Cancer Exosome Research Solution
Online InquiryExosomes are endosome-derived nanosized, lipid bilayer membrane-enclosed extracellular vesicles (EVs) ranging in diameter from 30 to 150. they have been identified as mediators of cell-to-cell communication by transferring their contents, such as proteins, metabolites, lipids, DNAs (mtDNA, ssDNA, dsDNA), and RNAs (mRNA, non-coding RNA). Exosomes can be secreted by a variety of cell types, including cancer cells. Cancer-derived exosomes affect not only the invasive potential of proximal cells, but also distal tissues. Based on their ability to participate in cell-cell communication, regulate tumor growth, and alter tumor microenvironment, there has been growing interest in their research and application in cancer.
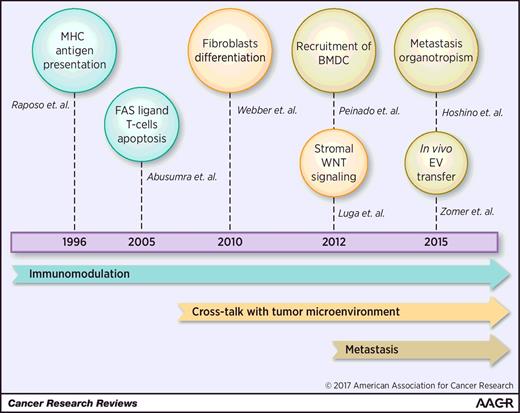 Fig. 1 Chronological highlights of studies on cancer exosomes. (Ruivo, Carolina F., et al., 2017)
Fig. 1 Chronological highlights of studies on cancer exosomes. (Ruivo, Carolina F., et al., 2017)
Exosome functions in cancer
During cancer progression, exosome biogenesis/secretion and "cargo" content are more regulated. The quantity and quality of exosomes released by normal and cancer cells are different. Current studies have suggested that the continuous exchange of information between tumor cells and their stromal microenvironment leads to cancer progression. Exosomes can both induce and promote a pro-tumoral microenvironment for tumorigenesis and regulate the immune response to tumor progression and survival by promoting angiogenesis, metastasis, and drug resistance. Thus, exosomes not only provide a new way to detect cancer biomarkers, but may also have great potential in cancer therapy. Exosomes can serve as carriers for anticancer drug delivery and offer potential targets for cancer therapeutic interventions.
- Exosomes in tumorigenesis regulation
- Exosomes in tumor growth and metastasis regulation
- Exosomes in tumor-associated immune regulation
- Exosomes are key components of the tumor microenvironment
- Exosomes in tumor angiogenesis regulation
- Exosomes and cancer-associated fibroblasts
- Cancer exosomes have been implicated in the remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
Cancer exosome research solution at Creative Proteomics
Based on our experienced scientists and well-established technologies, Creative Proteomics is able to provide a customized exosome isolation service that isolates exosomes from various biofluids. Notably, the choices of methods for exosome isolation and purification depend on the type of the sample. According to the pros and cons of each method and the sample types, we provide the most appropriate method to isolate and purify exosomes. In addition, our scientists have developed a platform for exosome identification. We applied several techniques to characterize exosomes, including nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), western blotting (WB), and mass spectrometry (MS). Our global team is able to provide cancer exosome research support to researchers in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and academic and government institutions, greatly facilitating subsequent cancer exosome research and accelerating our global clients' projects to the next stage.
- Breast cancer exosome research solution
- Pancreatic cancer exosome research solution
- Glioblastoma exosome research solution
- Prostate cancer exosome research solution
- Colorectal cancer exosome research solution
Our capability supports, including but not limited to:
| Exosome analysis services | |
|---|---|
| Exosome isolation and purification | Sucrose gradient centrifugation |
| Polymer-based exosome enrichment method | |
| Immunomagnetic bead method | |
| Size exclusion chromatography method | |
| Exosome identification | Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) |
| Electron microscopy analysis | |
| Western blot | |
| Exosome marker assay | Isolation and enrichment of exosomal CD9, CD63, CD81, TSG101, HSP70 proteins |
| Exosome surface protein identification and quantitative analysis | |
| Exosome engineering | Exosome labeling and tracking |
| Cargo loading | |
| Engineered exosome production | |
| Cargo loading assessment | |
| Exosomes labeling and tracking | Exosome fluorescent labeling |
| Fluorescence exosome purification | |
| Fluorescent exosome concentration labeling | |
| Exosome multiomics analysis | Exosome proteomics analysis: Exosome protein profile identification Exosome protein composition analysis Exosome protein expression level analysis Exosome protein differential expression analysis |
| Exosome metabolomics analysis: Exosome differential metabolite screening Qualitative and quantitative analysis of target metabolites/metabolic pathways | |
| Exosome lipidomics analysis: Exosome lipid composition and level analysis Differential expression analysis of exosomal lipid molecules Qualitative and quantitative analysis of targeted lipid molecules | |
| Exosomal biogenesis and identification | Our capabilities will provide strong support for the study of exosome biogenesis and its identification. |
| Exosomal cargo and loading mechanism | Our services can greatly help the study of exosomal cargo and loading mechanism, facilitating the diagnostic and therapeutic applications of exosomes. |
| Exosome function research | In vitro analysis of the function of exosomes In vivo analysis of the function of exosomes |
Advantages of our services
- An optimized and well-established platforms
- Professional technical support
- Ready to start your project once the contract is signed
- Best after-sale services
Creative Proteomics is committed to offering high-quality customized service and the best outcome to accelerate the research progress for our global customers. If you are interested in this area, please feel free to contact us.
References
- Zhu, Le, et al. "Isolation and characterization of exosomes for cancer research." Journal of hematology & oncology 13.1 (2020): 1-24.
- Kalluri, Raghu. "The biology and function of exosomes in cancer." The Journal of clinical investigation 126.4 (2016): 1208-1215.
- Ruivo, Carolina F., et al. "The Biology of Cancer Exosomes: Insights and New PerspectivesBiology of Cancer Exosomes." Cancer research 77.23 (2017): 6480-6488.
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.