High-Quality DIA Mass Spectrometry Data Acquisition
Mass spectrometry has emerged as a powerful analytical tool in proteomics, enabling researchers to elucidate the complex world of proteins, their functions, and their interactions within biological systems. Among the various mass spectrometry techniques, Data Independent Acquisition (DIA) has gained prominence for its ability to provide high-quality, comprehensive data that can greatly enhance our understanding of proteomes. Creative Proteomics specializes in proteomics and provides cutting-edge protein analysis services. We provide high-quality DIA mass spectrometry data acquisition solutions that are now effectively utilized in proteomics research.
High-Quality DIA Acquisition Method
- Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Mass Spectra (SWATH). SWATH, with its reproducibility and extensive proteome coverage, has become one of the most widely used DIA acquisition methods. It combines the benefits of data-dependent acquisition (DDA) and DIA by sequentially targeting specific m/z (mass-to-charge ratio) windows throughout the entire mass range of interest.
- Variable Window SWATH (V-SWATH). V-SWATH is an extension of the SWATH method that aims to improve the dynamic range and quantitative accuracy. It introduces variable isolation window widths based on precursor ion density, meaning that wider windows are used for areas with high precursor ion density and narrower windows for low-density regions.
- BoxCar DIA. BoxCar DIA is a variation of SWATH that uses overlapping windows. Instead of completely isolating one window at a time, BoxCar DIA overlaps the isolation windows, capturing data from multiple windows simultaneously.
- MSX DIA. MSX DIA is a recent development that introduces an additional level of fragmentation to DIA. In traditional DIA, only one round of fragmentation occurs for each precursor ion. MSX DIA, however, involves multiple rounds of fragmentation in a single acquisition. MSX DIA enhances the depth of proteome coverage and quantification accuracy by providing a richer set of fragment ions.
Technical Advantages of DIA Mass Spectrometry Data Acquisition
- Complete Coverage of the Proteome. DIA has several benefits, one of which being its ability to sample the proteome thoroughly. It provides an objective picture of the whole protein landscape by methodically breaking apart all precursor ions in a specific mass range, lowering the possibility of overlooking important or low-abundance proteins. This is especially helpful when working with biological samples that are complex.
- Better Determination. The robust measurement of proteins is made possible by DIA's capacity to collect all precursor ions. Because it offers trustworthy information on protein abundance, it is a priceless tool for comparative proteomics, the identification of biomarkers, and the investigation of dynamic changes in the proteome under various circumstances.
- Reproducibility. Because it continuously targets the same precursor ions during several runs, DIA excels at repeatability. For longitudinal investigations, when preserving data consistency is crucial, this capability is indispensable. Additionally, it lessens the influence of technical variance, producing data that is of higher quality.
- Improved Generation of Data Libraries. The acquired DIA data can be re-interrogated, facilitating the creation of extensive spectral libraries. These libraries, in turn, aid in the identification and quantification of proteins in subsequent experiments, thus increasing the efficiency of proteomic research.
Technical Process
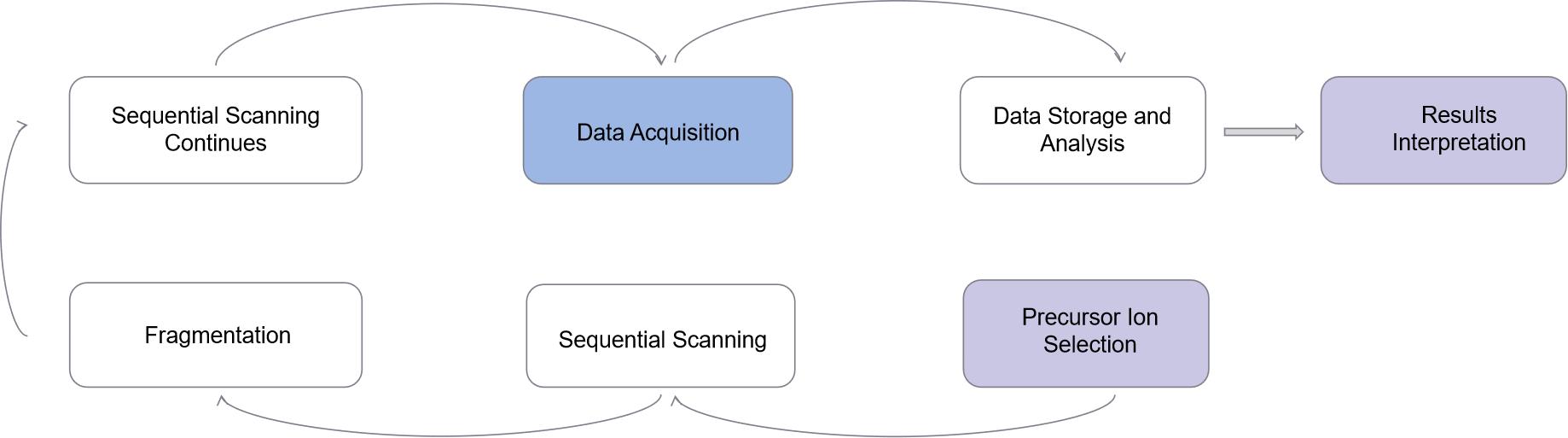
Excellent DIA mass spectrometry data gathering has several technological benefits, a quick and easy procedure, and many uses. It is now a mainstay in proteomic research, helping scientists better comprehend intricate biological systems and making contributions to a range of disciplines, including systems biology, medicine, and drug discovery.
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.



 4D Proteomics with Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA)
4D Proteomics with Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA)