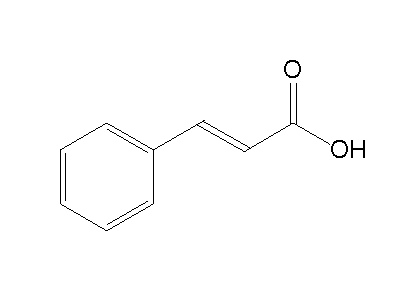
Cinnamic Acid is a white crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CHCHCO2H. Cinnamic Acid is slightly soluble in water and is soluble in many organic solvents. Cinnamic Acid is classified as an unsaturated carboxylic acid, which is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group (C(O)OH). There are cis and a trans isomer exist naturally in a number of plants and the trans isomer is more common.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of Cinnamic Acid levels in various samples, including Plant and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Cinnamic Acid (270 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Cinnamic Acid measurement, which enables us to analyze of Cinnamic Acid levels in vitro and in vivo.
Cinnamic Acid is is a key intermediate of the biosynthetic shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways. Shikimic acid is a cyclohexene and is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. For example, shikimic acid is a precursor for synthesis many alkaloids, aromatic amino acids, and indole derivatives. Phenylpropanoid are a class of plant metabolites based on phenylalanine and they are widely distributed in plants fulfilling many functions including plant defense mechanism, pigmentation and external signaling system. Cinnamic Acid is also the precursor of cinnamates, coumarines, caffeic acids, ferulic acids, and sinapic acids. Cinnamic Acid and Its derivatives, for instance, esters and carboxylic functional derivatives are also can be used as important components for producing flavours, perfumes, synthetic indigo and pharmaceuticals. Cinnamic Acid is also a kind of self-inhibitor produced by fungal spores to prevent plants germination, which is is the process by which a plant grows from a seed.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique "chromatography". Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in Cinnamic Acid Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Plant and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of Cinnamic Acid (270 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of Cinnamic Acid measurement, which enables us to analyze of Cinnamic Acid levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







