indicum Metabolomics Analysis Techniques
To undertake a comprehensive Sesamum indicum metabolomics analysis, a wide array of analytical techniques is at our disposal. At Creative Proteomics, we employ state-of-the-art mass spectrometry-based techniques to unravel the metabolic complexities of sesame seeds.
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
One of the cornerstone techniques in Sesamum indicum metabolomics is Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS). LC-MS combines the separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the mass analysis precision of mass spectrometry. Our advanced LC-MS instruments, such as the Thermo Fisher Scientific Q Exactive series, enable high-resolution analysis, allowing us to identify and quantify a vast array of metabolites within sesame seeds.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
For volatile and thermally stable metabolites, we employ Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). Creative Proteomics utilizes cutting-edge GC-MS systems, including the Agilent 7890B GC coupled with the Agilent 5977A Mass Selective Detector, to analyze compounds like fatty acids, terpenoids, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in Sesamum indicum.
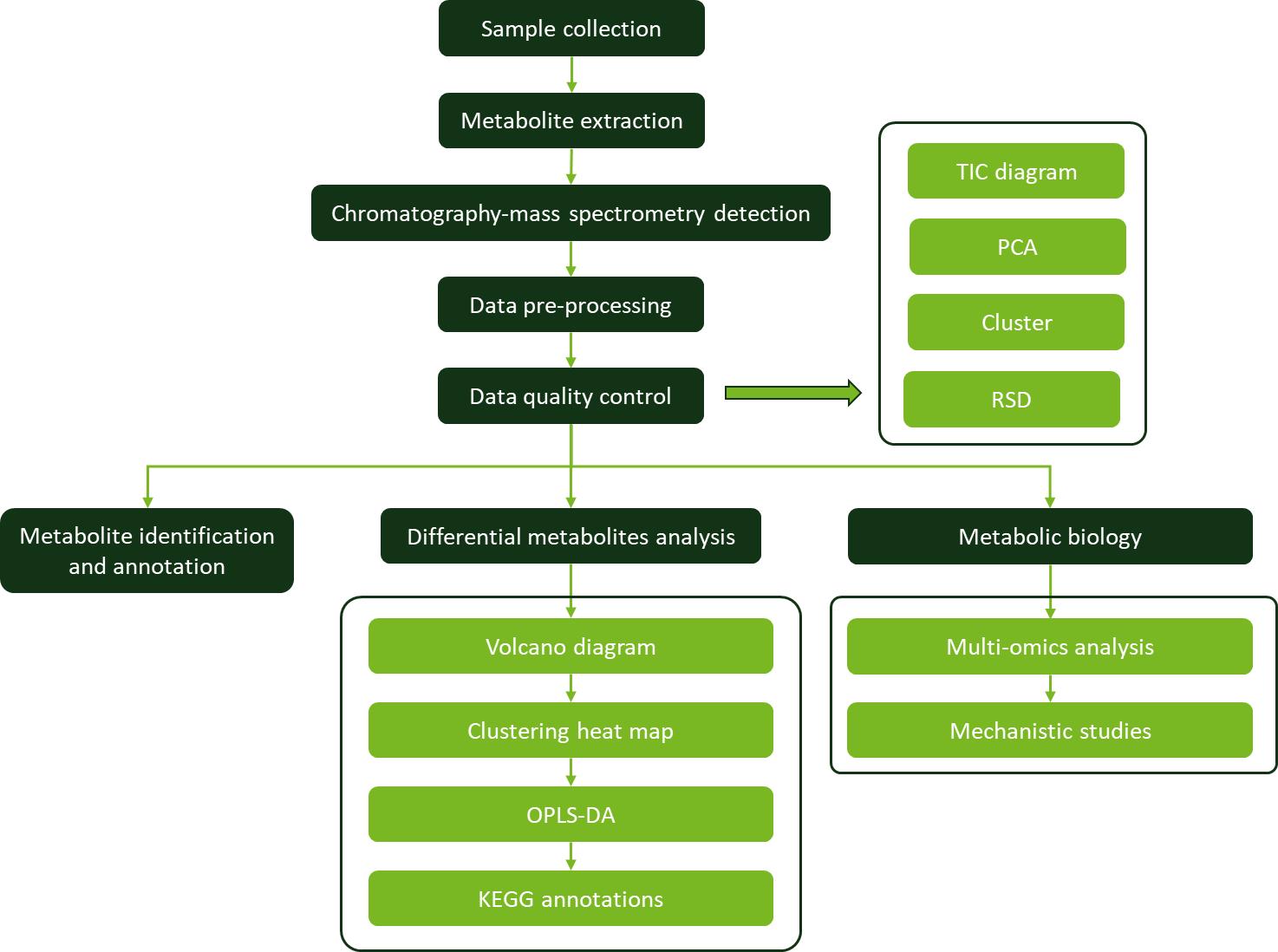 Workflow for Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Metabolomics Service
Sample Requirements for Sesamum indicum Metabolomics
| Sample Type |
Sample Amount |
Sample Preparation |
Storage Conditions |
| Sesame Seeds (Whole) |
100 grams |
Grind seeds into a fine powder. |
Store at -80°C |
| Sesame Oil |
10 milliliters |
Extract metabolites using appropriate solvent. |
Store in amber vials |
| Soil |
50 grams |
Homogenize and extract metabolites. |
Store at -20°C |
| Plant Tissues |
20 grams |
Homogenize and extract metabolites. |
Store at -80°C |
| Sesame Products |
Varies |
Prepare samples as required (e.g., extraction). |
Follow specific guidelines |
Case 1. Metabolite Profiling of Sesame Tissues: Unveiling Tissue-Specific Accumulation and Insights into Phytochemical Diversity
Background:
Sesame is a globally recognized oilseed crop with significant nutritional and therapeutic importance. This study aimed to investigate the distribution and variability of metabolites in different sesame tissues, shedding light on the diversity of bioactive compounds present in the plant.
