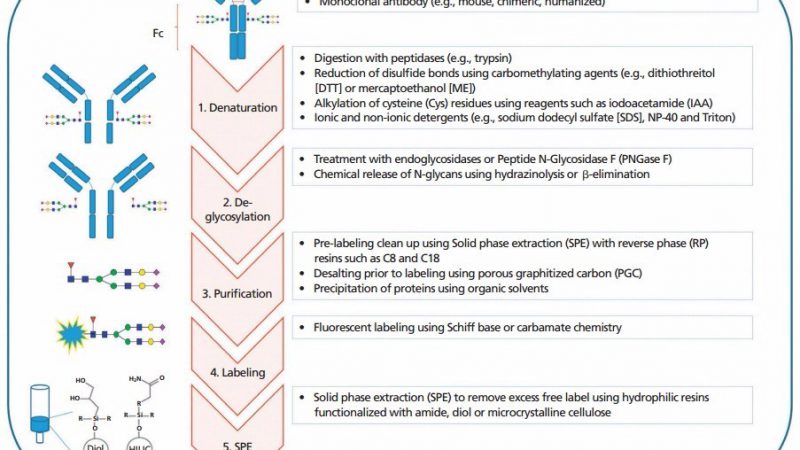
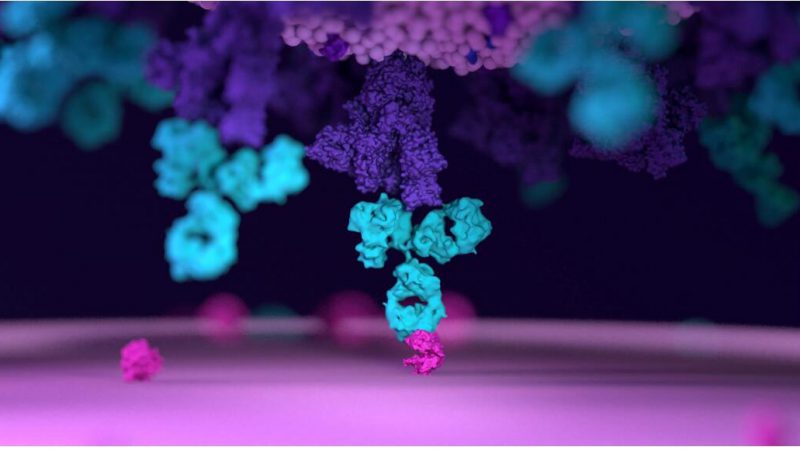
Immunoglobulin is a serum glycoprotein. There are five types of IgM, IgA, IgD, IgG and IgE found in humans. IgG
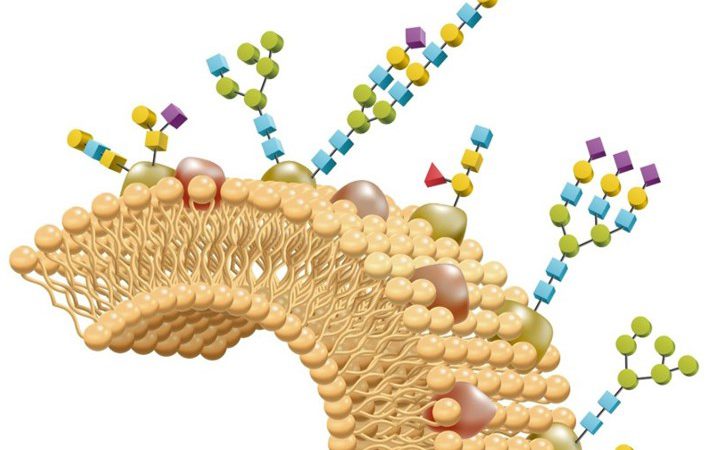
Protein glycosylation is a very common, complex and diverse post-translational modification of proteins. In eukaryotes, protein glycosylation process mainly occurs
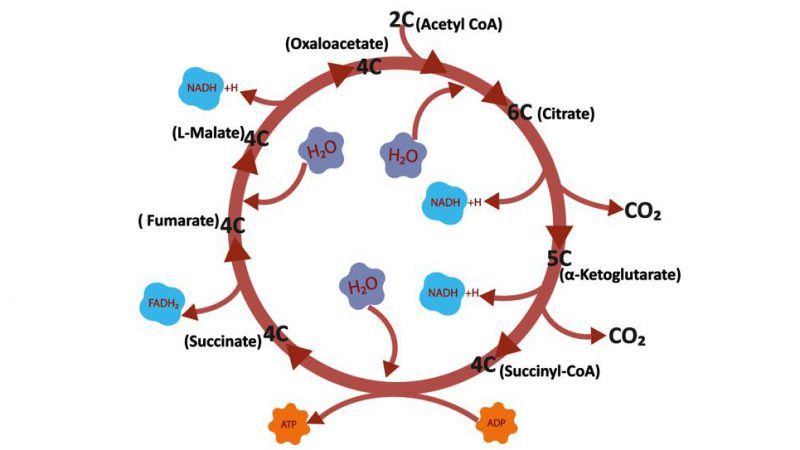
The tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA Cycle) is a cyclic reaction system consisting of a series of enzymatic reactions, starting with
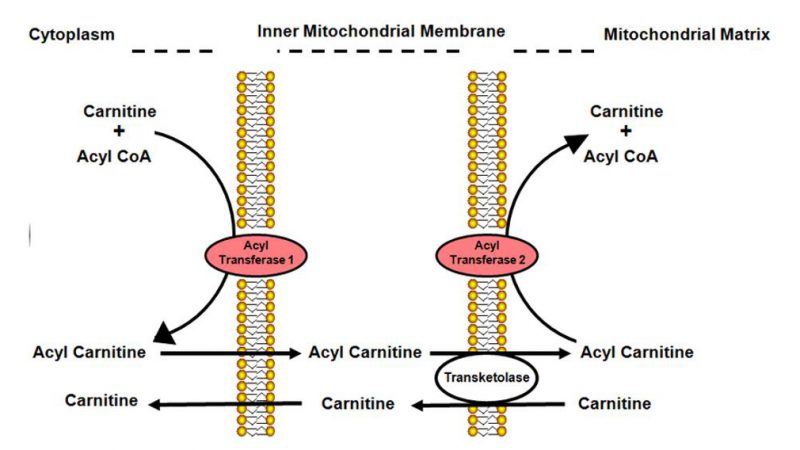
Carnitine (L-3hydroxy-4-trimethylaminobutyric acid), a water-soluble tetramine compound, is mainly distributed in tissues with high energy requirements, such as skeletal muscle
