Nucleus Isolation and Nuclear Protein Purification Service
Online InquiryCreative Proteomics offers nucleus isolation and nuclear protein purification services for animal tissues, cells and yeast and help you obtain purified nuclei and nuclear proteins for subsequent assays.
Nucleus is the most prominent organelle in eukaryotic cells. It is highly compartmentalized and separated from the cytoplasm by nuclear envelope and extension of rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Nucleus with the genetic mutations on chromosomes inside nucleus, and dysfunction of translocation of transcription factors, and so forth. To better investigate numerous processes of primary importance in cell biology, including chromatin structure, subcellular localization of proteins, nuclear apoptosis, and so forth, it is necessary and the first step to isolate nuclei and nuclear proteins.
Advantages of Our Nucleus Isolation and Nuclear Protein Purification Services:
- Rich experience in nuclei separation and purification.
- Obtained pure nuclei with low impurities and intact nuclear envelope and pore structure.
- Nuclei can be isolated and purified from tissues, cultured cells, yeast and plant cells.
- Protein can be extracted from nuclei without cytoplasmic contamination.
- We will conduct purity verification tests to ensure that the isolated protein reaches the target purity, otherwise there is no charge.
We Provide the Following Services, including but not Limited to:
- Single organelle separation and purification
- Nuclei and cytoplasm separation and purification
- Nuclear protein extraction
Methods of Nucleus Isolation and Nuclear Protein Purification Service:
1. Single organelle - nuclei separation and purification
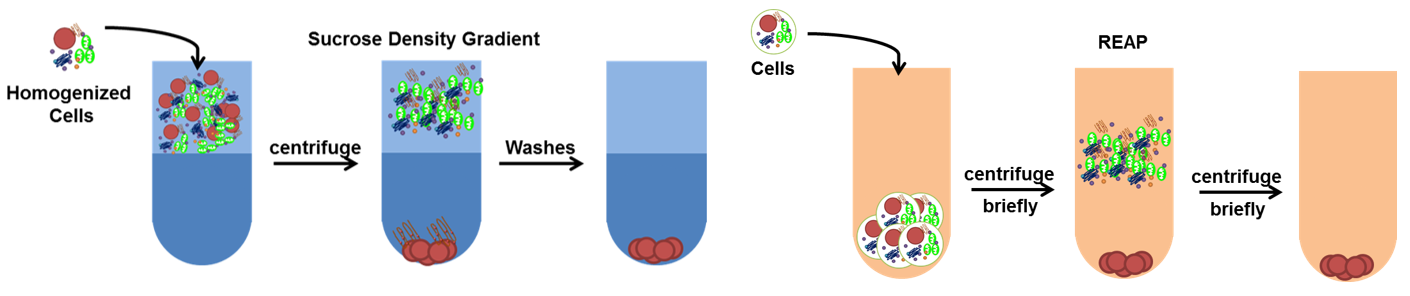
Since the first attempt to isolate nuclei, challenges include cytoplasmic contamination, nuclear damage that induces stress responses, protein complex disassembly, protein modification, protein diffusion outside the nucleus, and protein degradation. Nowadays, there are several standard methods for isolating nuclei that employ gentle, non-ionic detergents, etc. Nuclei are the largest organelles in the cells, so it is easy to separate from other organelles and detergent-soluble contaminants by low speed centrifugation and repeated washes in buffers. The sucrose density gradient is the traditional and most common used method to isolate nuclei from tissues, culture cells, yeast, and plant cells. This method yields very clean and pure nucleus, but takes long process with high probability of proteins degrading, modified or translocated. We also provide another method called rapid, efficient, and practical (REAP) to isolate pure nucleus in shorter time. This method only takes less than 5 minutes to isolate total cytosolic and nuclear fractions with little or no cross-contamination. However, the detergent used in REAP methods might affect protein complex integrity and enzyme activity. Both methods are efficient and productive. We will choose the optimal method based on your experimental goals and subsequence purposes.
The purity requirements for nuclear purity determine the appropriate method required. Depending on your sample types and subsequent experiment, different detergents and methods will be optimized to meet your needs.
2. Isolation and purification of multiple organelles
If you need multiple organelle proteins, then we will use the organelle fractionation method to separate and enrich the organelle proteins you need.
3. Extraction of nuclear proteins
We used a simplified small-scale method to extract nuclear proteins rapidly using hypo-osmotic lysis buffer, which is based on Sucrose Density Gradient, and just requires a small number of cells. The extracted nuclear proteins can be used for subsequent electrophoretic mobility shifty assays, proteomics, and so forth.
Delivery
Experimental protocol, purity analysis report, extracted nuclei and purified protein sample.
Want to learn more about nuclear protein characterization, protein-protein interaction analysis and other analysis services? We provide one-stop analysis of nuclear proteomics.
References
- Suzuki K, Bose P, Leong-Quong R YY, et al. REAP: A two minute cell fractionation method. BMC Research Notes, 2010, 3:294.
- Nabbi A, Riabowol K. Isolation of nuclei. Cold Spring Harb Protoc; doi:10.1101/pdb.top074583.
- Nabbi A, Riabowol K. Rapid Isolation of Nuclei from Cells In Vitro. Cold Spring Harb Protoc; doi:10.1101/pdb.prot083733.
- Brewer O. Isolation of Myogenic Nuclei from Whole Muscle Tissue, Undergraduate Honors Theses. (2015).954.
- Watson N. Isolation and Use of Mammalian Cell Nuclei.
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.