Samples:
The study utilized sesame varieties cultivated under uniform conditions in northern China. Various tissue samples were collected, including middle leaves (ML), white flowers (WF), fresh capsules, purple flowers (PF), fresh seeds (FS), and fresh carpels (FC).
Methods:
Chemicals: LC–MS gradient grade solvents were used, along with other chemicals and standards.
Sample Preparation and Extraction: Samples were vacuum freeze-dried, crushed, and then dissolved in 70% methanol for metabolite extraction.
High-resolution UPLC Analysis: Chromatographic conditions included a specific column, mobile phase, and gradient elution system.
ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS: Mass spectrometry analysis was conducted with ESI source in both positive and negative ion modes.
Identification and Quantification of Metabolites: Metabolites were identified using a self-built database and reference databases. Quantification was performed using the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode.
Multivariate Data Analysis: Data quality assessment, Z-score standardization, unsupervised PCA, hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), Pearson correlation coefficients (PCC) calculations, OPLS-DA for differential metabolite detection, KEGG annotation, and Metabolite Sets Enrichment Analysis (MSEA) were carried out.
Results
- A total of 776 metabolites were identified across the different sesame tissues.
- HCA and PCA revealed significant differences in metabolite profiles between sesame tissues, especially between fresh seeds and other tissues.
- Flavonoids were the most abundant class of metabolites, particularly in flowers, and were associated with various biological processes.
- Purple flowers were distinguished by 50 significantly differential metabolites, including anthocyanins and flavonols.
- Sesame leaves were rich in various bioactive compounds, including terpenoids, quinones, tannins, vitamins, and specific metabolites with potential therapeutic properties.
- Sesamin, a major sesame lignan, was detected primarily in seeds and fresh carpels.
- A cooperative relationship between developing seeds and carpels was observed, suggesting dynamic metabolic exchanges during seed development.
