Venom Phylogenies and Evolutionary Analysis
The venom of poisonous species has evolved over millions of years. In addition to helping to defend against predators, it can also cause paralysis of prey and systemic destruction of homeostasis. In this process, a series of extraordinary biochemical components have been developed, including toxins with amazing specificity and affinity for various types of cells and receptors. Therefore, venoms and toxins are considered to be rich sources of new biochemical compounds for drug design and development.
Molecular phylogeny can help the pharmacological study of toxins by suggesting the clade that is most likely to contain pharmacological compounds. Creative Proteomics provides venom transcriptomics, proteomics, phylogeny and evolution analysis services to reveal the true biodiversity of toxins and provide valuable information for drug design and development.
What Creative Proteomics Can Offer
We provide phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis of venom, which mainly includes two parts: building a phylogenetic tree and evolutionary analysis.
The structure and function of the venom tend to be conserved in the evolution process. Related toxins show similar characteristics, and the classification of traits is related to the increase of the phylogenetic distance between toxins. Therefore, the establishment of the phylogeny of the toxin sequence helps to determine their function. We use software to generate toxin sequence alignment to establish the phylogeny of the toxin:
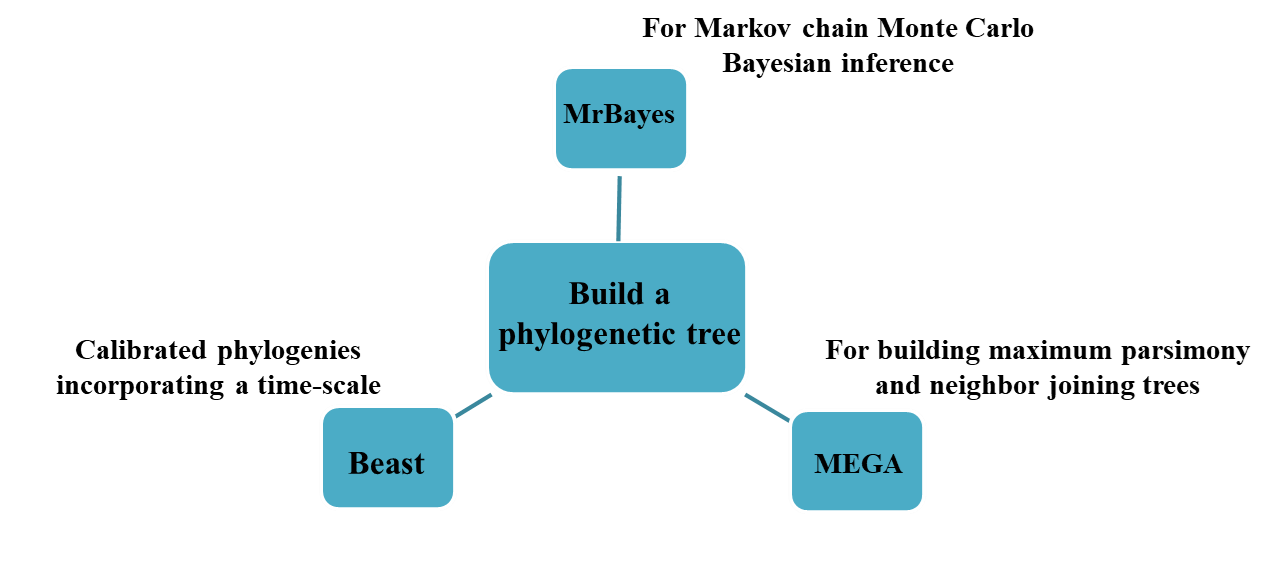
Describing the evolution of the venom on the prey provides information for the discovery of new toxins with drug activity and an understanding of the evolutionary mode of its function. We help customers determine the positions under selective pressure in order to determine toxin functions.
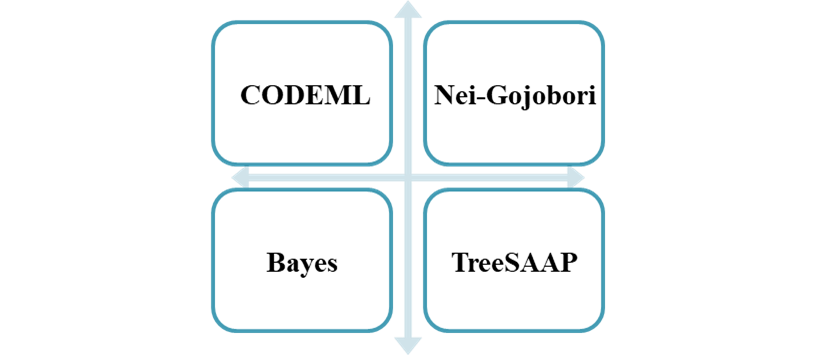
- The CODEML of the PAML (Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Analysis) package is used to evaluate the ratio between non-synonymous and synonymous nucleotide substitution rates.
- The evaluation result of the Nei-Gojobori model based on MEGA is significantly greater than 1, which indicates that the corresponding position is positively selected and can be used for function optimization.
- Bayes method better estimates the selection pressure of a series of toxin families.
- TreeSAAP works at the protein level to test a variety of scenarios for toxins.
Solved Problem
- Solve the classification deviations of snakes, spiders, scorpions and most of the toxic biological lineages that have been studied, as well as the venomous lineages that need to be developed.
- Perform phylogenetic analysis to reconstruct the molecular evolutionary history of each toxin type.
- Shape the evolutionary selection pressure of the venom component, including the pressure acting on different areas of the same venom component.
Advantages
Creative Proteomics tracks the evolutionary relationship between toxins, taking into account the specific mechanisms of rapid evolution and the interaction between toxic species and prey, and provides some phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis methods to accurately predict the specificity of toxins. We help customers reveal the phylogeny and evolution of different toxins, and provide a wealth of information for future drug design and development.
For the phylogenies and evolutionary analysis of venom toxin bioinformatics data, if you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Quentin K, David C. Bioinformatics-Aided Venomic. Toxins, 2015, 7(6):2159-2187.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.


