Nuclear Pore Complex Proteomics Services
Online InquiryNuclear pore complex (NPC) mediates the shuttle movement of macromolecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. NPC is located in the nuclear membrane, forming a hydrophobic channel. It enables macromolecular substances such as proteins to bind to transport receptors for transmembrane transport. This transmembrane transport through the nuclear pore complex plays an important physiological function in life activities such as cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and individual development.
Creative Proteomics provides a one-stop service for nucleolar proteomics, and conducts a comprehensive analysis of nucleolar proteomics from a holistic perspective. The main contents include: 1) Study the structural composition and dynamic changes of nuclear pore complexes; 2) Study the role of nuclear pore complexes in life activities such as embryonic development, gene transcription and translation, cell differentiation, and apoptosis; 3) Study the trans-nuclear membrane transport mode of macromolecular substances; 4) Study the regulatory mechanism of matter through the nuclear pore complex; 5) Data analysis and bioinformatics analysis.
We Provide the Following Services, including but not Limited to:
- Study on the Structure and Dynamic Changes of Nuclear Pore Complex
- Physiological Function of Nuclear Pore Complex
- Role of Nuclear Pore Complex Proteins in Molecular Transmembrane Transport
- Bioinformatics Analysis
1. Study the formation of nuclear pores
2. Study the location of nuclear pore complexes
3.
Investigate the structural composition of nuclear pore complex
4. Investigate the conformational changes
of NPC that small or large molecules may cause through the nuclear pore complex.
5. Investigate the role
of cytoplasmic and nucleoplasmic loops in the process of material transport.
1. Study on the function of nuclear pore complex characteristic proteins. For example: nuclearlamin, emerin
2. Investigate the role of nuclear porin components in spindle orientation and mitosis
3.
Investigate the role of nuclear porin complexes in life development such as embryo development, gene
transcription and translation, cell differentiation, and apoptosis
4. The connection between nuclear pore
complex and aging
1. Trans-nuclear membrane transport mode of macromolecular substances
Study nuclear translocation signals
and transport vectors which contain importin, exportin, and transportin.
2. Regulation mechanism of
substances passing through nuclear pore complex
For example, nucleolar protein domain function analysis, homology analysis and evolution analysis.
Advantages of the Nuclear Pore Complex Proteomics Services:
- One-stop service: we will customize a solution for you based on your samples and needs. You can also choose which technique to use for analysis.
- High performance mass spectrometry system: equipped with Q Exactive Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap and Agilent 6540 Q-TOF high performance mass spectrometer which effectively improving the identification and quantification of low abundance subcellular related proteins.
- Multi-database integration: by integrating multiple related high-quality protein databases, the accuracy and flux of subcellular protein localization can be greatly improved.
- Multi-dimensional data analysis: in addition to the comparison with the more complete related subcellular database, multiple software was used for the prediction analysis of subcellular localization based on the calculation method to further increase the identification flux.
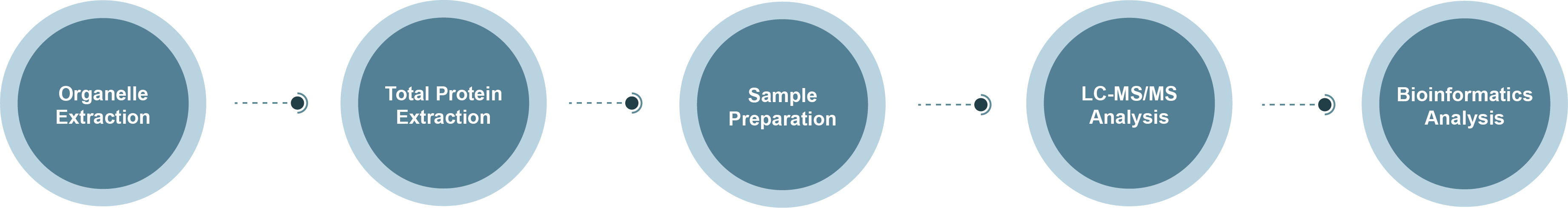
Nuclear Pore Complex Proteomics Technology Roadmap
Data Analysis of Nuclear Pore Complex Proteomics
| 1. Data output statistics and quality control | 2. Protein identification analysis (Density map, Scatter plot, Venn diagram) | 3. Quantitative protein analysis (Density map, Scatter plot, Venn diagram) |
| 4. Protein GO analysis | 5. Protein pathway analysis | 6. Protein COG analysis |
| 7. GO enrichment analysis of differential proteins | 8. Pathway enrichment analysis of differential proteins | 9. COG analysis of differential proteins |
References
- Cronshaw J M, Krutchinsky A N, et al. Proteomic analysis of the mammalian nuclear pore complex. The Journal of cell biology, 2002, 158(5): 915-927.
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, et al. The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature, 2007, 450(7170): 695-701.
- Knockenhauer K E, Schwartz T U. The nuclear pore complex as a flexible and dynamic gate. Cell, 2016, 164(6): 1162-1171.
Related Services
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.