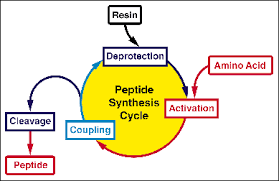
Solid phase peptide synthesis, also known as SPPS, was developed in 1963 by R.Bruce Merifield, who had made a breakthrough in the field of peptide synthesis. This is also a mile stone in the history of peptide synthesis.
Main advantages of solid phase peptide synthesis are lying in the whole reaction process can be performed in the same reaction vessel, for the initial reactants and products are attached to a solid carriers. This is also convenient for automatic operation and a high yield of the product may be obtained with an excess of reactant, while the product is easy to separate.
However, during the process of peptide synthesis experiment, there are main four tips should be paid more attention.
1. Solid phase carrier
Solid phase carriers are the main feature to distinguish solid phase peptide synthesis from other techniques. Solid phase carriers used for peptides synthesis should meet following requirements:
A. With reactive sites or reaction group for the attachment of peptide chain and then they will be removed after the whole reaction.
B. Being inactive under physical and chemical conditions during synthesis.
C. Carriers must contact rapidly and unimpededly between the growing peptide chain and reagents.
D. Carriers must be equipped with enough sites, in order to allow an effective yield of peptide can be obtained from per unit volume of the carrier and minimize the interaction between peptide chain bounded by carriers.
Currently, polymer carriers available for solid phase peptide synthesis are main three types: polystyrene-divinyl benzene cross-linked resin, polyacrylamide and polyethylene-glycol-based resin and derivatives
2.Protection
In order to synthesize peptides with special amino acid sequence, the protection of amino and carboxy forming amide bond is necessary. And the active group on amino acid side chain should be protected until the completion of the reaction.
3.Analysis
Pillars and pump system, used in HPLC analysis, can be subjected to high pressure, which allows the very fine particles (3-10μm) as fillers. Whereby the polypeptide should be analyzed within a few minutes. There are two categories in HPLC: ion exchange and reverse. The former one is depending on the interaction of direct charge between solid phase and polypeptide. The later is attached to pillars through hydrophobic interaction and eluted in order to reduce ionic strength.
4.Approaches to improve the stability of polypeptide
A.Site-directed mutagenesis
Replacing residues related to instability or introducing residues increasing the stability.
B. Chemical modification
There are too many approaches for chemical modification. PEG is the one that widely applied and studied. After the combination of PEG and polypeptide can improve the solubility of polypeptide and regulate the biocompatibility and then increase the thermal stability.
C. Additive
By adding additives, such as sugars, polyhydric alcohols, gelatin, salts, and certain amino acids, can improve the stability of the polypeptide
D. Lyophilization
A series of chemical reactions, such as deamidation, β-eliminate and hydrolysis need the participation of water, which can be used as the mobile phase of other reactants. Further, to reduce the content of water can rise the polypeptide’s temperature. So lyophilization can improve the stability of polypeptide.
Solid phase peptide synthesis is regarded as a mile stone of peptide synthesis field. Although there are some advantages of this technique, the further study is still necessary.
More related services: