Molecular weight is a fundamental physicochemical property of organic compounds and is the sum of the relative atomic masses of the individual atoms in the chemical formula of a compound. The correct molecular weight often represents the correct structure of the organic compounds and biological macromolecules measured. Molecular weight is the primary parameter in the identification of polysaccharides, peptides, proteins, etc.
There are two main types of molecular weight determination: relative molecular weight determination and accurate molecular weight determination. The common determination methods include gel permeation chromatography (GPC), size exclusion chromatography (SEC), mass spectrometry, SDS-PAGE, etc.
Relative molecular weight determination
The relative molecular weights of polysaccharides and peptides are usually determined using gel permeation chromatography (GPC) or size exclusion chromatography (SEC). This method provides not only the average molecular weight value but also information on the molecular weight distribution in the polymer sample. It can also be combined with other detectors (e.g. light scattering or viscosity detectors) to provide information on the structure and size of molecules in solution.
The relative molecular weight of proteins and peptides can also be determined using the SDS-PAGE method. The principle is that the addition of SDS to the electrophoresis system opens the hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds of the protein and binds to the protein molecule, making the electrophoretic mobility dependent only on the molecular size as a factor. Therefore, the molecular weight of the unknown can be obtained from the standard curve made by the logarithm of the molecular weight and mobility of the standard protein.
Accurate molecular weight determination
The exact molecular weight of proteins, peptides, amino acids, glycoproteins and other compounds is usually determined by mass spectrometry. Mass spectrometry molecular weight analysis combined with peptide mapping can help determine the correct amino acid sequence. This can be done by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry testing or by full-scan acquisition using other high-resolution liquid masses, which are then measured using deconvolution software.
Creative Proteomics has a team of experienced experts and advanced equipment to provide professional and reliable molecular weight determination services to pharmaceutical and scientific users.
For relative molecular weight determination needs, Creative Proteomics provides GPC column and SEC column separation, UV detector, differential detector, light scattering detector, viscosity detector, and GPC software analysis through a liquid chromatograph. It is also equipped with an electrophoresis instrument and equipped with a sandwich type vertical plate electrophoresis tank and a thin film electrophoresis tank for relative molecular weight determination of polysaccharides, peptides and proteins.
For accurate molecular weight determination needs, Creative Proteomics is equipped with a high-resolution mass spectrometer Q Exactive HF with Orbitrap detector and deconvolution by the deconvolution software BioPharma Finder, which enables accurate molecular weight determination of proteins, peptides, amino acids, glycoproteins, etc. The precision reaches 1 Da, which greatly improves the accuracy compared with the traditional determination methods such as gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and SDS-PAGE, and can meet the needs of protein characterization and analysis of protein modifications.
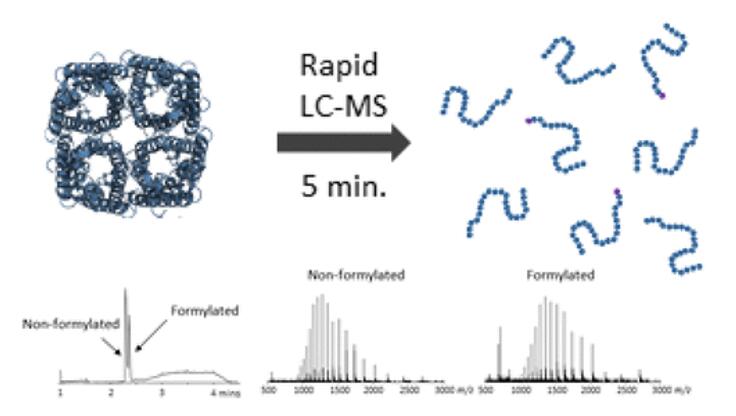
LC-MS Method for Accurate Molecular Weight Determination[1]
Reference
[1] Lippens, J. L., Egea, P. F., et al. (2018). Rapid LC–MS Method for Accurate Molecular Weight Determination of Membrane and Hydrophobic Proteins. Analytical chemistry, 90(22), 13616-13623.