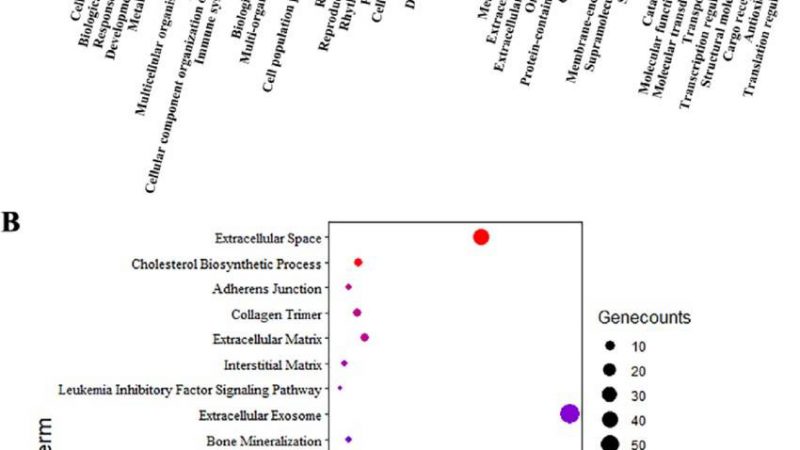
Understanding the Basics of Gene Ontology (GO) Gene Ontology (GO) provides a standardized framework for annotating genes and their products,
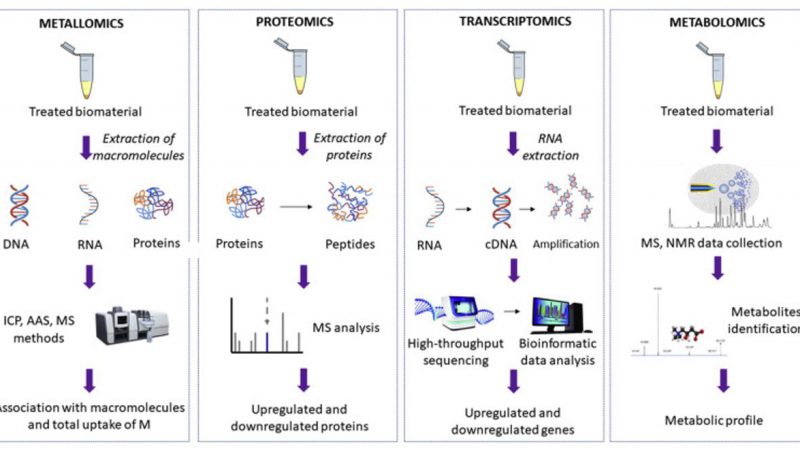
Introduction to Metallomics Metallomics is a rapidly emerging and highly interdisciplinary field that focuses on the systematic study of the
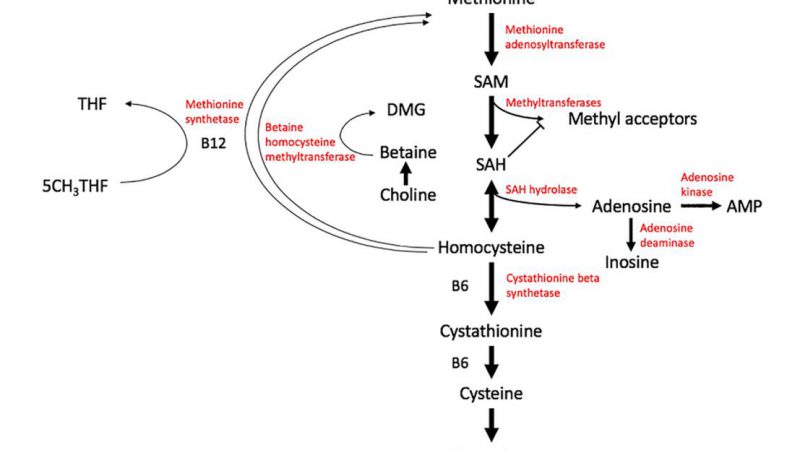
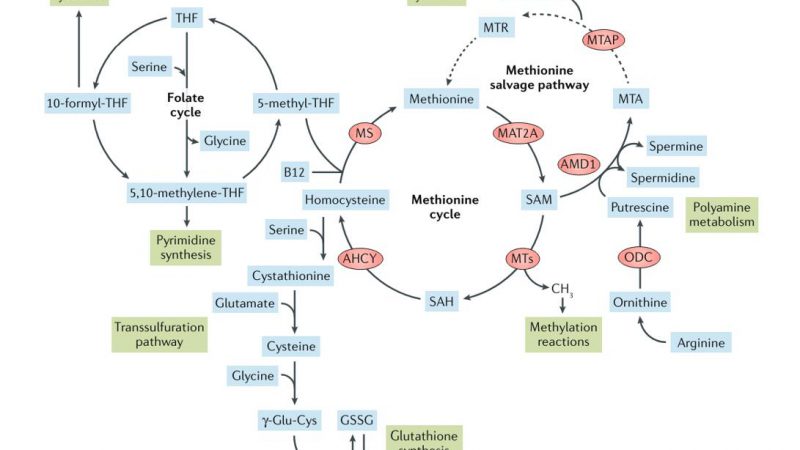
What is the difference between SAM and SAH? S-adenosylmethionine (SAM): The Universal Methyl Donor SAM, or S-adenosylmethionine, is one of
