Title: Study of gene expression and steviol glycosides accumulation in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni under various mannitol concentrations
Journal: Molecular Biology Reports
Published: 2019
Background
Stevia rebaudiana produces sweet steviol glycosides that are significantly sweeter than sugar and have beneficial effects on human health, including anti-hyperglycaemic properties. Tissue culture is an effective method for propagating stevia, and abiotic stress, such as osmotic stress from mannitol, influences steviol glycoside content in stevia plants. The study focuses on the impact of mannitol on the expression of key genes involved in steviol glycoside biosynthesis, including UGT74G1, UGT76G1, kaurene oxidase, and kaurene synthase. The findings show that different mannitol concentrations affect gene expression and the accumulation of stevioside and rebaudioside A, suggesting that mannitol can optimize the production of steviol glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana under in vitro conditions.
Materials & Methods
Plant Materials and Culture Conditions:
Stevia rebaudiana plants were obtained from Zagros Bioidea Co., Razi University Incubator, Kermanshah, Iran. Stevia propagation was carried out via tissue culture. Axillary buds of approximately 1.5 cm in length were excised from the shoots. The culture medium used was MS medium, supplemented with different concentrations of mannitol (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 g/l). The cultures were incubated at 25 ± 1°C under a 16-hour light/8-hour dark photoperiod, with a light intensity of 3000 Lux and a relative humidity of 72–75%. Shoot proliferation occurred in mediums with varying mannitol concentrations.
RNA Extraction:
Total RNA was extracted from fresh leaves using the Cinnaclon RNX plus™ kit (Sinaclon, Iran), according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNA quantification was performed using a NanoDrop Spectrophotometer (Nanodrop®, ND-1000, Nanodrop Technologies, USA).
Expression Analysis of UGT74G1, UGT76G1, KO, and KS Genes:
For cDNA synthesis, 10 µg of total RNA was reverse transcribed using M-Mulv reverse transcriptase and a 20 µL master mix. β-Actin served as the internal control gene. Primers for target genes and β-Actin were designed using Oligo 7 Primer Analysis Software. RT-qPCR was conducted using SYBR green two-step RT-qPCR in a 36-well plate. Each reaction consisted of 6.4 µL RNase-free water, 0.4 µL of each primer (10 µmol/L), 10 µL SYBR green mix, and 2 µL of cDNA (5 ng/µL), totaling 20 µL per reaction. Thermal cycling conditions were 95°C for 30 seconds, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 5 seconds and 60°C for 30 seconds. A melting curve analysis (60–95°C) was performed to verify amplicon specificity. Data were analyzed using Rotor-Gene Q Series Software, with relative quantification calculated using the formula RQ=2−∆∆Ct.
HPLC Analysis:
Stevioside and rebaudioside A contents were determined using HPLC. Dried leaves of stevia treated with various mannitol concentrations (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 g/l) were extracted with 80% methanol, followed by drying and defatting with hexane. The remaining extract was dissolved in acetonitrile and filtered. Chromatographic separation was performed using a Symmetry Xbridge amide column at 50°C with an isocratic mobile phase of acetonitrile: water (80:20) and detection at 210 nm. The injection volume was 10 µL with a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min. Stevioside and rebaudioside A were quantified in three independent replicates.
Statistical Analysis:
Data were analyzed using Excel and SPSS Ver. 16 software. The data followed a normal distribution and were used directly for statistical analysis. Mean comparisons were conducted using Duncan's multiple range test with a significance level of p < 0.05.
Results
Shoot Proliferation
The shoot proliferation of nodal explants in various concentrations of mannitol after 28 days. The shoot proliferation was observed to be influenced by different concentrations of mannitol.
Gene Expression
- UGT76G1 Gene: The highest expression of the UGT76G1 gene was observed in plants grown under 20 g/l mannitol, with significant differences compared to other concentrations.
- KS Gene: The highest gene expression was seen in plants grown in 40 g/l mannitol medium, with no significant difference from the 20 g/l mannitol treatment. The lowest expression was observed in plants treated with 10 g/l mannitol.
- KO Gene: The highest expression was found in 50 g/l mannitol treatment, with the lowest expression observed in 30 g/l mannitol. The expression of UGT74G1 was similar to that of KO, with the highest expression in 50 g/l mannitol and lowest in 30 g/l mannitol.
- UGT74G1 Gene: The gene expression of UGT74G1 had less variability compared to the other genes under different treatments.
Overall, mannitol treatments increased the expression of the UGT76G1 gene, while the UGT74G1 gene showed less fluctuation in response to different treatments.
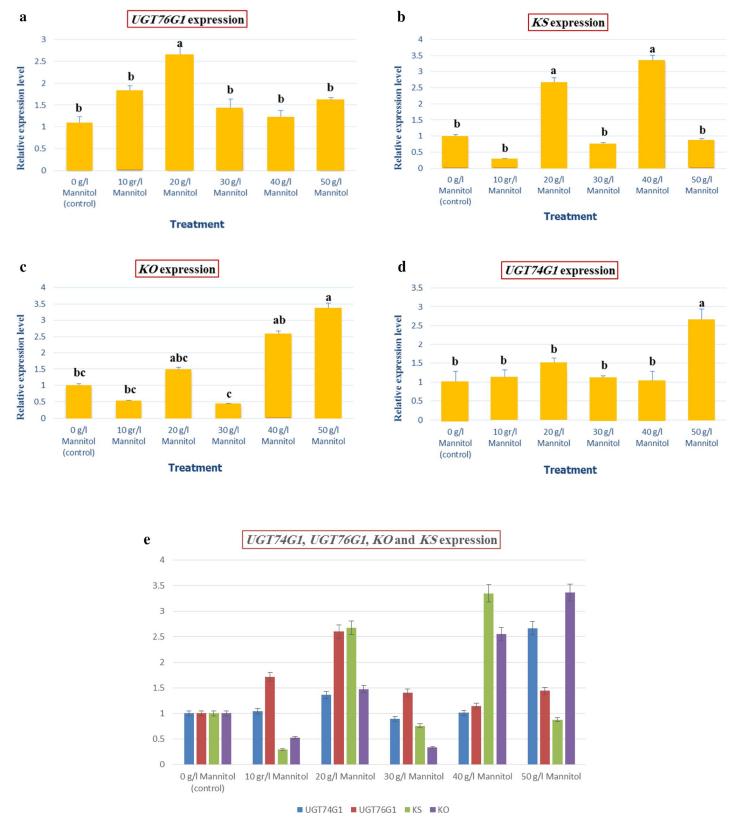 Relative Quantification plot of target genes levels in leaf tissues of S. rebaudiana conducted by Real Time PCR.