Host cell proteins (HCPs) are one of the key process-related impurities generated during the production of biologics, which can lead
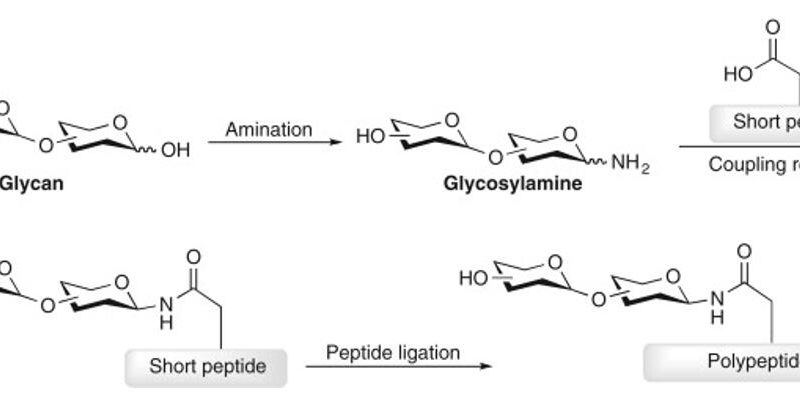
The complexity of glycan chains poses a great challenge for accurate qualitative and quantitative glycomic analysis. The study of glycomics
Since May 7, the UK Health and Safety Executive reported the first confirmed case of monkeypox. According to the latest
Arachidonic acid (AA) is the most widely distributed endogenous active substance in living organisms. The metabolic pathway of arachidonic acid
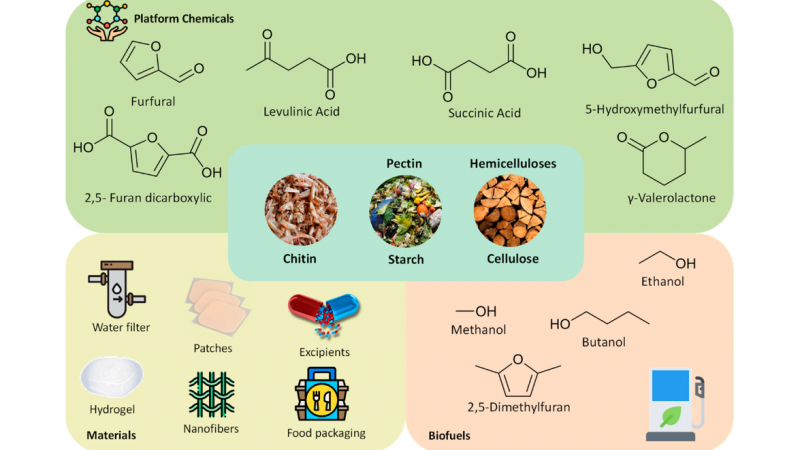
Polysaccharides, along with nucleic acids, proteins and lipids, are the four basic substances of living organisms and play an important
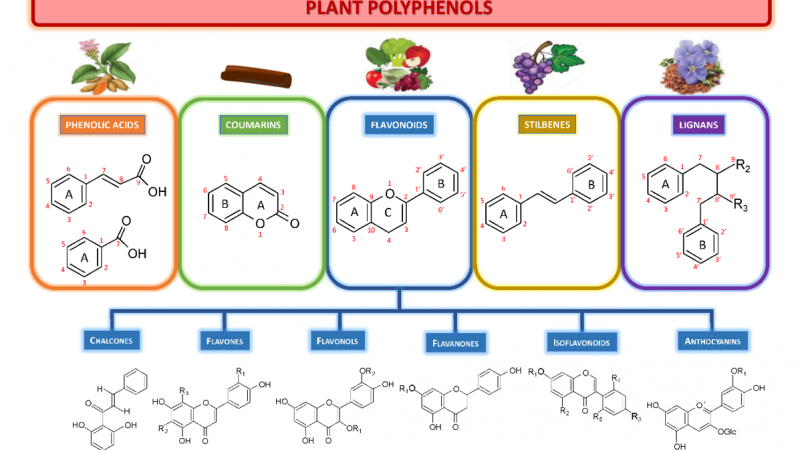
Types of plant polyphenols Plant polyphenols are a class of compounds with multiple phenolic hydroxyl structures present in plants, which