TMT Protein Quantitation Service
Online Inquiry- Service Details
- Case Study
Creative Proteomics' tandem mass tag (TMT) in vitro labeling-based mass spectrometry platform provides protein quantification services to help find differentially expressed proteins.
TMT are composed of three parts: molecular weight reporter, molecular weight normalization part and reaction group, forming two, six or ten kinds of ectopic tags with equal relative molecular mass. The TMT reagent can efficiently label the enzymatic peptides through the reactive group. In the first-order mass spectrum, the molecular weight normalization part makes the same peptide in different samples labeled with any one of the TMT reagents show the same mass-to-charge ratio. In tandem mass spectrometry, the cuttable arms can preferentially break to release molecular weight reporters. Each reporter has its own unique molecular weight, and can reflect the sample abundance of the labeled peptide in MS / MS analysis. The quantitative information of the same peptides between samples can be obtained based on the signal intensity value of the reporter ion, and then passed through the software Processed to get quantitative information on the protein.
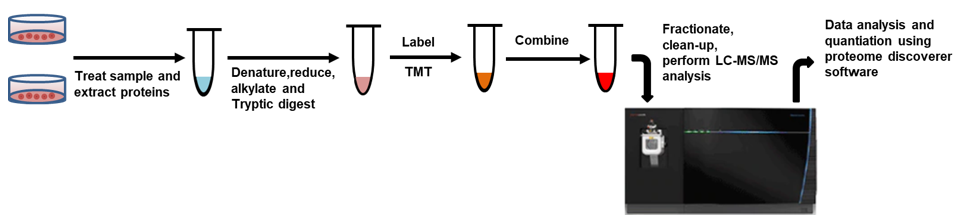
The Workflow of TMT Protein Quantitation Service
The process for MS experiments using TMT are summarized as follows. protein extracts isolated from cells or tissues are reduced, alkylated, and then digested using protein lysate or equivalent. The sample is then labeled with TMTpro reagent before the sample is mixed, fractionated, and purified. Prior to data analysis, labeled samples were analyzed on a high-resolution Orbitrap LC-MS / MS mass spectrometer to identify peptides and quantify the relative abundance of the reported ions.
Technology Platform
Orbitrap LC-MS/MS Mass Spectrometer.
Advantages of TMT Protein Quantitation Service:
- Increased sample throughput for parallel MS analysis for multiple samples, enabling the simultaneous quantitative analysis of up to 11 (TMT) or 16 (TMTpro) different samples from different samples from cells, tissues or biological fluids.
- Improved multi-channel analysis capabilities reduce loss of quantitative data.
- A variety of chemical groups can be used to specifically label different functional groups, and the labeled functional groups can be specifically enriched with anti-TMT solid phase resin.
- Amine, cysteine, and carbonyl-reactive chemicals can use effective strategies to efficiently label target functional groups.
- Optimized for high-resolution MS/MS platforms using SP2 or SPS MS3 quantitation mode, Proteome Discoverer software fully supports corresponding data analysis to improve multi-channel analysis capabilities and reduce loss of quantitative data.
- With high throughput, one assay can simultaneously obtain the quantitative and quantitative information of thousands of proteins.
- The TMT experiment cycle is short, which can reduce the entire experiment cycle and the experimental error between samples.
- Compared with gel-separated protein quantification technology, TMT mass spectrometry technology can detect more types of protein molecules, such as low-abundance proteins, strong acid (basic) proteins, 10KD or 100KD protein molecules.
- The fragmentation efficiency of the second mass spectrometry is more conducive to the analysis of protein interactions and expression patterns.
Sample Requirements
- Plant leaf samples: wet weight≥1g.
- Plants rich in impurities or samples with low protein content, such as plant roots, rhizomes, xylem, phloem tissue: dry weight≥5g.
- The number of cell samples must reach 107 (It is recommended to use lysate for lysis before sending).
- Fresh human, animal and plant tissue:≥100mg.
- Serum/plasma≥500ul.
- Urine≥25mL.
- Body fluids such as saliva, amniotic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid≥5mL.
For other special samples, please contact us if you have any questions.
Application of TMT Protein Quantitative Technology
- Screening for disease markers
- Molecular mechanism research
- Plant stress resistance research
- Drug target research
- Special function protein screening
Delivery
Complete proteomics experiment report (including specific experimental procedures), target protein candidate peptide secondary mass spectrum matching map, skyline analysis of target peptide TMT results, quantitative results and statistical analysis of target peptides and proteins.
Want to Know about Other Proteomics Quantitative Analysis Techniques?
- SILAC Quantitation Service
- ICAT Quantitation Service
- TMT Quantitation Service
- iTRAQ Quantification Service
- SRM/MRM Quantitation Service
- PRM Quantitation Service
References
- Venable JD, Steckler C, Ou W, et al. (2015) Isotope-Coded Labeling for Accelerated Protein Interaction Profiling Using MS. Anal Chem,2015, 87:7540−7544.
