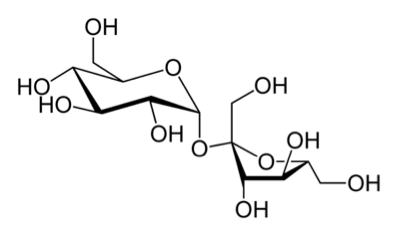
Sucrose is also named as saccharose, which is an obsolete name for sugars in general. Sucrose is a kind of carbohydrate and is found in many plants and plant parts. The chemical molecular formula of Sucrose is C12H22O11 and is hard, white, odorless crystals, lumps, or powder. Sucrose tastes sweet and very soluble in water, methanol, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ethyl ether. Sucrose was named by William Miller, who is an English chemist in 1857 and the word "Sucrose" comes from the French sucre.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Sucrose levels in various samples, including Food, Beverage and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Sucrose levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Sucrose measurement, which enables us to analyze of Sucrose levels in vitro and in vivo.
Sucrose is present in many plants, especially in their roots, fruits and nectars naturally due to Sucrose can be used to store energy, which is important for the development of the plants. Sucrose accumulated in plants is the main food source for many mammals, birds, insects and bacteria. Honeybees are very important for humans due to their ability to accumulate Sucrose accompanying with honey, which is an especially key foodstuff according the consumption perspective of humans. The carbohydrates in honey are fructose, glucose and little amounts of Sucrose only. The Sucrose content in the fruits ripen rises sharply in general because the accumulation of photosynthesis, which is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy and then is stored in carbohydrate molecules.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Sucrose Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Sucrose Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Food, Beverage and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Sucrose levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Sucrose measurement, which enables us to analyze of Sucrose levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







