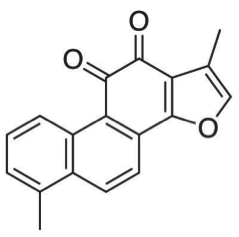
The chemical molecule formula of Tanshinone I is C18H12O3. Tanshinone I is sluble in DMSO. Tanshinones are the major bioactive compounds isolated from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, which have been used for the treatment many diseases in Chinese traditional medicine.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Tanshinone i levels in various samples, including Plant Tissue and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Tanshinone I (270 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Tanshinone I measurement, which enables us to analyze of Tanshinone I levels in vitro and in vivo.
Tanshinone I is cytotoxic to cancer cells and can inhibits cell migration and invasion. There are many research papers have suggested that Tanshinone I can inhibit the migration, invasion, and gelatinase activity of the cancer cells in vitro culture system. Tanshinone I is also can reduce the tumorigenesis and metastasis of cancer cells in the immune-deficient mice. Tanshinone I did not have direct cytotoxicity to the cancer cell line, which is different from Tanshinone IIA. Tanshinone IIA is believed to induce cell apoptosis. Tanshinone I can reduce the transcriptional activity of interleukin-8 demonstrated by the real-time quantitative PCR, luciferase reporter assay, and electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Interleukin-8 can attenuate DNA-binding activity with activator protein-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB and resulting in the anti-tumor activity. Tumor-related genes responding to Tanshinone I may be associated with the Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase and Rac1 signaling pathways. These results suggest that Tanshinone I has a remarkable anticancer action and it has the potent to be a drug candidate for cancer treatment.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Tanshinone I Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Tanshinone I Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Plant Tissue and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Tanshinone I (270 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of I measurement, which enables us to analyze of Tanshinone I levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