- Yu C, Huszagh AS, Viner R, et al. Developing a Multiplexed Quantitative Cross-linking Mass Spectrometry Platform for Comparative Structural Analysis of Protein Complexes. Anal Chem, 2016, 88(20):10301–10308.
Case: Optimizing TMT Proteomics for Alzheimer's Biomarker Discovery in Cerebrospinal Fluid.
Background
Proteomic analysis using tandem mass tag (TMT) labeling in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is crucial for Alzheimer's Disease (AD) biomarker discovery. However, challenges such as ratio compression, contamination, and normalization methods need careful consideration for accurate and reliable results.
Samples
The study involves CSF samples, addressing the heterogeneous nature of CSF and its impact on quantitation accuracy. Technical aspects such as sample preparation techniques (FASP and in-solution), TMT labeling efficiency, and the choice of TMT amount are explored to enhance the understanding of experimental variables.
Technical Methods
MS2 vs. MS3 Quantification: Comparison of TMT ratios in MS2 and MS3 modes reveals that MS3 mitigates ratio compression but leads to a reduced number of identified proteins due to decreased detection sensitivity.
Sample Preparation Techniques: Evaluation of FASP and in-solution protocols demonstrates that while FASP identifies more proteins, it is more susceptible to contamination, particularly from keratins. In-solution digestion, although less efficient, shows lower contamination levels.
TMT Labeling Efficiency: Analysis of TMT labeling efficiency indicates that reducing the TMT amount has minimal impact on labeling efficiency, suggesting applicability of the recommended TMT protocol to CSF samples.
Normalization Methods: Various normalization methods, including median-based approaches, quantile normalization, and others, are applied to an AD clinical dataset. Results highlight the superiority of median-based approaches and quantile normalization in improving p-values and identifying robust biomarker candidates.
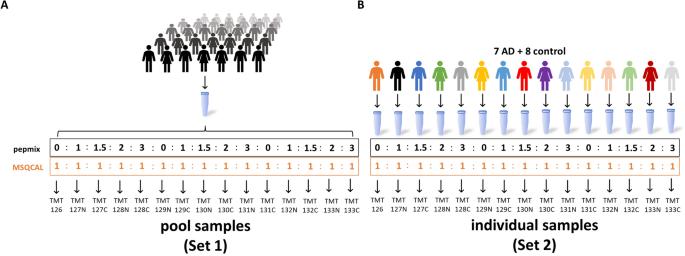 Experimental design to evaluate technical and total variation as well as an optimal normalization approach for our in-solution based TMT protocol.
Experimental design to evaluate technical and total variation as well as an optimal normalization approach for our in-solution based TMT protocol.
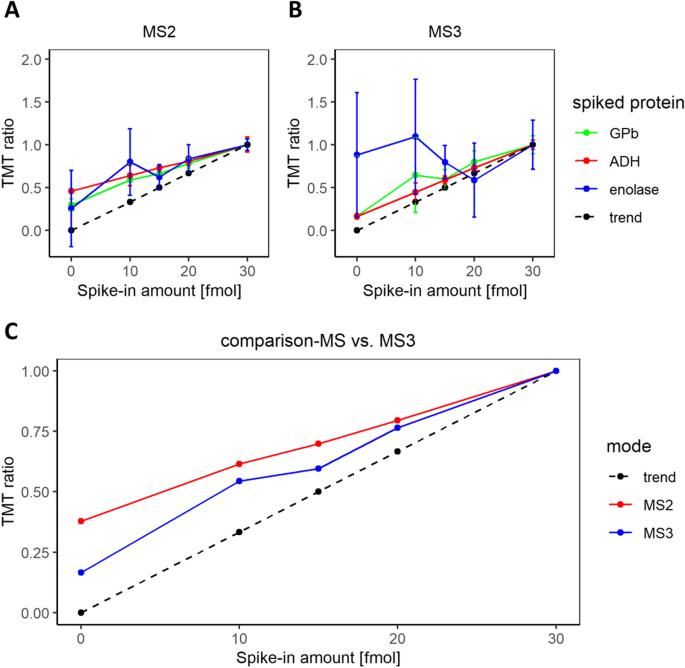 Measured TMT ratios of spiked pepmix proteins in MS2 and MS3 mode.
Measured TMT ratios of spiked pepmix proteins in MS2 and MS3 mode.
Results
The study concludes that careful consideration of experimental variables, including choice of quantification mode, sample preparation technique, TMT labeling amount, and normalization method, is essential for accurate TMT proteomic analysis in CSF. A list of 64 potential biomarker candidates for AD is identified, offering insights into altered biological processes associated with the disease. The findings provide guidance for future studies in CSF biomarker discovery and underscore the importance of method optimization in TMT proteomics.
Reference
- Moulder, Robert, et al. "Analysis of the plasma proteome using iTRAQ and TMT‐based Isobaric labeling." Mass Spectrometry Reviews 37.5 (2018): 583-606.
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.