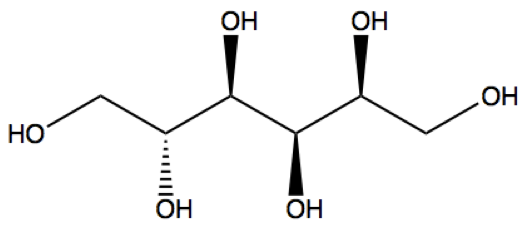
Sorbitol is also known as glucitol and is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste. Sorbitol can be obtained by reduction of glucose, in which the aldehyde group has changed into a hydroxyl group. Sorbitol also can be found in apples, pears, peaches, and prunes although most Sorbitol is made from corn syrup. Sorbitol is an isomer of mannitol, which is another sugar alcohol and derived from mannose by reduction. The orientation of the hydroxyl group on carbon 2 is the only difference between the two different sugar alcohols. The two sugar alcohols also have very different nature sources, melting points, and uses.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Sorbitol levels in various samples, including Food, Beverage and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Sorbitol levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Sorbitol measurement, which enables us to analyze of Sorbitol levels in vitro and in vivo.
If too much Sorbitol trapped in retinal cells, the cells of the lens, and the Schwann cells that myelinate peripheral nerves can lead to the damage of these cells resulting in retinopathy, cataracts and peripheralneuropathy, respectively. Aldose reductase is responsible for the reduction of glucose to Sorbitol and is the first enzyme in the Sorbitol-aldose reductase pathway. The inhibitors of aldose reductase, which are substances that can prevent or delay the action of aldose reductase, are now being studied as drug candidates to prevent or slow down these diseases. It is believed that these inhibitors may help to prevent the accumulation of intracellular Sorbitol, which can lead to the damage of cells.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Sorbitol Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Sorbitol Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Food, Beverage and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Sorbitol levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Sorbitol measurement, which enables us to analyze of Sorbitol levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







