What is Anthocyanin?
Anthocyanidin is a flavonoid compound, a type of water-soluble pigment that can be widely found in plants, and also the main coloring substance of plants. Free anthocyanins are rare under natural conditions, and often form anthocyanins through glycosidic bonds with one or more glucose, rhamnose, galactose, xylose, arabinose, etc. The glycoside groups and hydroxyl groups in anthocyanins can also form acylated anthocyanins with one or several molecules of coumaric acid, ferulic acid, caffeic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid and other aromatic acids and fatty acids through ester bonds.
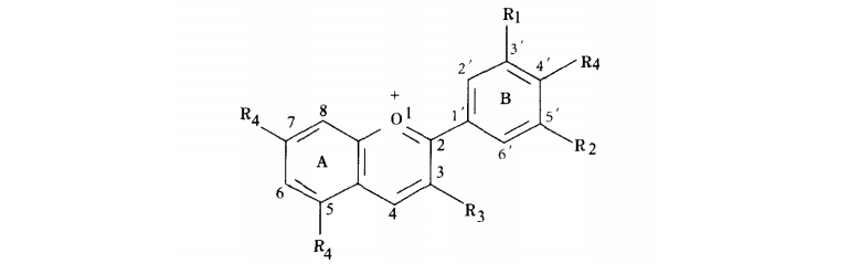
R1 and R2 are H, OH or OCH3, R3 is glycosyl or H, R4 is glycosyl or OH
Figure 1. Basic structure of anthocyanin
Benefits of Anthocyanin
The most prominent role of anthocyanins is to enable plants to display colors. Anthocyanins are also a class of active ingredients with health benefits:
- Have a strong antioxidant effect by removing free radicals in the body
- Decrease the activity of oxidase
- Have found to reduce the glycerolipid level in hyperlipidemia rats and improve the catabolism of high glycerolipid lipoproteins
- Inhibit cholesterol absorption and reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol content
- Anti-mutation, anti-tumor, anti-allergic, protection of gastric mucosa and other functions
Methods to analyze anthocyanin
Anthocyanin extraction: It mainly includes solvent extraction and auxiliary extraction.
- Solvent extraction method: Dry and crush plant materials or crush fresh materials directly into solvent extraction.
- Auxiliary extraction method:
1. Ultrasonic assisted extraction method: The strong cavitation effect produced by ultrasonic energy accelerates the penetration of the solvent into plant tissues and improves the efficiency of solute leaching. At present, this method is widely used in the extraction of bioactive substances such as plant polyphenols and polysaccharides.
2. Microwave-assisted extraction method: It uses the heat generated by the microwave to promote the extraction speed and efficiency of the solvent.
3. Enzyme-assisted extraction method: Add a certain amount of enzyme to the extraction solvent to break the wall of plant cells, which is conducive to the dissolution of the target product.
4. Aqueous two-phase extraction method: The aqueous two-phase extraction method uses short-chain alcohols (ethanol, methanol, and isopropanol) and inorganic salts (such as phosphate and sulfate) to form a stable and adjustable two-phase system. It provides a mild and non-toxic environment for the target product. This method has a preliminary purification effect on the sample while extracting.
5. Supercritical fluid extraction method: High-pressure and high-density supercritical fluid is used as a solvent to extract the required components from the raw materials. The solvent is then separated from the extracted components by heating, reducing pressure, or both.
Separation, purification and identification of anthocyanins
The crude anthocyanin extract contains a lot of carbohydrates, organic acids, amino acids and proteins, etc., which not only has low content, low color value, but can also absorb moisture easily. In practical applications, a large amount of precipitation will be produced, which greatly hinders the needs of activity research and structure identification. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a cost-effective purification method to eliminate impurities.
Column chromatography: Separation process occurs according to the different partition coefficients of each component in the sample mixture in the stationary phase and the mobile phase. Columns can be divided into macroporous resin column, silica gel column, polyamide column, gel column and ion exchange column, according to the different principle of packing matrix and sample distribution and exchange.
High performance liquid chromatography: The separated product has the advantages of high purity, high recovery rate and high separation efficiency, and has a large sample processing capacity. This technique is widely used in the separation, enrichment and purification of anthocyanins. Since anthocyanins are stable under acidic conditions, chromatographic materials with strong acid resistance should be used.
Liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (LC-MS) are used to separate the components with a wide selective liquid chromatography, and then the structure and composition are analyzed with a high-sensitivity mass detector.
