In his State of the Union Address to Congress in 2015, President Barack Obama proposed a national cancer moon-landing mission, with a planned $1 billion investment in it for the next year, focusing mainly on immunotherapy, genomics and combined therapy. Thomas P. Conrads, from the Inova Schar Cancer Institute, co-published this latest article with Emanuel F Petricoin from the University of George Mason. They wished scientist to pay more attention to the importance of Proteomics in precision medicine, especially cancer. While agreeing with the cancer moon-landing mission, they thought it should not focus solely on genomics, but also proteomics which was also an important aspect.
After all, genomes are only recording information, while proteins are the real executors of cell activity. And proteins make up most of the biomarkers used for cancer detection, as well as antigens that drive immune responses and information exchange inside & outside the cell. In addition, almost every targeted therapytargets proteins, so protein should be an important research direction in cancer moon-landing program. Here is a summary of recent advances in proteomics.
Identification of autoimmune pathological evidence of bilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss (S-SNHL) by proteomics analysis
S-SNHL is a kind of inner ear disorder and has sudden hearing loss within 3 days. However, the pathological mechanism of the disease remains unclear in nowadays, although autoimmunity is considered one of the hypothetical causes, especially in bilateral hearing loss. Recently, researchers used proteomics to provide evidence for the involvement of autoimmunity in bilateral S-SNHL. The study found that autoimmunity was indeed involved in the development of bilateral S-SNHL. In addition, the researchers also investigated the presence of circulating auto-antibodies and candidate antigens. Finally, the researchers noted that these findings could provide the necessary basic evidence for the development of diagnostic biomarkers and could help people understand the pathology mechanism of bilateral S-SNHL.
Longitudinal investigation of salivary proteomics in the development of early caries in Chinese children
Recently, a new study investigated the expression of different peptides in saliva during the early dental caries (ECC) period of 3-4-year-old children. An observation on 82 children without caries was carried through 1 year. The whole saliva of the subjects was collected at 0, 6 and 12 months respectively by stimulating gland. The results showed that for the 3 time nodes, in C group, the peaks of 9 peptides were obvious different from others, which may be associated with the development of caries. Of the 9 peptides, 3 increased over time and the other 6 gradually decreased. The researchers chose 3 peptides (1346.6, 2603.5 and 3192.8 Da) that could best show their efficacy, in order to build a high-risk model of children's caries. One peptide (1346.6 Da) was identified to have proline. It indicates that the application of peptide can help identify and discover new biomarkers during the development of ECC.
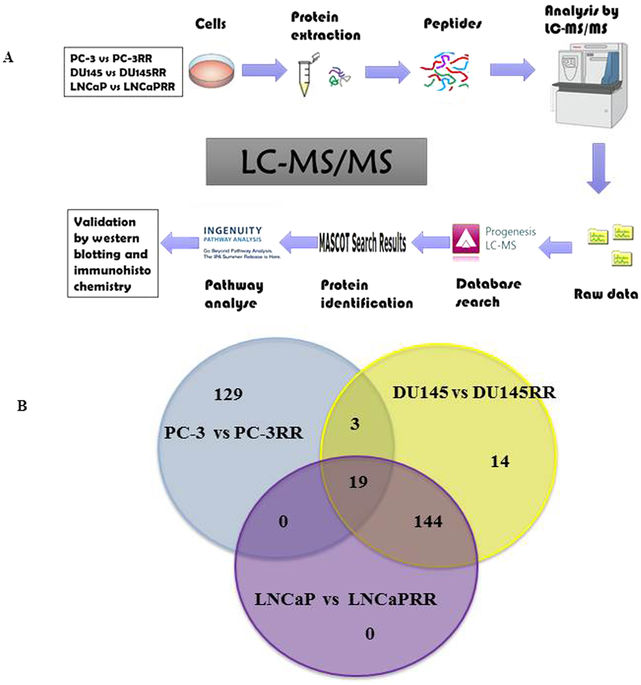
Identification of protein biomarkers and association between signaling pathways and prostate cancer radioresistance by label-free LC-MS/MS proteomics
The identification of biomarkers and signaling pathways is important in the control of prostate cancer (CaP) radioresistance. Recently, researchers studied protein biomarkers as well as the association between signal pathways and prostate cancer radioresistance. The results showed that the combination of aldolase A (ALDOA) deletion and radiotherapy in CaP-RR cell line could effectively reduce the formation of population, induce more apoptosis and increase radiosensitivity. Finally, the researchers pointed out that the CaP radiation resistance was caused by the characteristics of multi-factor. The down-regulation of ALDOA expression could increase the radiosensitivity of CaP-RR cells. At the same time, they also showed that the control of these identified proteins / signaling pathways and combination with radiotherapy may overcome radio-resistance of CaP cells.
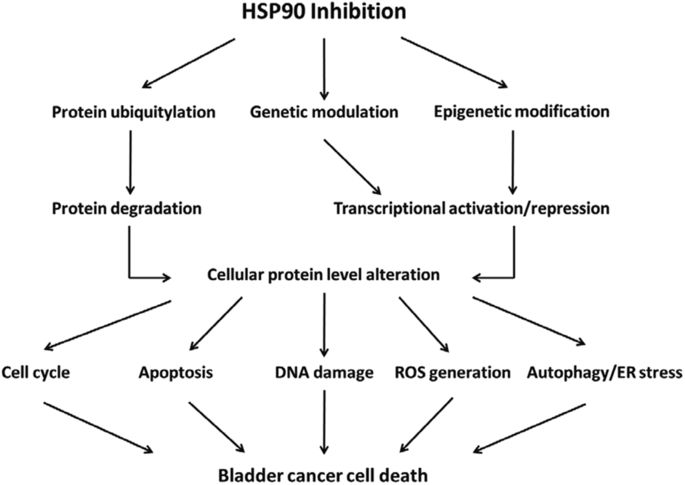
Proteomic analysis of proteome and histone post-translations(PTMs) in the treatment of bladder cancer with inhibition and regulation of heat shock protein 90(HSP90)
The inhibition of HSP90 is a very attractive strategy for cancer treatment. Some HSP90 inhibitors have shown promising results in clinical cancer trials. However , there is little knowledge about the mechanisms underlying HSP90 regulation and inhibition of bladder cancer therapy. Recently, researchers reported a number of proteomic studies, for example, the response assessment to HSP90 inhibition by bladder cancer when changes in protein expression and PTMs. The study showed that 5 kinds of HSP90 inhibitors (AUY922, ganetespib, SNX2112, AT13387 and CUDC305) which significantly inhibited the proliferation of bladder cancer 5637 cells, and showed a dose- and time-dependent mode. In 5637 cells treated with AUY922 and ganetespib, the researchers used quantitative proteome methods to identify 14 types of PTMs in 93 markers of core histones, including 34 new histone markers like butyrylation, citrullination, 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation, methylation, glycosylation, propionylation and succinylation.
Reference:
Chang L, Ni J, Beretov J, et al. Identification of protein biomarkers and signaling pathways associated with prostate cancer radioresistance using label-free LC-MS/MS proteomic approach[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7.
Li Q Q, Hao J J, Zhang Z, et al. Proteomic analysis of proteome and histone post-translational modifications in heat shock protein 90 inhibition-mediated bladder cancer therapeutics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 201.