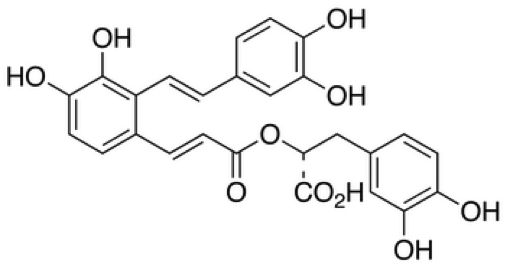
Salvianolic Acid A is also abbreviated as SAA, which is the major active component of Salviae Miltiorrhizae Bunge. The chemical molecular formula of Salvianolic Acid A is C26H22O10. Salvianolic Acid A is light yellow crystal and soluble in ethanol and ethyl ether. There are several pharmacological studies have reported that Salvianolic Acid A is a multi-target compound and has a variety of pharmacological activities, for example, antiplatelet and anti-thrombosis, improvement of microcirculation, anti-inflammation and antioxidant.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Salvianolic Acid A levels in various samples, including Plant Tissue and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Salvianolic Acid A (286 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Salvianolic Acid A measurement, which enables us to analyze of Salvianolic Acid A levels in vitro and in vivo.
Salvianolic Acid A is also the most most potent anti-oxidative agent among these compounds extracted from the root of red-rooted salvia. Salvianolic Acid A can act as scavengers of reactive oxygen species resulting in reducing the adherence of leukocytes to endothelial cells. Salvianolic Acid A also can inhibit matrix metalloproteinases and inflammation. Salvianolic Acid A can suppress cell apoptosis, reduce the lipid peroxidation and decrease the leakage of lactic acid dehydrogenase in the damaged cardiac resulting in the cardioprotective effects in the cardiac tissue. Salvianolic Acid A is cell protective antioxidant isolated from Salvia naturally so that it has been found to attenuate PDGF-induced ROS formation in hepatic stellate cells and then protecte against isoproterenol-induced myocardial damage in rats.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Salvianolic Acid A Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Salvianolic Acid A Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Plant Tissue and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Salvianolic Acid A (286 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Salvianolic Acid A measurement, which enables us to analyze of Salvianolic Acid A levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







