Exosome Engineering
Online InquiryCreative Proteomics aims to provide high-quality exosome-related services to customers in different fields worldwide. Our services can help researchers and professionals to optimize the isolation, purification, and identification of exosomes from various samples as well as perform exosome engineering for therapeutic applications. We load and engineer exosomes in different methods, including electoporation, transfection of donor cells, and so on.
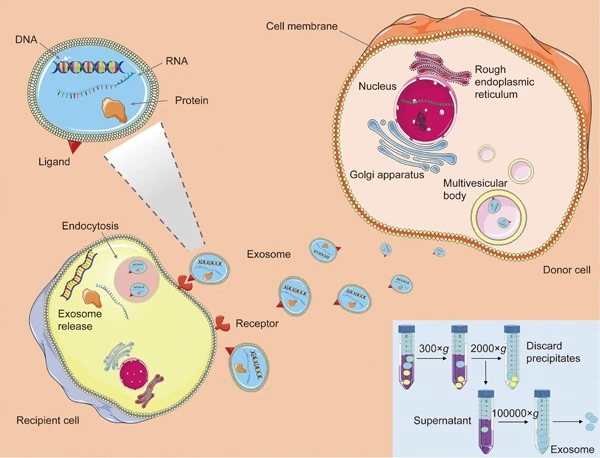 Fig. 1 Exosome generation, secretion and cargo transfer from the donor cells to the recipient cells. (Luan, Xin, et al., 2017)
Fig. 1 Exosome generation, secretion and cargo transfer from the donor cells to the recipient cells. (Luan, Xin, et al., 2017)
Exosome engineering
Exosomes can be loaded with cargo endogenously during their biogenesis or exogenously after exosome isolation. Moreover, the loading strategy includes direct or indirect loading. The latter is the loading of cargo into donor cells, which will release exosomes containing the cargo, usually involving incubation and transfection. Currently, there are several different strategies reported to directly load cargos into exosomes, including dialysis, sonication, electroporation, freeze and thaw cycles, and extrusion. Among them, electroporation (EP) is a powerful tool to introduce genes easily into eukaryotic cells with high efficiency and low toxicity. With years of optimizing and adapting, EP is a broadly applicable and well-established method for transient cargos in exosomes. This method has been mainly utilized to load small RNAs (such as miRNA and siRNA) into exosomes.
High-quality engineered exosomes for preclinical research
Creative Proteomics has been working with exosome research and analysis for years. Our exosome engineering services can create customized and high-quality engineered exosomes for you. There are four major parts in our services, including exosome labeling and tracking, loading cargo into exosomes, engineered exosome production, and cargo loading assessment. Just tell us what surface markers (protein and RNA) and cargo (such as miRNA, small molecules, and proteins) you need and we'll do it for you!
- Exosome labeling and tracking
Monitoring exosomes in vitro and in vivo can provide important information about their mechanism of targeting action, biodistribution, migration abilities, physiological functions, and toxicity.
-Exosomal lipid labeling
-Exosomal protein labeling
-Exosomal RNA labeling
- Cargo loading
The ability of exosomes to transport active substances makes exosomes a powerful tool for labeling cells, providing therapies, studying biological processes, and other applications. With years of experience in exosome loading technology, we are confident that we can load cargo to exosomes for our customers worldwide.
-Nucleic acids, including DNA, miRNA, lncRNA, mRNA
-Proteins
-Small molecules
- Engineered exosome production
Our standardized manufacturing process is strictly in accordance with good manufacturing practice (GMP), involving the specific cell types and optimal cultivation conditions (such as dissociation enzyme, culture medium, and cultivation system). We can work with you to develop the following manufacturing stages.
-Creation and culture of stable cell lines producing engineered exosomes
-Engineered exosome purification
-Engineered exosome quality control (QC)
- Cargo loading assessment
In addition to exosome uptake efficiency, we provide customized exosome cargo loading assessment services to determine cargo loading efficiency.
Advantages of our services
- Batch and fed-batch manufacture
- Flexible production capabilities
- Suitable for in vivo applications
- One-stop service: from designing your own exosomes to having them delivered directly to your door
Custom exosomes designed by you and engineered by us. Contact us today for a free quote.
Reference
- Luan, Xin, et al. "Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery." Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 38.6 (2017): 754-763.
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.