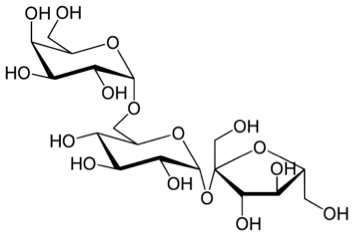
Raffinose is consisted of galactose, glucose, and fructose and is a trisaccharide. The enzyme named α-galactosidase, which is abbreviated as α-GAL can catalyze the hydrolysis of Raffinose into D-galactose and sucrose. The chemical molecular formula of Raffinose is C18H32O16 and it can be found in beans, cabbage, brussels sprouts, broccoli, asparagus, other vegetables, and whole grains.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Raffinose levels in various samples, including Food, Beverage and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Raffinose levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Raffinose measurement, which enables us to analyze of Raffinose levels in vitro and in vivo.
The Raffinose family of oligosaccharides, abbreviated as RFOs, is alpha-galactosyl, which are the derivatives of sucrose. Among these derivatives of sucrose, the most famous are the trisaccharide Raffinose, the tetrasaccharide stachyose, and the pentasaccharide verbascose. Oligosaccharide is a saccharide polymer containing a small number of simple sugars (also known as monosaccharides) and the number of the simple sugars is typically three to ten. Oligosaccharide is can be found in the almost plants and has an abundant amount in the seeds. Humans and other monogastric animals, such as pigs and poultry do not possess the α-GAL enzyme and cannot catalyze the hydrolysis of Raffinose into D-galactose and sucrose. These oligosaccharides pass through the stomach and upper intestine with the undigested form.They are fermented by gas-producing bacteria which possess the in theα-GAL enzyme in the lower intestine. Raffinose can be used to provide hypertonicity for cell desiccation prior to freezing during the procedures of cell cryopreservation. Raffinose or sucrose is also can be used as a base substance for sucralose.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Raffinose Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Raffinose Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Food, Beverage and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Raffinose levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Raffinose measurement, which enables us to analyze of Raffinose levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







