What Is ATP
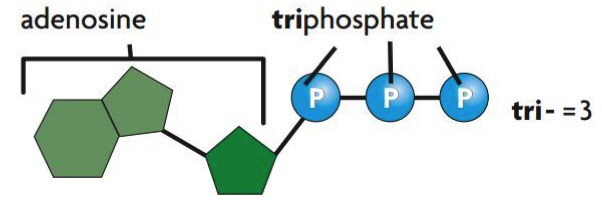
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is the abbreviation of Adenosine triphosphate, which is the basic unit of intracellular energy transfer. ATP consists of an adenine ring, a ribose sugar and three phosphate groups. The phosphoryl groups, starting with the group closest to the ribose, are named as the alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) phosphates respectively and the two phosphoanhydride bonds are responsible for the high energy content of this molecule.
ATP is the main energy source for the majority of cellular functions, which includes the biosynthesis of DNA, RNA and protein. ATP is also very important to the macromolecules transport across cell membranes, for example, exocytosis and endocytosis. ATP also participates to maintain the cell structure by facilitating assembly and disassembly of elements of the cytoskeleton. ATP also is required for the shortening of actin and myosin filament crossbridges, which is responsible for muscle contraction. ATP can be recognised by purinergic receptors, which might be the most abundant receptors in mammalian tissues as a signalling molecule and is important in both the central and peripheral nervous system of human beings. ATP also can be used as source of phosphate groups in the phosphate transfer reactions of kinases.
ATP Detection Method
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique "chromatography". Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
 (Jing Tao et al,. Food Bioscience 2023)
(Jing Tao et al,. Food Bioscience 2023)
ATP Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics provides a comprehensive ATP Analysis Service to advance your research in ATP analysis. Our cutting-edge High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) platform ensures precise measurement of ATP levels (at 254 nm) in various biological samples. This methodology delivers accurate, dependable, and consistent ATP measurements, facilitating both in vitro and in vivo analyses of ATP levels.
Technical Features and Advantages
√ Selectivity, Precision and accuracy: Targeted detection of metabolites, greatly improving the sensitivity, accuracy, specificity and reproducibility of detection, leading to absolute quantitative study of metabolites and information mining of metabolites.
√ Stability: Strict quality control system, ultra-high resolution ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry system, and professional data pre-processing and analysis capabilities
√ Simple, sensible, durable and fast method
Sample Requirements
| Sample type | Recommended sample size | Pre-treatment and storage |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue | >200mg | Snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80°C. |
| Urine | >0.3ml | 5000×g 4°C Centrifuge for 30-60min, remove supernatant, store at -80°C. |
| Serum/plasma | >0.3ml | Collected serum/plasma, snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80°C. |
| Cerebrospinal fluid, amniotic fluid, bile and other body fluids | >0.3ml | 4°C Centrifuge for 10min, (or filter using 0.22μm membrane), remove supernatant and store at -80°C. |
| Suspension cells | >107 | Centrifuge and collect cells after liquid nitrogen snap freezing and store at -80°C. |
| Walled cells | >107 | Cultured walled cells are stored in 1.5ml centrifuge tubes, snap freezing in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C |
| Cell supernatant | >10ml | centrifuge at 4℃ for 3 minutes, take the supernatant and store at -80℃. |
The recommended number of sample replicates for targeted metabolomics is as follows
| Animal samples (various tissues, blood plasma) | ≥ 6 replicates per group |
| Plant, microbial samples (leaf, root tissue) | 3 replicates per group |
| Cell samples | 3 replicates per group |
| Clinical samples (serum, urine, various tissues, etc.) | ≥ 10 replicates per group |







