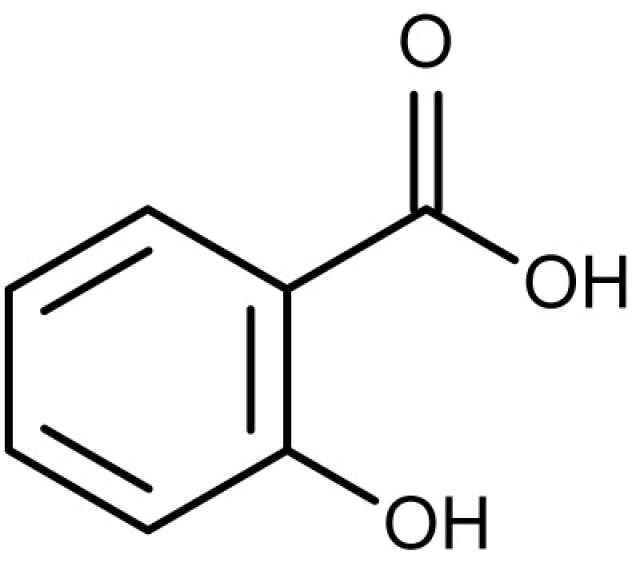
Salicylic Acid is a mono-hydroxybenzoic acid, which is a type of phenolic acid and a beta hydroxy acid. It is derived from the metabolism of salicin and its formulation is C7H6O3. It is also known as 2-hydroxybenzoic acid and it is poorly soluble in water.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Salicylic Acid levels in various samples, including Plant, Tissue and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Salicylic Acid (240 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Salicylic Acid measurement, which enables us to analyze of Salicylic Acid levels in vitro and in vivo.
Salicylic Acid (SA) is a phenolic phytohormone and is found in plants. It’s involved in the plant growth and development, photosynthesis, transpiration, ion uptake and transport. For example, SA can induce specific changes in leaf anatomy and chloroplast structure. SA also plays a role in the endogenous plant immunity signaling, mediating the plant to defense against pathogens by inducing the production of pathogenesis-related proteins. It is involved in the systemic acquired resistance in which a pathogenic attack on one part of the plant induces resistance in other parts. The signal can also move to nearby plants by Salicylic Acid being converted to the volatile ester, methyl salicylate. The medicinal use of Salicylic Acid is known for its ability to ease aches and pains and reduce fevers. It is used as an anti-inflammatory drug because these medicinal properties, particularly fever relief, have been known since ancient times. In addition, Salicylic Acid is used as a food preservative, a bactericidal, and an antiseptic.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Salicylic Acid Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Salicylic Acid Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Various Sample Type
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Salicylic Acid (240 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Salicylic Acid measurement, which enables us to analyze of Salicylic Acid levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







