After protein expression and purification, protein sequences should be verified at each end to ensure that the N-terminal and C-terminal sequences are accurate. Meanwhile, Edman degradation sequencing is one of the most mature methods for N-terminal sequence analysis of proteins and is widely used in studying protein products.
Creative Proteomics can provide the N-terminal sequencing service (Edman degradation sequencing service) for purified protein products, antibodies, and protein vaccines for researchers of all fields. Our sequencing system is capable of reading and determining 30 amino acids of the N-terminus. Additionally, our specific protein loading system is capable of reading and determining 60-70 amino acids of the N-terminus.
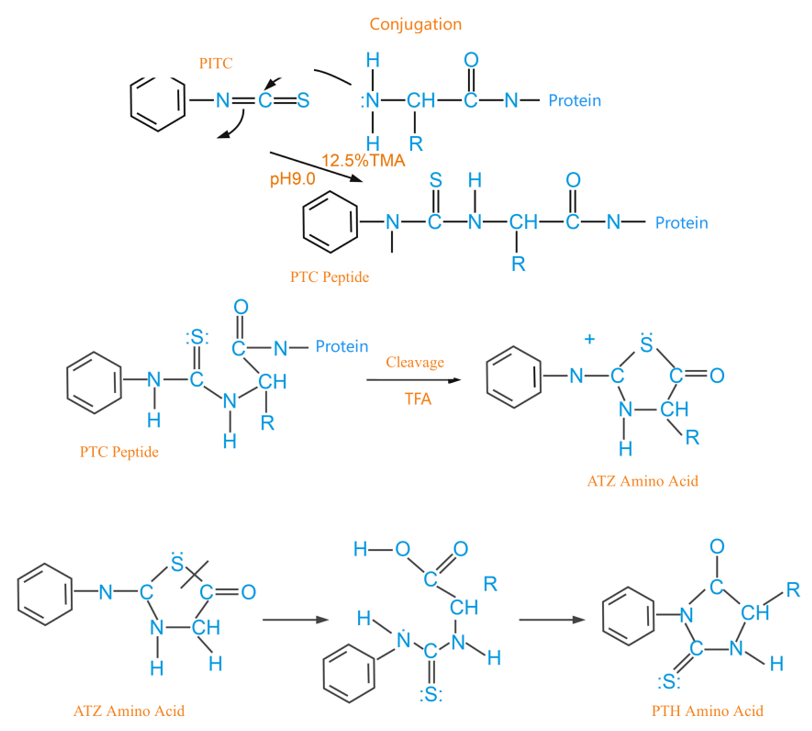
Edman Principle
The basic Edman principle includes three main chemical steps: phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) conjugation to the N-terminal residues of proteins, cleavage of the phenylamino thiocyanate Formylphthalein (PTC-peptide), and conversion of thiazolinone-aniline (ATZ) into phenylisothiourea amino acid (PTH-amino acid). During each step of the reaction cycle, an amino acid residue is cleaved at the N-terminus while exposing new free amino acids for the next Edman degradation cycle. Hence, the protein sequence is determined by the identification of transferred PTH-amino acid (PTH-AA) residues.
Our N-terminal Edman Sequencing Services
Protein N-terminal Edman sequencing services
1D SDS gel electrophoresis of proteins (Optional)
1D SDS PAGE separation of heavy and light chains (Antibodies)
Transfer gel to PVDF membranes and staining
Edman sequencing of N-terminus
Determination of up to 30 amino acids (Up to 20 amino acids per chain of antibodies)
Key Features
- High sensitivity in detecting PTH-AA at low picomole level
- Analyze 30 N-Terminal amino acids
- Most updated HPLC analysis system utilizing the UV_VIS SPD-20A detector
- Accurately discriminate amino acids of high similarity; i.e., I/L and Q/K
Applications
- Determination of N-terminal sequence of Proteins/Peptides/Antibodies/Vaccines
- Verification of the correct translation of Recombinant Proteins
- Verification of the sequence of Synthetic Peptides
Service Workflow
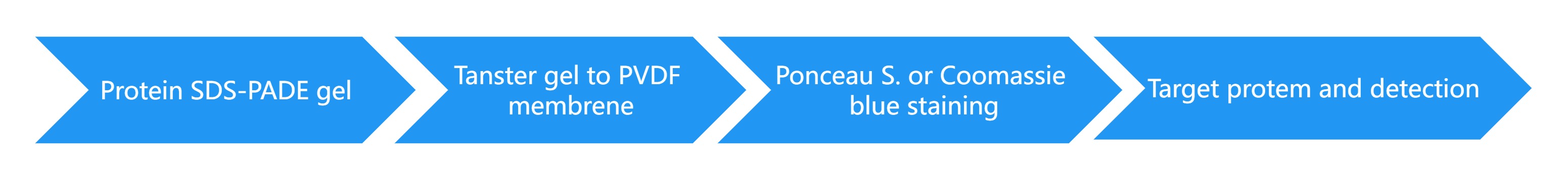
Note: protein samples with purities greater than 95% can be directly detected by spotting protein samples onto the PVDF membrane.
Sample Requirements
Sample type: dry powder or solution
Sample concentration and purity: total amount > 200 µg, purity > 90%, concentration > 0.5 mg/mL
Salt content: volatile inorganic salt < 20 mM, non-volatile inorganic salt < 5 mM; Tris buffer system is not recommended; provision of theoretical sequences of samples is recommended
Although the Edman degradation method has been widely used, there are still shortcomings. For example, the Edman degradation method cannot efficiently sequence the N-terminus that lacks free α-amino groups (circularization, blocking) nor obtain signals of modified proteins. To overcome these shortages, Creative Proteomics uses mass spectrometry, which is not limited by N-terminal blockade, and can efficiently identify post-translational modifications of side chain groups to complement the traditional Edman degradation sequenceing method.








