Proteins are vital molecules involved in numerous cellular processes, and carry out important functions such as cell growth, material transportation, and signal transduction. Therefore, understanding protein expressions is crucial to studying vital cell functions. The quantitative comparison of protein abundance across a large number of biological or patient samples represents an important proteomics challenge that needs to be addressed for proteomics discovery applications.
Discovery Proteomics Services
Using our DIA MS technologies, we provide a variety of discovery proteomics services, including protein identification, protein expression level quantification, post-translational modification identification, protein interaction analysis, and large-scale phosphorylation proteomics analysis. Our discovery proteomics will help researchers accelerate their research progress, shorten the research cycle, and provide them with the key insights they need to move forward. And we are interested in developing and implementing new proteomics methods to study unique scientific projects.
About Our DIA MS Platform
Our label-free DIA quantitative proteomics strategy is designed to quantify as many proteins as possible in a dynamic range, which can analyze up to 9,000 proteins per sample under different conditions and identify significantly regulated proteins. This platform is ideal for detecting the differences of multiple samples in protein abundance and low abundance proteins.
a) SWATH
b) SRM™
c) MSX-DIA
d) PCT-DIA
e) GPF-DIA
Our Discovery Proteomics Services Include:
Workflow
Discovery Proteomics strategy uses DIA technique, which divides the whole scanning range of mass spectrum into several windows instead of selecting, segmenting and detecting all ions of each window at high speed in a cycle. All ion fragments in the sample can be obtained without omission, which greatly improves the protein utilization. Then data is analyzed with the database built by OpenSWATH and Skyline softwares.

Bioinformatics Analysis
| Problems to be Solved |
Bioinformatics Analysis |
| Quality Assessment of Protein |
SWATH Data Analysis |
| Protein Comparison of Different Samples |
Multivariate PCA Analysis |
| Protein Statistical Analysis |
Venn Diagram |
| Volcano Plot |
| Functional Annotation |
KEGG Annotation |
| GO Annotation |
| COG Annotation |
| Clustering Analysis |
Hierarchical Clustering |
| K-Means Clustering |
| Network Analysis |
STRING Analysis |
Analytical Platforms
AB SCIEX Triple-TOF 5600-plus, Q-Exactive, Orbitrap Fusion
Key Features
- High accuracy
- High throughput, more than 9000 proteins can be identified and quantitated at once
- Quantitatively identify nearly all detectable molecules, covering low abundance proteins/peptides
- High repetition rate
- Complete and comprehensive information storage of samples in the first analysis
- High repetition rate
Sample Requirements
Based on our special protein extraction technology, we can quickly extract proteins from various samples and design personalized experimental schemes according to different experimental purposes. Specific requirements are as follows:
| Sample Type |
Protein |
Cell |
Animal Tissue |
Plant Tissue |
Blood |
Urine |
Serum |
Microbes |
| Quantify |
100 ug |
1×107 cells |
1 g |
200 mg |
1 mL |
2 mL |
0.2-0.5 mL |
Dry weighed: 200 mg |
Note:
- Please prepare enough dry ice or ice packs to ensure low temperature during sample delivery
- Our service is for research use only and is not intended for diagnosis.
Applications
1) Biomarker discovery and validation
2) Target discovery
3) Pathological study of disease
4) Genetic association study
5) Microorganisms proteomics research
6) Crop proteomics research
7) Quantitative comparison of proteomes in multiple biological samples
Reports
- Experiment report
- Relative parameters of the mass spectrometer
- MS raw data files
- Bioinformatics analysis
- Peptide/Protein identifications and intensities
Case Enhancing Identification and Accuracy through Narrow Precursor Mass Range DIA
Background
The study aimed to establish a rapid and reliable Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) workflow for comprehensive mapping of urinary proteomes. The research focused on biomarker discovery in pediatric emergency room (ER) patients experiencing abdominal pain, utilizing a urine-based approach for efficient and clinically relevant analysis.
Samples
The research utilized 87 urine samples from pediatric emergency room patients presenting with abdominal pain. The diverse sample set included cases of ovarian cysts, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and a control group representing other abdominal pain causes and indeterminate cases.
Technical Methods
DIA Method Optimization:
- Balanced mass range coverage achieved through simultaneous fragmentation or 20–50 Th fragmented windows.
- Implementation of 30 windows with 20 Th width on a Q Exactive mass spectrometer for a m/z range of 400–1000.
- Adoption of the ultrahigh-field Orbitrap mass analyzer (Q Exactive HF) with 30,000 resolution settings.
- Rectangular isolation window shape for accurate peptide isolation.
Spectral Library Selection:
- Evaluation of five spectral libraries, including in-house generated project-specific libraries and publicly available human libraries.
- Consideration of peptide and protein identification, as well as reproducibility, for library assessment.
- Preference for project-specific libraries over publicly available ones due to higher reproducibility.
Highly Reproducible Peptide Detection and Quantitation:
- Comparison of DIA-based and DDA-based quantification using an optimized workflow.
- DIA method demonstrated a significant increase in identified peptides and proteins per replicate, with improved reproducibility.
- Calculation of coefficients of variation (CV) for precise quantification, revealing lower CVs in DIA-based quantification compared to DDA-based methods.
Comprehensive Urinary Proteome Coverage:
- Application of the optimized DIA workflow to analyze 87 urine samples in less than 4 days.
- Achievement of ~1300 proteins per sample, almost twice as many as traditional DDA analyses.
- Reduction of missing values, enhancing confidence in biomarker candidate identification.
