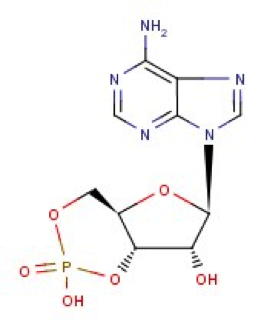
cAMP is the abbreviation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and also known as 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate. cAMP is biosynthesized form ATP by adenylate cyclase, which locates on the inner side of cell membrane and anchored in the interior of the cell. The enzyme named phosphodiesterase can catalyze cAMP to decompose into AMP.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of cAMP levels in various samples, including Animals, Plants, Microorganisms, Cells and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of cAMP (254 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of cAMP measurement, which enables us to analyze of cAMP levels in vitro and in vivo.
cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for a second messenger for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms in the cAMP-dependent pathway. cAMP is also involved in the activation of protein kinases in order to modulate the effects of adrenaline. cAMP also can bind to the ion channels such as the HCN channels and then regulates the function of ion channels. cAMP also can bind with a few other cyclic nucleotide-binding proteins such as Epac1 and RAPGEF2 to regulate the related signal transduction pathway. There are some research has suggested that the deregulation of cAMP and activation of the cAMP-controlled genes are involved in the growth of some cancers. Recent research also suggests that cAMP has effect on the the function of higher-order thinking in the prefrontal cortex by regulation the function of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, which are ion channels that function in response to the binding of cyclic nucleotides.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
cAMP Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in cAMP Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Animals, Plants, Microorganisms, Cells and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of cAMP (254 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of cAMP measurement, which enables us to analyze of cAMP levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







