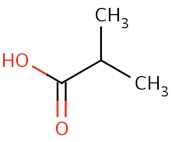
Isobutyric acid is also known as 2-methylpropanoic acid. It is a carboxylic acid and its structural formula is (CH3)2-CH-COOH. Isobutyric acid can be found in the free state in Ceratonia siliqua, in the root of Arnica dulcis, invanilla and as an ethyl ester form in croton oil. Isobutyric acid is an isomer of butyric acid and they have same chemical formula C4H8O2 but a different structure. Isobutyric acid can be produced by the by the hydrolysis of isobutyronitrile with alkalis artificially. It is also prepared by the oxidation of isobutanol with potassium dichromate and sulfuric acid. The action of sodium amalgam on methacrylic acid can also produce isobutyric acid. Isobutyric acid is a liquid form with an unpleasant smell under common conditions. The gravity of isobutyric acid is 0.9697 at 0 °C and it is boiled at 155 °C. Isobutyric acid can be stored at -20°C under desiccating conditions for a long time and up to 12 months. It is soluble in water to 100 mM. Isobutyric acid decomposes to form carbon dioxide and acetone when it is heated with a chromic acid solution to 140 °C. α-hydroxyisobutyric acid is formed by the oxidization by the alkaline potassium permanganate from isobutyric acid. The chemical formula alpha-hydroxyisobutyric acid is (CH3)2-C(OH)-COOH. The salts of isobutyric acid are more soluble in water than those of butyric acid.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Isobutyric acid levels in various samples, including Tissue, Plant, Bacterial, Cells and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Isobutyric acid levels in a lot of biological samples.
Isobutyric acid can be manufactured using engineered bacteria with a sugar feedstock commercially. Isobutyric acid is a reserved trivial name according the rules issued by the IUPAC. Isobutyric acid can be oxidative dehydrogenated into methacrylic acid by the iron phosphate and cesium/iron diphosphate, which are known to be present in an industrial and complex iron cesium phosphate. α-(Methylamino)isobutyric acid is one of glutamine transport inhibitor. It is selective for Na+-dependent amino acid transport system A over system B transporters.
Sample Type
Tissue, Plant, Bacterial, Cells and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) using a differential refractive index detector (RID) for the determination of Isobutyric acid levels in a lot of biological samples, Tissue, Plant, Bacterial, Cells and more. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Isobutyric acid measurement, which enables us to analyze of Isobutyric acid levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