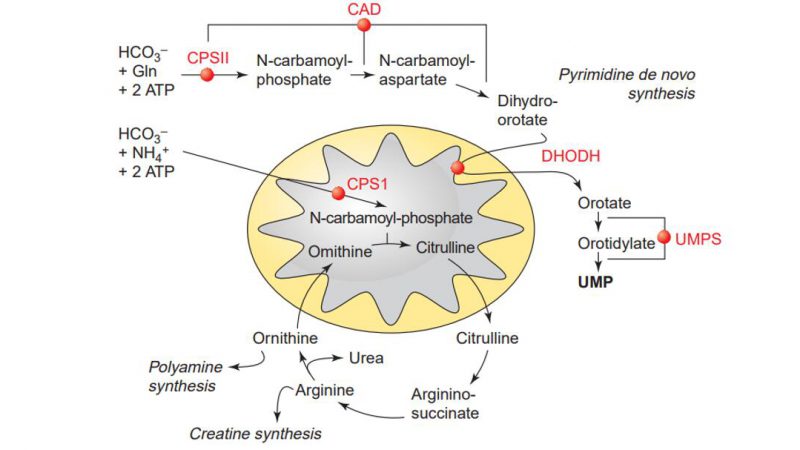
Pyrimidine metabolism is a fundamental biochemical pathway that plays an essential role in the synthesis and degradation of nucleotides, the
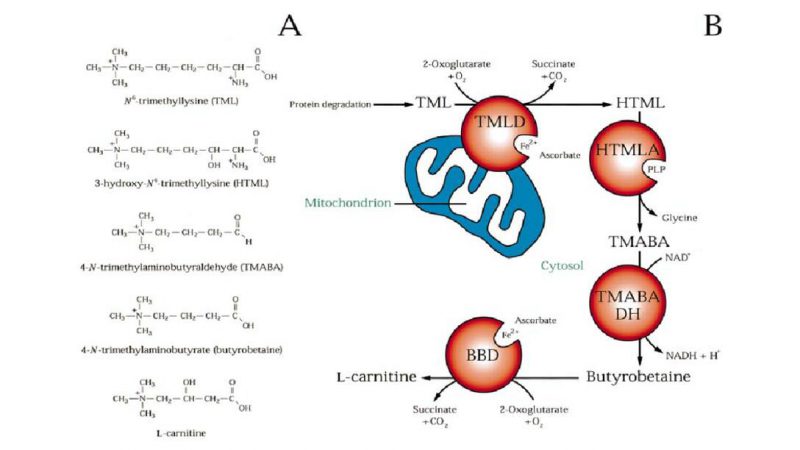
Carnitine, a quaternary ammonium compound, is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in energy production by transporting long-chain
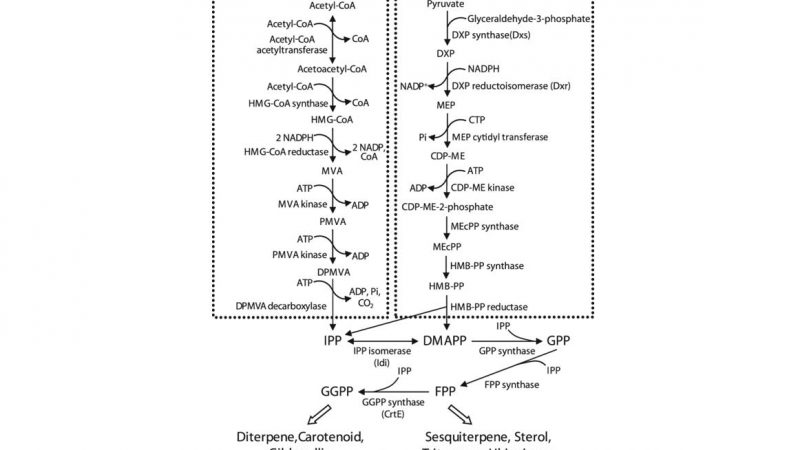
Isoprenoids, also known as terpenoids, are a vast and diverse class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from five-carbon isoprene
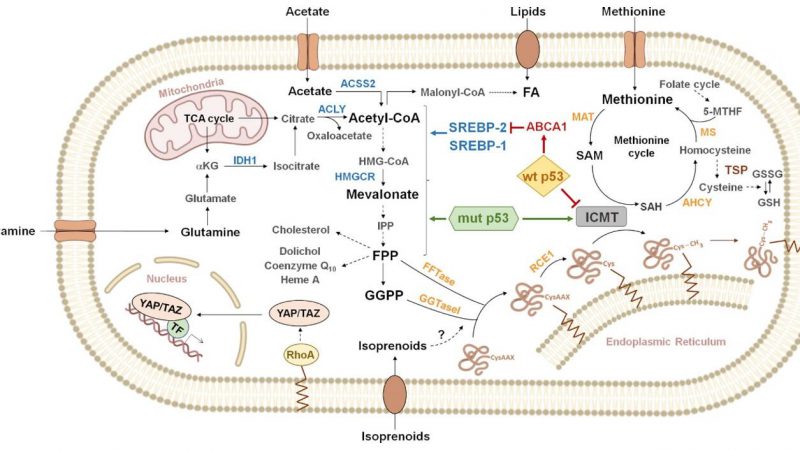
