Protein Phosphorylation Analysis
In organisms, phosphorylaton is the most common but important form of covalent modificaton for protein post-translatonal modificatons that regulate both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Phosphoryla- ton plays an important regulatory role in the proper functoning of proteins.
DOWNLOAD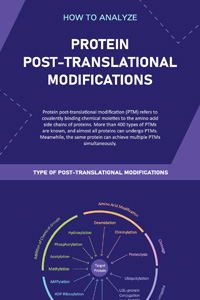
Protein Post-Translational Modification Analysis
Protein post-translational modification (PTM) refers to covalently binding chemical moieties to the amino acid side chains of proteins. More than 400 types of PTMs are known, and almost all proteins can undergo PTMs. Meanwhile, the same protein can achieve multiple PTMs simultaneously.
DOWNLOAD
Membrane Proteomics Solution
Cell membrane proteins perform important functions such as exchange of materials in and out of the cell, cell recognition and immune response, signal transduction and regulation, and energy transfer. To better understand their functions, it is necessary to reveal the characteristics of membrane proteins and monitor the modification and regulation of their expression. As many drugs target membrane proteins currently, research on them becomes even more important to help develop new drug targets and new treatments. This infographic introduces the design solutions of membrane proteins and some specific proteomics services.
DOWNLOAD
Exosome Proteomics Solution
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles that can affect cell functions by transferring substances such as nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids between cells. For example, they play an important role during antigen presentation in antigen-presenting cells, in the development of tumor cells, and in signal transduction in nerve cells. The detection and analysis of exosomes can accelerate disease-related basic research, assist in disease diagnosis, drug development, therapeutic research, and drug efficacy evaluation. This infographic introduces some specific proteomics services and the design solutions of exosome proteomics.
DOWNLOAD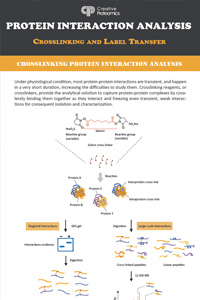
Crosslinking & Label Transfer Protein Interaction Analysis
Many protein-protein interactions in the body are weak and transient. Cross-linking and label transfer protein interaction analysis can be used to detect such interactions. Protein crosslinking can immobilize weakly interacting molecules in complexes that are sufficiently stable for separation and characterization. Combining label transfer and crosslinking techniques enables the discovery of new interactions, verification of protein-protein interactions detected by other methods, and the study of interfaces of interacting proteins.
This infographic contains the principle, workflow, and characteristics of these two technologies.