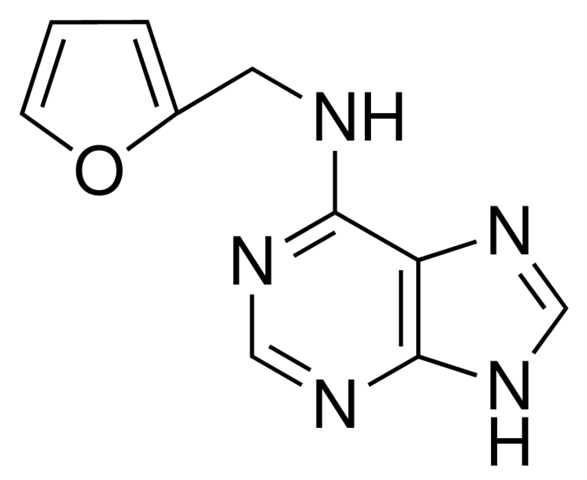
Kinetin is a type of cytokinin, which is a class of plant growth substances, also named as phytohormones that promote cell division in plant roots and shoots. Kinetin is isolated as a chemical compound from the autoclaved herring sperm DNA with cell division-promoting activity by a Swedish-born American plant physiologist Skoog, who was a pioneer in the field of plant growth regulators, particularly cytokinins. The molecular formula of Kinetin is C10H9N5O and is slightly soluble in cold water, methanol, ethanol, freely soluble in dilute aqueous hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Kinetin levels in various samples, including Plant, Tissue and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Kinetin (254 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Kinetin measurement, which enables us to analyze of Kinetin levels in vitro and in vivo.
The name Kinetin means that it has ability to induce cell division when it was present in the medium. So, Kinetin is mainly used in conjunction with auxin in plant tissue culture to induce the formation of callus, and then to promote the regeneration of the shoot tissue from callus. It was believed that Kinetin is an artificial chemical compound produced form the deoxyadenosine residues of DNA degraded when standing for a long time or heated during the process of isolation and does not exist naturally. However, Kinetin exists naturally in the DNA of cells from almost all organisms and is proved in 1996. Kinetin is now is mainly used in the field of producing new plants from tissue cultures.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Kinetin Analysis Service Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Kinetin Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Various Sample Type
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Kinetin (254 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Kinetin measurement, which enables us to analyze of Kinetin levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