The methionine cycle, also known as the one-carbon metabolism pathway, is a fundamental biochemical pathway involved in the synthesis and
The Genesis of Mevalonate Pathway: Origins and Reactions The Mevalonate Pathway, a cornerstone of cellular metabolism, begins with the conversion
Water-soluble vitamins encompass a group of organic compounds that are soluble in water and can be easily absorbed into the
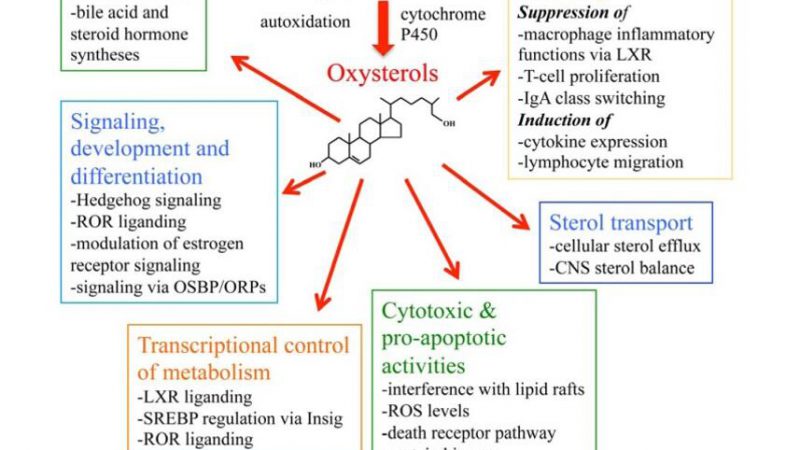
Function of Oxysterols xysterols, as oxidized derivatives of cholesterol, play multifaceted roles in biological systems, exerting diverse functions that are