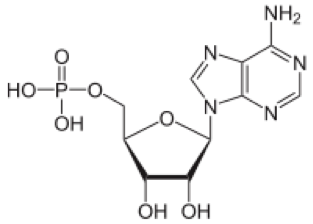
AMP is the abbreviation of Adenosine monophosphate and is also known as 5'-adenylic acid. AMP is an ester is used as structural subunit of RNA. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine like ADP and ATP.
Scientists at Creative Proteomics utilize a highly quantitative method with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of AMP levels in various samples, including Animals, Plants, Microorganisms, Cells and more. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of AMP (254 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of AMP measurement, which enables us to analyze of AMP levels in vitro and in vivo.
Adenosine can be linked to a chain of one, two, or three phosphate groups to form adenosine monophosphate, is abbreviated as AMP, adenosine diphosphate, which is abbreviated as ADP, or adenosinetriphosphate, also is abbreviated as ATP respectively. The phosphate bonds of the ADP and ATP are called high-energy bonds due to their ability to store energy that can be hydrolyzed to release a large amount of free energy. AMP can be produced by the hydrolysis of one high energy phosphate bond of ADP and hydrolysis of two high energy phosphate bond of ATP. AMP is also produced when RNA is broken down by living systems because AMP is the basic structural subunit of RNA. A cyclic structure known as cyclic AMP, which is abbreviated as cAMP is another form of AMP. cAMP can be produced by the enzyme named adenylate cyclase form ATP. cAMP plays an important role in intracellular signaling as a second messenger.
The Russian-Polish botanist M. Tswett is generally recognized as the first person to establish the principles of chromatography. In a paper he presented in 1906, Tswett described how he filled a glass tube with chalk powder (CaCO3) and, by allowing an ether solution of chlorophyll to flow through the chalk, separated the chlorophyll into layers of different colors. He called this technique “chromatography”. Fundamentally, chromatography is a technique used to separate the components contained in a sample. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method able to separate non-volatile, thermally unstable, and polar components separate or in a mixture. HPLC is a type of chromatography that, because of its wide application range and quantitative accuracy, is regarded as an indispensable analytical technique, particularly in the field of organic chemistry. It is also widely used as a preparation technique for the isolation and purification of target components contained in mixtures.
AMP Analysis Service at Creative Proteomics supports your research in AMP Analysis. HPLC Based Analysis Service Platform enable us at Creative Proteomics offers you a state-of-the-art Analysis Service.
Sample Type
Animals, Plants, Microorganisms, Cells and more
Method
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is used for the determination of AMP (254 nm) levels in a lot of biological samples. This Methodology provides accurate, reliable, and reproducible results of AMP measurement, which enables us to analyze of AMP levels in vitro and in vivo.
Send us your samples, you will get all information that you need!







