What is a Free Thiol Group?
A free thiol group is a specific structural feature formed by a sulfur atom within a cysteine residue. These free thiol groups exhibit high reactivity and have the capacity to interact with other proteins, thereby inducing alterations in their structure and function. Additionally, they can engage in reactions with oxygen molecules, resulting in oxidative damage to cells and tissues. The quantification of free thiol groups is a fundamental analytical task, particularly for protein-based bioproducts like antibodies. For instance, antibodies containing free thiol groups may occasionally experience compromised or significantly altered biological functions compared to intact antibodies. Hence, the rapid and precise quantification of free thiol groups in protein-based bioproducts holds paramount importance, both in the early stages of process development and during later-stage production monitoring.
Significance of Free Thiol Group Detection
Thiols and disulfide bonds frequently serve as active groups in various biochemical processes, including enzyme catalysis, cofactor binding, and the preservation of protein conformational integrity. The quantity of free thiol groups is intricately linked to the characteristics and functions of proteins, rendering it a pivotal parameter in the assessment of quality within the realm of biopharmaceutical processes.
For instance, thiols play a crucial role in the formation of disulfide bonds in peptide drugs. However, some thiols may exist in a free state, and these free thiol groups can to some extent influence the structure and even the structural function of peptide drugs. Additionally, differences in peptide drug production processes, such as cell lines, cell culture methods, and purification, can result in variations in thiol content. Therefore, accurate measurement of free thiol groups in peptide drugs holds significant value in ensuring drug quality and efficacy.
Methods and Principles of Free Thiol Group Quantification
The Ellman method is a well-established technique utilized for the determination of free thiol group concentrations. This method hinges on the interaction between the DTNB reagent and free thiol groups, resulting in the formation of 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoic acid (TNB-). Under neutral or alkaline pH conditions, TNB- undergoes ionization, yielding TNB2- divalent anions. These TNB2- ions manifest a distinct yellow coloration, and their abundance can be quantified by measuring the absorbance of visible light at 412nm. Subsequently, the quantification of free thiol groups can be achieved either through the utilization of cysteine standards or by employing methods based on molar absorptivity.
Our Free Thiol Group Quantification Service
Creative Proteomics has established a free thiol group quantification platform based on the Ellman method's principles. We offer a comprehensive analysis service for quantifying the content of free thiol groups in peptide drugs, providing you with a one-stop solution for your needs.
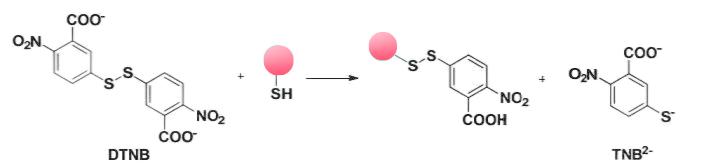 Figure 1. Principle of Thiol Detection Using the Ellman Method
Figure 1. Principle of Thiol Detection Using the Ellman Method
Scope of Analysis
Protein samples, including but not limited to intermediates, raw materials, finished products, and stability samples.
Equipment
Plate Reader: SpectraMax M4, Molecular Devices
Sample Requirements
Quantity: >4mg
State: Clear colorless liquid/white solid
Purity: >95%
Our Advantages
Professional Technical Team: We have an experienced team with a rich background in new drug development and pharmaceutical analysis projects.
Independent and Compliant Quality System: We possess a fully independent and compliant quality management system.
Using the plate reader to measure absorbance, we establish a standard curve and calculate the content of free thiol groups in the test samples.
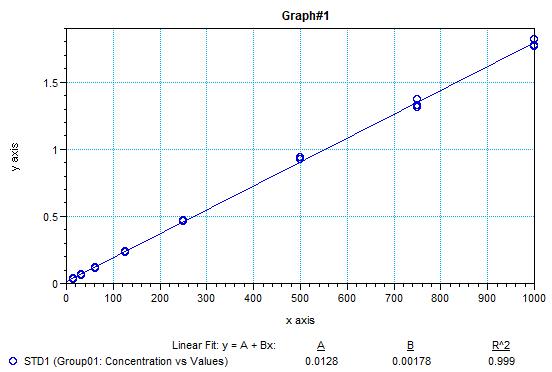 Figure 2. Regression Equation for the Cysteine Standard Curve
Figure 2. Regression Equation for the Cysteine Standard Curve
Table 1. Determination of Free Thiol Concentration in Sample Cases
| Free Thiol Concentration (μM) |
SPL-1 |
SPL-2 |
SPL-3 |
Average |
RSD% |
| Sample |
36.63 |
36.90 |
37.39 |
36.97 |
1.0 |
Q 1: What Factors Affect the Ellman Method's Measurement of Free Thiols?
A: EDTA Quantity: Adding an appropriate amount of EDTA helps stabilize the colorimetric product TNB and ensures that the measurement results exhibit a linear relationship with the concentration of cysteine.
Buffer Solution: Different buffer solutions may slightly affect the maximum absorption wavelength of TNB. Therefore, suitable measurement conditions should be determined based on the chosen buffer solution.
pH Value: The degradation rate of DTNB accelerates with increasing pH. Therefore, measurements should be conducted within an appropriate pH range.
Temperature: The molar absorptivity varies at different temperatures, and it may decrease as the temperature rises.
Q 2: What are the Advantages of the Ellman Method for Measuring Free Thiols?
A: The Ellman method offers several advantages, including high sensitivity, simplicity of operation, and short assay time. By measuring absorbance at 412nm, free thiol content can be quantified rapidly and accurately. This method finds widespread use in thiol content analysis and is widely employed in fields such as biochemistry and molecular biology.

 Figure 1. Principle of Thiol Detection Using the Ellman Method
Figure 1. Principle of Thiol Detection Using the Ellman Method Figure 2. Regression Equation for the Cysteine Standard Curve
Figure 2. Regression Equation for the Cysteine Standard Curve