Extracellular Vesicles Proteomics Services
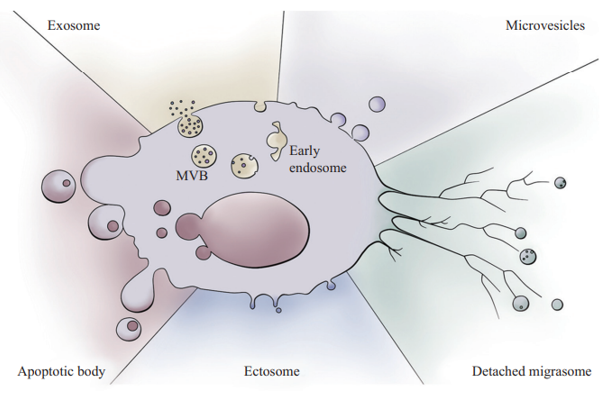
Online InquiryExtracellular vesicles include microvesicles, ectosome, migrasome, apoptotic body and extracellular vesicles. Almost all cells are capable of producing extracellular vesicles. They contain lipids, proteins, nucleic acids (DNA, mRNA and noncoding RNA such as microRNA, lncRNA, circRNA) and many other biologically active components of parent cell origin. These informative substances are encapsulated in vesicles or carried on membranes. They are involved in inflammatory immune response, intercellular signaling communication, cell survival and apoptosis, angiogenesis, thrombosis, and autophagy, and play important roles in the maintenance of physiological states and the course of diseases. Specific types of extracellular vesicles are expected to become new molecular markers to assist in disease diagnosis and prognosis, and have broad prospects in anti-tumor therapy, regenerative medicine, immune regulation, etc. They can open new pathways for stem cell therapy of non-cellular pathways, and may be used as natural carriers of vaccines or drugs for clinical treatment.
Protein is an important component of extracellular vesicles. Due to the development of proteomics technologies, proteomic studies of extracellular vesicles are developing rapidly and are becoming an important source of molecular markers of disease. Creative Proteomics provides extracellular vesicle proteomics services based on high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to help analyze extracellular vesicles of different cellular origins and help understand the mechanisms of disease development at the protein level.
We Provide but Are Not Limited To:
Isolation and enrichment of extracellular vesicles
We have a standard process from collection of body fluid samples or in vitro cultured cell samples to sample analysis, with the option/combination of ultra-centrifugation or density gradient centrifugation, affinity purification, nanotechnology, microfluidic analysis and other methods to obtain purer extracellular vesicles.
Extracellular vesicle protein identification service
Unknown protein identification. Discovery of new proteins.
Free-labeled extracellular vesicle protein quantitative analysis
Screening of differential proteins by free-labeled quantitative proteomics technology
Extracellular vesicle modification proteomics service
We can provide a variety of post-translational modification services for extracellular vesicle proteins, including phosphorylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, methylation, etc.
Take phosphorylation analysis as an example:
- Full spectrum identification of protein phosphorylation modifications: Identification of all phosphorylation modified proteins and corresponding phosphorylation modification sites in extracellular vesicles of the sample.
- Protein phosphorylation modification iTRAQ quantification: Based on high precision and high sensitivity mass spectrometer, iTRAQ quantification technique is combined with TiO2 enrichment technique to identify and relatively quantify the modified proteins of extracellular vesicles.
- Phosphorylated PRM quantification: quantitative validation of target phosphorylated modified proteins by liquid-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
Microvesicles proteomics and exosome proteomics analysis
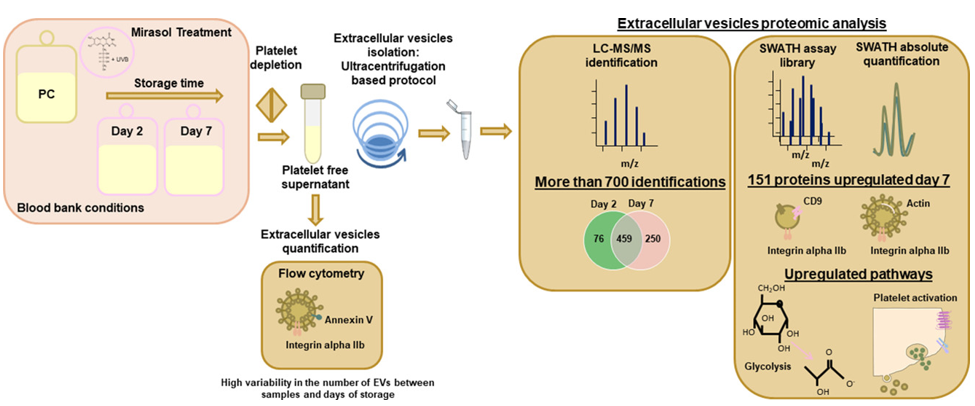 Proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicles (Hermida et
al., 2020)
Proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicles (Hermida et
al., 2020)
Data Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles Proteomics
| 1. Data output statistics and quality control | 2. Protein identification analysis (Density map, Scatter plot, Venn diagram) | 3. Quantitative protein analysis (Density map, Scatter plot, Venn diagram) |
| 4. Protein GO analysis | 5. Protein pathway analysis | 6. Protein COG analysis |
| 7. GO enrichment analysis of differential proteins | 8. Pathway enrichment analysis of differential proteins | 9. COG analysis of differential proteins |
Reference
- Hermida-Nogueira, L., Barrachina, M. N., et al. (2020). Proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicles derived from platelet concentrates treated with Mirasol? identifies biomarkers of platelet storage lesion. Journal of proteomics, 210, 103529.
Related Services
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.