Relative Quantification plot of target genes levels in leaf tissues of S. rebaudiana conducted by Real Time PCR.
Steviol Glycosides Content
- Stevioside: The highest amount of stevioside was accumulated in the plants treated with 20 g/l mannitol.
- Rebaudioside A: Maximum accumulation of rebaudioside A was observed under 30 g/l mannitol treatment.
These findings suggest that mannitol supplementation in specific concentrations increases the content of steviol glycosides in stevia leaves.
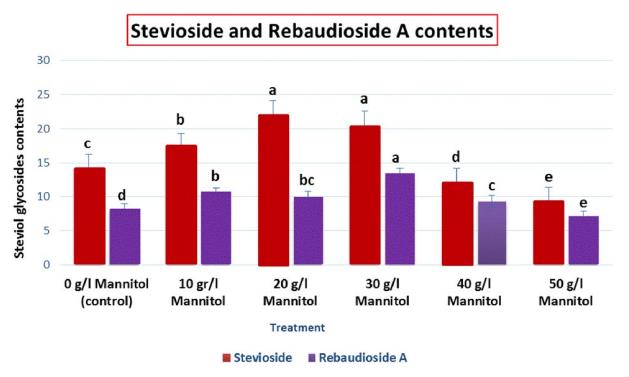 Steviol glycosides contents in leaf tissues of S. rebaudiana subjected to different concentration of Mannitol
Steviol glycosides contents in leaf tissues of S. rebaudiana subjected to different concentration of Mannitol
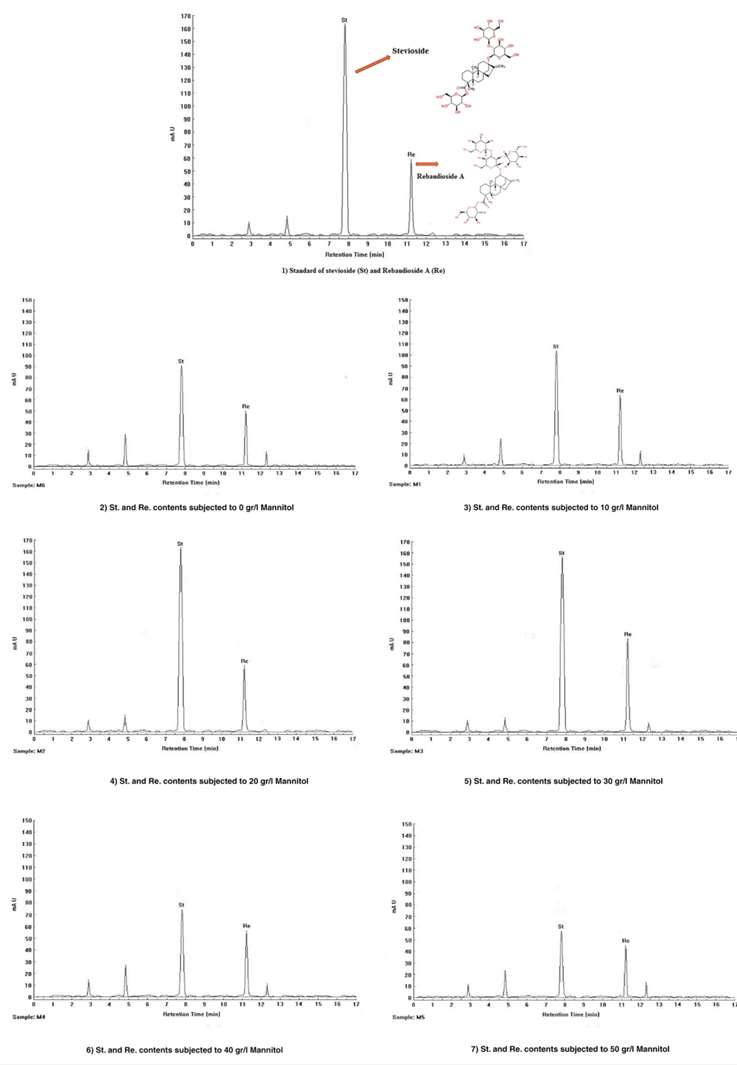 Representative HPLC chromatograms for quantification of Stevioside and Rebaudioside A in methanolic extract of S. rebaudiana leaf tissues
Representative HPLC chromatograms for quantification of Stevioside and Rebaudioside A in methanolic extract of S. rebaudiana leaf tissues
Reference
- Ghaheri, Matin, et al. "Study of gene expression and steviol glycosides accumulation in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni under various mannitol concentrations." Molecular biology reports 46.1 (2019): 7-16.