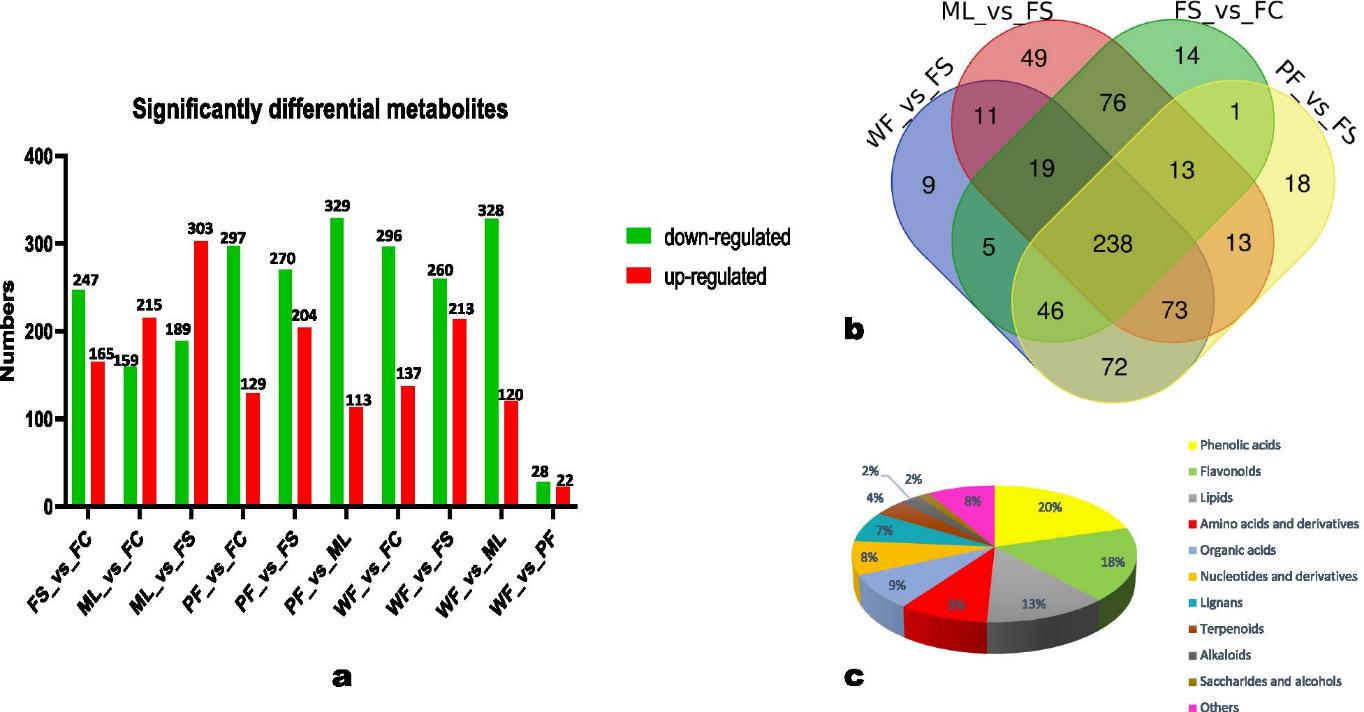 Differential metabolites across the sesame tissues.
Differential metabolites across the sesame tissues.
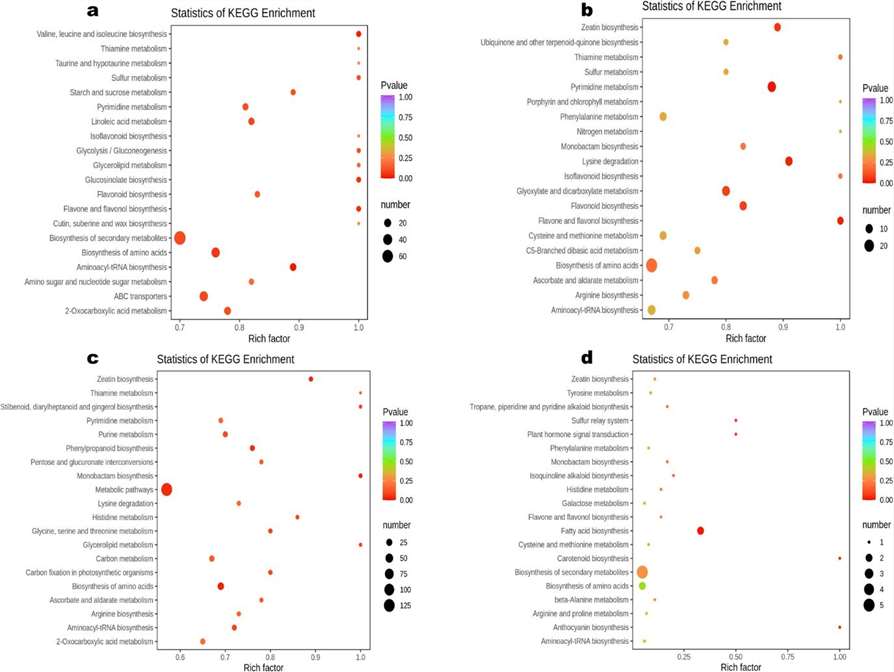 KEGG annotations and enrichment of differentially expressed metabolites
KEGG annotations and enrichment of differentially expressed metabolites
Reference
- Dossou, Senouwa Segla Koffi, et al. "Comparative metabolomics analysis of different sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) tissues reveals a tissue-specific accumulation of metabolites." BMC Plant Biology 21.1 (2021): 1-14.


 Workflow for Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Metabolomics Service Differential metabolites across the sesame tissues.
Differential metabolites across the sesame tissues. KEGG annotations and enrichment of differentially expressed metabolites
KEGG annotations and enrichment of differentially expressed metabolites