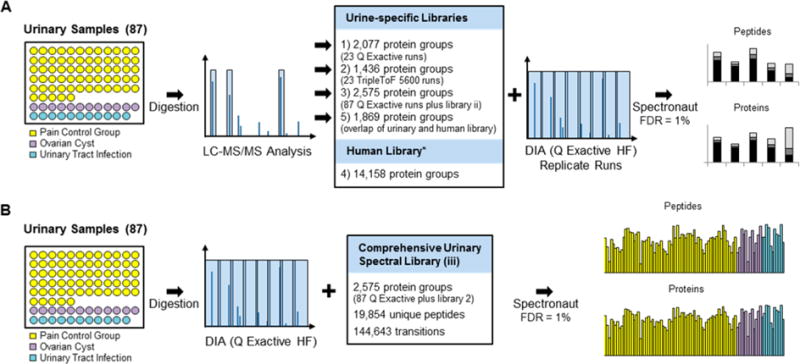 Workflow. (A) Generation of spectral library. (B) DIA sample acquisition.
Workflow. (A) Generation of spectral library. (B) DIA sample acquisition.
Results
DIA Workflow Efficiency:
- The DIA workflow almost doubled the number of identified peptides and proteins compared to standard DDA experiments.
- Improved quantification precision (CV) in DIA-based quantifications, allowing for reduced replicate runs.
Biomarker Discovery Study:
- Identification of biomarker candidates for UTI and ovarian cysts in pediatric ER patients with abdominal pain.
- Application of area under the receiver-operating characteristic (AUROC) analysis for assessing biomarker performance.
Comprehensive Urinary Proteome Coverage:
- High peptide and protein identification numbers achieved without prefractionation and within a short LC gradient time.
- Significantly fewer missing values in DIA data compared to DDA data, increasing confidence in biomarker identification.
- Exploration of bacterial proteins for UTI-specific differences, though inconclusive.
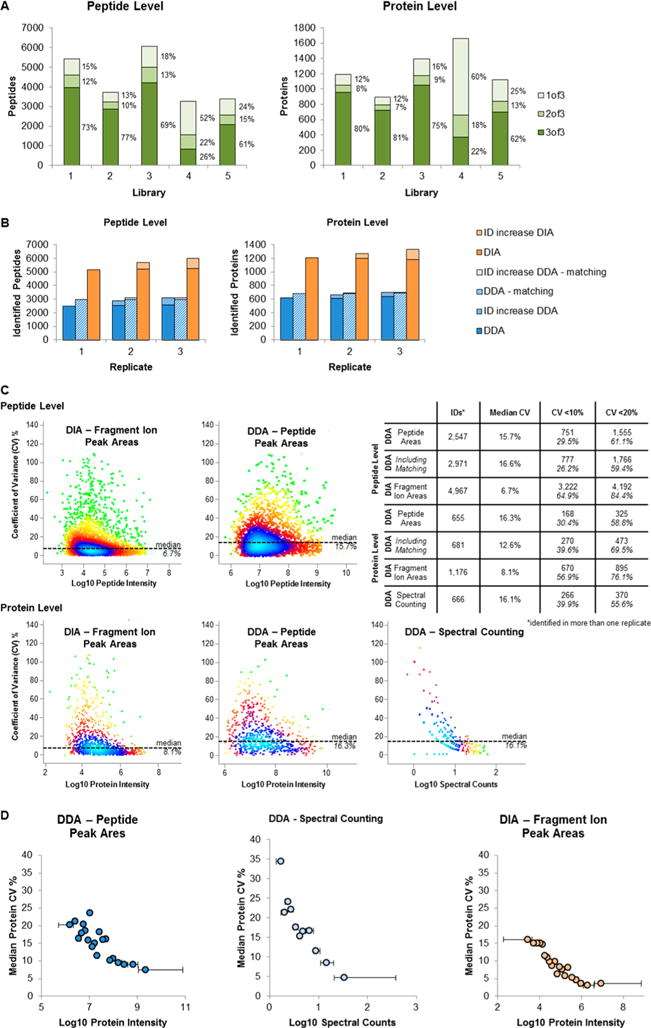 Validation of workflow. (A) Influence of spectral library. (B) Number of peptide and protein identifications in replicate runs. (C) Quantification precision. (D) Protein %CV in relation to protein abundance.
Validation of workflow. (A) Influence of spectral library. (B) Number of peptide and protein identifications in replicate runs. (C) Quantification precision. (D) Protein %CV in relation to protein abundance.
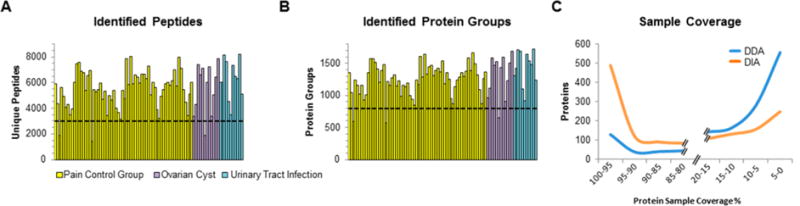 Overview of DIA data set.
Overview of DIA data set.
Reference:
- Muntel, Jan, et al. "Advancing urinary protein biomarker discovery by data-independent acquisition on a quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometer." Journal of proteome research 14.11 (2015): 4752-4762.


 Workflow. (A) Generation of spectral library. (B) DIA sample acquisition.
Workflow. (A) Generation of spectral library. (B) DIA sample acquisition. Validation of workflow. (A) Influence of spectral library. (B) Number of peptide and protein identifications in replicate runs. (C) Quantification precision. (D) Protein %CV in relation to protein abundance.
Validation of workflow. (A) Influence of spectral library. (B) Number of peptide and protein identifications in replicate runs. (C) Quantification precision. (D) Protein %CV in relation to protein abundance. Overview of DIA data set.
Overview of DIA data set.
 4D Proteomics with Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA)
4D Proteomics with Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA)