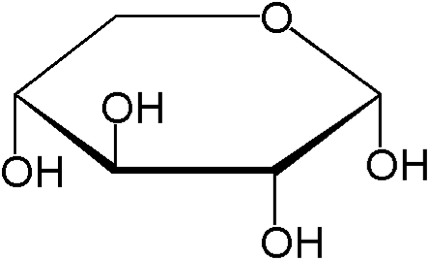
Xylose is the first sugar isolated from wood, and then named for it because the mean of the xylon is wood. Xylose contains five carbon atoms and a formyl functional group, so Xylose is classified as a monosaccharide of the aldopentose type. Xylose is the derivative of hemicellulose, which is one of the main constituents of biomass. Xylose can adopt several structures depending on conditions like most sugars. Xylose is a reducing sugar because it contains a free carbonyl group.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Xylose levels in various samples, including Food, Beverage and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Xylose levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Xylose measurement, which enables us to analyze of Xylose levels in vitro and in vivo.
Xylose is not a major human nutrient and mainly excreted by the kidneys. Xylose contains 0 calories per gra and humans must obtain Xylose from their diet. An enzyme named xylosyltransferase can transfer Xylose from UDP to a serine in the core protein of proteoglycans. Xylose is used to test for malabsorption by administration in water to the animal after fasting in animal medicine. Xylose has been absorbed by the intestines if it is detected in blood or in urine within the next few hours. High Xylose intake, just about 100g/kg of animal body weight is relatively well tolerated in pigs and is consistent with the human studies.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Xylose Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Xylose Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Food, Beverage and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Xylose levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Xylose measurement, which enables us to analyze of Xylose levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







